 W
WClassical Arabic or Quranic Arabic is the standardized literary form of the Arabic language used from the 7th century and throughout the Middle Ages, most notably in Umayyad and Abbasid literary texts such as poetry, elevated prose and oratory, and is also the liturgical language of Islam.
 W
WClassical Armenian is the oldest attested form of the Armenian language. It was first written down at the beginning of the 5th century, and all Armenian literature from then through the 18th century is in Classical Armenian. Many ancient manuscripts originally written in Ancient Greek, Persian, Hebrew, Syriac and Latin survive only in Armenian translation.
 W
WClassical Chinese, also known as Literary Chinese, is the language of the classic literature from the end of the Spring and Autumn period through to the end of the Han dynasty, a written form of Old Chinese. Classical Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese that evolved from the classical language, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese. Literary Chinese was used for almost all formal writing in China until the early 20th century, and also, during various periods, in Japan, Korea and Vietnam. Among Chinese speakers, Literary Chinese has been largely replaced by written vernacular Chinese, a style of writing that is similar to modern spoken Mandarin Chinese, while speakers of non-Chinese languages have largely abandoned Literary Chinese in favor of their respective local vernaculars. Although languages have evolved in unique, different directions from the base of Literary Chinese, many cognates can be still found between these languages that have historically written in Classical Chinese.
 W
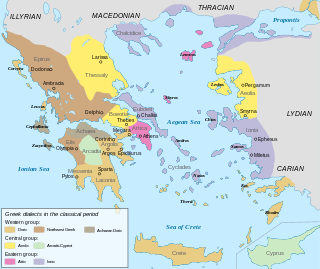
WAttic Greek is the Greek dialect of the ancient region of Attica, including the polis of Athens. Often called classical Greek, it was the prestige dialect of the Greek world for centuries and remains the standard form of the language that is taught to students of ancient Greek. As the basis of the Hellenistic Koine, it is the most similar of the ancient dialects to later Greek. Attic is traditionally classified as a member or sister dialect of the Ionic branch.
 W
WBiblical Hebrew, also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanite branch of Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Israel, roughly west of the Jordan River and east of the Mediterranean Sea. The term "Hebrew" (ibrit) was not used for the language in the Bible, which was referred to as שפת כנען or יהודית, but the name was used in Ancient Greek and Mishnaic Hebrew texts.
 W
WClassical Latin is the form of Latin language recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later periods, it was regarded as good or proper Latin, with following versions viewed as debased, degenerate, vulgar, or corrupted. The word Latin is now understood by default to mean "Classical Latin"; for example, modern Latin textbooks almost exclusively teach Classical Latin.
 W
WClassic Maya is the oldest historically attested member of the Maya linguistic family. It is the main language documented in the pre-Columbian inscriptions of the classical period of the Maya civilization. It is also a direct descendant of Proto-Mayan and the common ancestor of the Cholan branch of Mayan languages. Contemporary descendants of classical Maya include Ch'ol and Ch'orti'. Speakers of these languages can understand many Classic Mayan words.
 W
WOdia is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the official language in Odisha where native speakers make up 82% of the population, and it is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh. Odia is one of the many official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The language is also spoken by a sizeable population of at least 1 million people in Chhattisgarh.
 W
WSanskrit is a classical language of South Asia belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies.
 W
WTamil is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry. Tamil is spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors.
 W
WThe Sangam literature historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram : the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam literature is 100 BCE to 250 CE, based on the linguistic, prosodic and quasi-historic allusions within the texts and the colophons.