 W
WThe Asia-Pacific is the part of the world in or near the Western Pacific Ocean. Asia-Pacific varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Oceania.
 W
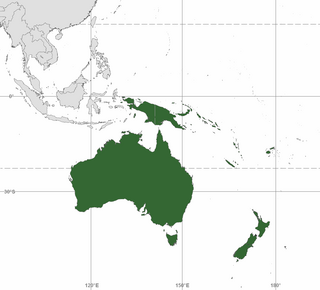
WAustralasia comprises Australia, New Zealand, and some neighbouring islands. It is used in a number of different contexts including geopolitically, physiogeographically, and ecologically where the term covers several slightly different but related regions.
 W
WMaritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Southeast Asia. The 16th-century term "East Indies" and the later 19th-century term "Malay Archipelago" are also used to refer to maritime Southeast Asia.
 W
WMelanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from New Guinea island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Tonga.
 W
WMicronesia is a subregion of Oceania, composed of thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south; as well as with the wider Austronesian peoples.
 W
WThe Pacific Rim comprises the lands around the rim of the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Basin includes the Pacific Rim and the islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Rim roughly overlaps with the geologic Pacific Ring of Fire.
 W
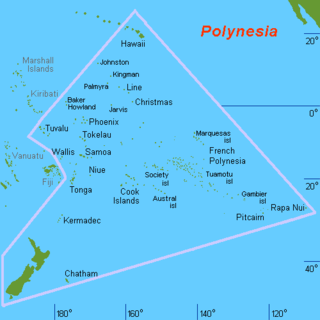
WPolynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians, sharing many similar traits including language family, culture, and beliefs. Historically, they had a strong tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand.