 W
WThe southern island group of Mindanao in the Philippines is divided into six administrative regions. Each region is subdivided into provinces.
 W
WAn autonomous region of the Philippines is a first-level administrative division that has the authority to control a region's culture and economy. The Constitution of the Philippines allows for two autonomous regions: in the Cordilleras and in Muslim Mindanao. Currently, Bangsamoro, which largely consists of the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao, is the only autonomous region in the country.
 W
WA barangay, sometimes referred to by its archaic name barrio, is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district, or ward. In metropolitan areas, the term often refers to an inner city neighbourhood, a suburb, or a suburban neighborhood. The word barangay originated from balangay, a kind of boat used by a group of Austronesian peoples when they migrated to the Philippines.
 W
WA barangay, sometimes referred to by its archaic name barrio, is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district, or ward. In metropolitan areas, the term often refers to an inner city neighbourhood, a suburb, or a suburban neighborhood. The word barangay originated from balangay, a kind of boat used by a group of Austronesian peoples when they migrated to the Philippines.
 W
WFederalism in the Philippines is a proposed form of government in the country.
 W
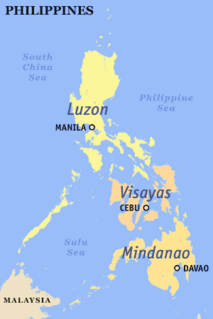
WThe Philippines is divided into three island groups of Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao. Luzon and Mindanao are both named after the largest island in their respective groups, while the Visayas is an archipelago.
 W
WA municipality is a local government unit (LGU) in the Philippines. A municipality is called town in its archaic term: a municipality has the function of a town since its inception. It is distinct from city, which is a different category of local government unit. Provinces of the Philippines are divided into cities and municipalities, which in turn, are divided into barangays – villages. As of 7 September 2019, there are 1,488 municipalities across the country.
 W
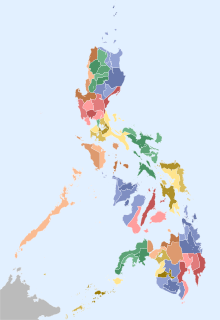
WThe provinces of the Philippines are the primary political and administrative divisions of the Philippines. There are 81 provinces at present, further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The local government units in the National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and an elected governor.