 W
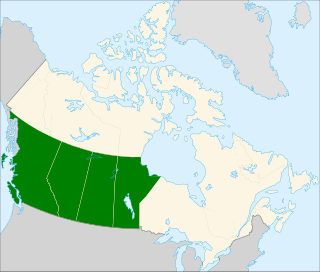
WWestern Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces and more commonly known as the West, is a region of Canada that includes the four provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan. British Columbia is culturally, economically, geographically, and politically distinct from the other parts of Western Canada and is often referred to as the "west coast" or "Pacific Canada", while Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba sometimes form a subset together as the Prairie Provinces.
 W
WBritish Columbia (BC) is the westernmost province in Canada, between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. With an estimated population of 5.1 million as of 2020, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, the fifteenth-largest metropolitan region in Canada, named for Queen Victoria, who ruled during the creation of the original colonies. The largest city is Vancouver, the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada, the largest in Western Canada, and the second-largest in the Pacific Northwest. In October 2013, British Columbia had an estimated population of 4,606,371. The province is currently governed by the British Columbia New Democratic Party, led by John Horgan with a majority government.
 W
WGinger beef is an Western Canadian dish made from beef, ginger, and a distinctive sweet sauce.
 W
WThroughout the 18th and 19th centuries, the plains bison and wood bison populations were hunted by nomadic indigenous hunters and white hunters alike. By the 1850s, the bison was nearly extinct, spurring a movement to save the few herds that remained. Federal government wildlife policy evolved from preservation of wilderness to utilitarian, scientific conservation and management of bison populations. The goals of these policies often contradicted themselves, aiming to simultaneously preserve wildlife, promote recreation, commercialize the bison, and assert state control over Aboriginal Canadians. Bison conservation efforts were shaped by the federal government's colonialist and modernist approach to Canada's north, the management of national parks and reserves, and the influence of scientific knowledge.
 W
WThe Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the front ranges of the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.
 W
WThe North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) made their initial journey to the Canadian prairies in March West, between July 8 and October 9 1874. The force was deployed to the Alberta border in response to the Cypress Hills Massacre and subsequent fears of a United States military intervention. Their ill-planned and arduous journey of nearly 900 miles (1,400 km) became known as the "March West" and was later portrayed by the force as an epic journey of endurance.
 W
WThe Royal Aviation Museum of Western Canada is a museum in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The museum is temporarily closed for relocation, and is scheduled to reopen in 2021.
 W
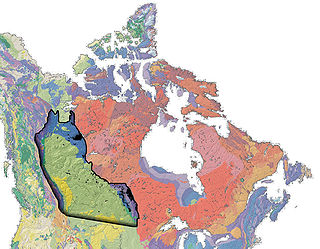
WThe Western Canada Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) is a vast sedimentary basin underlying 1,400,000 square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. It consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 16,000,000,000 cubic feet (450,000,000 m3) per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.