 W
WThe Canadian Arctic tundra is a biogeographic designation for Northern Canada's terrain generally lying north of the tree line or boreal forest, that corresponds with the Scandinavian Alpine tundra to the east and the Siberian Arctic tundra to the west inside the circumpolar tundra belt of the Northern Hemisphere.
 W
WChinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are föhn winds in the interior West of North America, where the Canadian Prairies and Great Plains meet various mountain ranges, although the original usage is in reference to wet, warm coastal winds in the Pacific Northwest.
 W
WBecause of its location in the centre of the North American continent, the climate of Manitoba is extreme. In general, temperatures and precipitation decrease from south to north, and precipitation also decreases from east to west. Since Manitoba is far removed from the moderating influences of both mountain ranges and large bodies of water, and because of the generally flat landscape in many areas, it is exposed to numerous weather systems throughout the year, including cold Arctic high-pressure air masses that settle in from the northwest, usually during the months of January and February. In the summer, the air masses often come out of the southern United States, as the stronger Azores High ridges into the North American continent, the more warm, humid air is drawn northward from the Gulf of Mexico, generally during the months of July or August.
 W
WNova Scotia lies in the mid-temperate zone, and although the province is almost surrounded by water, the climate is closer to continental rather than maritime. The temperature extremes of the continental climate are moderated by the ocean.
 W
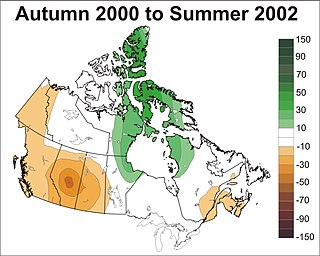
WProlonged, large-area droughts are among Canada's costliest natural disasters having major impacts on a wide range of sectors including agriculture, forestry, industry, municipalities, recreation, human health, society and ecosystems. They frequently stress water availability by depleting soil moisture, reducing stream flows, lowering lake and reservoir levels, and diminishing groundwater supplies. This ultimately affects several economic activities including for example, decreased agricultural production, less hydro-electric power generation, and increased freshwater transportation costs. Droughts also create major environmental hazards such as reduced water quality, wetland loss, soil erosion and degradation, and ecological habitat destruction.
 W
WThe Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In summer it weakens and splits into two centres, one near Davis Strait and the other west of Iceland. It is a principal centre of action in the atmosphere circulation of the Northern Hemisphere, associated with frequent cyclone activity. It forms one pole of the North Atlantic oscillation, the other being the Azores High.
 W
WThe Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.