 W
WEast Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying on the Indian Ocean side of the continent, separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It lies almost entirely within the Eastern Hemisphere and its name has been accepted for more than a century. It is generally higher than West Antarctica and includes the Gamburtsev Mountain Range in the centre.
 W
WWest Antarctica, or Lesser Antarctica, one of the two major regions of Antarctica, is the part of that continent that lies within the Western Hemisphere, and includes the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from East Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains and is covered by the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. It lies between the Ross Sea, and the Weddell Sea. It may be considered a giant peninsula stretching from the South Pole towards the tip of South America.
 W
WAdélie Land is a claimed territory on the continent of Antarctica. It stretches from a portion of the Southern Ocean coastline all the way inland to the South Pole. France has administered it as one of five districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands since 1955 and applied the Antarctic Treaty System rules since 1961. Article 4 deals with territorial claims, and although it does not renounce or diminish any preexisting claims to sovereignty, it also does not prejudice the position of Contracting Parties in their recognition or non-recognition of territorial sovereignty. France has had a permanent station in Adélie Land since April 9, 1950. The current Dumont d'Urville Station has a winter population around 25, but this goes up to about 78 during the Antarctic summer.
 W
WCoats Land is a region in Antarctica which lies westward of Queen Maud Land and forms the eastern shore of the Weddell Sea, extending in a general northeast-southwest direction between 20º00´W and 36º00´W. The northeast part was discovered from the Scotia by William S. Bruce, leader of the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition, 1902-04. He gave the name Coats Land for James Coats, Jr., and Major Andrew Coats, the two chief supporters of the expedition.
 W
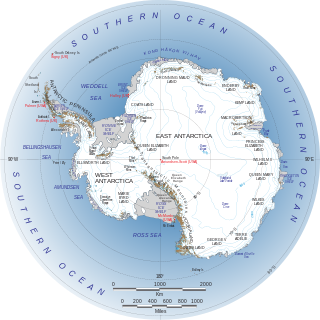
WMarie Byrd Land is the portion of West Antarctica lying east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon the leading role of the American Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd in the exploration of this area. The name was originally applied by Admiral Byrd in 1929, in honor of his wife, to the northwestern part of the area, the part that was explored in that year.
 W
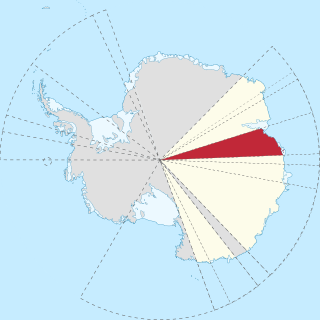
WPrincess Elizabeth Land is the sector of Antarctica between longitude 73° east and Cape Penck. The sector is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory, although this claim is not widely recognized.
 W
WQueen Elizabeth Land is portion of mainland Antarctica named by the government of the United Kingdom and claimed as part of the British Antarctic Territory, which is the largest of the 14 British Overseas Territories. Situated south of Weddell Sea and between longitudes 20°W and 80°W, stretching from Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf to the South Pole. That territory was unnamed until 2012, though most of it was unofficially known as Edith Ronne Land in 1947–68 and includes areas claimed by the United Kingdom, Chile and Argentina.
 W
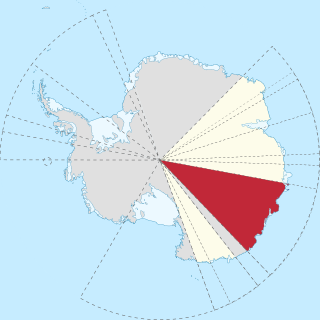
WWilkes Land is a large district of land in eastern Antarctica, formally claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory, though the validity of this claim has been placed for the period of the operation of the Antarctic Treaty, to which Australia is a signatory.