 W
WArtes mechanicae are a medieval concept of ordered practices or skills, often juxtaposed to the traditional seven liberal arts. Also called "servile" and "vulgar", from antiquity they had been deemed unbecoming for a free man, as ministering to baser needs.
 W
WAuthentica habita, or Privilegium Scholasticum, was a document written in 1155 ca. by the Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa. In it, he set out for the first time some of the rules, rights and privileges of universities. It is a key founding document in the history of the medieval university in Europe.
 W
WCathedral schools began in the Early Middle Ages as centers of advanced education, some of them ultimately evolving into medieval universities. Throughout the Middle Ages and beyond, they were complemented by the monastic schools. Some of these early cathedral schools, and more recent foundations, continued into modern times.
 W
WThe Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, the world's largest city by then, where Islamic scholars and polymaths from various parts of the world with different cultural backgrounds were mandated to gather and translate all of the known world's classical knowledge into Syriac and Arabic.
 W
WThe Latin school was the grammar school of 14th- to 19th-century Europe, though the latter term was much more common in England. Emphasis was placed, as the name indicates, on learning to use Latin. The education given at Latin schools gave great emphasis to the complicated grammar of the Latin language, initially in its Medieval Latin form. Grammar was the most basic part of the trivium and the Liberal arts — in artistic personifications Grammar's attribute was the birch rod. Latin school prepared students for university, as well as enabling those of middle class status to rise above their station. It was therefore not unusual for children of commoners to attend Latin schools, especially if they were expected to pursue a career within the church. Although Latin schools existed in many parts of Europe in the 14th century and were more open to the laity, prior to that the Church allowed for Latin schools for the sole purpose of training those who would one day become clergymen. Latin schools began to develop to reflect Renaissance humanism around the 1450s. In some countries, but not England, they later lost their popularity as universities and some Catholic orders began to prefer the vernacular.
 W
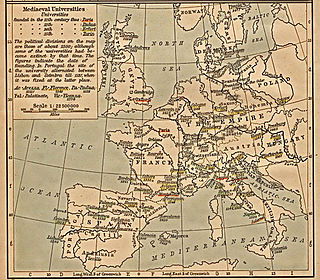
WThe list of medieval universities comprises universities which existed in Europe during the Middle Ages. It also includes short-lived foundations and European educational institutions whose university status is a matter of debate. The degree-awarding university with its corporate organization and relative autonomy is a product of medieval Christian Europe. Before 1500, more than eighty universities were established in Western and Central Europe. During the subsequent Colonization of the Americas the university was introduced to the New World, marking the beginning of its worldwide spread as the center of higher learning everywhere.
 W
WA medieval university was a corporation organized during the Middle Ages for the purposes of higher education. The first Western European institutions generally considered to be universities were established in the Kingdom of Italy, the Kingdom of England, the Kingdom of France, the Kingdom of Spain, and the Kingdom of Portugal between the 11th and 15th centuries for the study of the arts and the higher disciplines of theology, law, and medicine. During the 14th century there was an increase in growth of universities and colleges around Europe. These universities evolved from much older Christian cathedral schools and monastic schools, and it is difficult to define the exact date when they became true universities, though the lists of studia generalia for higher education in Europe held by the Vatican are a useful guide.
 W
WIn liberal arts education, the quadrivium consists of the four subjects or arts taught after the trivium. The word is Latin, meaning 'four ways', and its use for the four subjects has been attributed to Boethius or Cassiodorus in the 6th century. Together, the trivium and the quadrivium comprised the seven liberal arts, as distinguished from the practical arts.
 W
WA scholaster, from the Latin scholasticus (schoolmaster), or magister scholarum, was the head of an ecclesiastical school, typically a cathedral school, monastic school, or the school of a collegiate church, in medieval and early-modern Europe. Depending on the size of the school and the status of the institution to which it was attached, the scholaster might be the only teacher, the head of a considerable educational establishment, or have oversight over all the schools in their city or territory. The scholaster might be a dignitary in a cathedral or collegiate chapter, alongside the provost, dean, cantor, succentor, precentor, archdeacon, treasurer, cellarer, sacristan or almoner. It was not unknown for a scholaster to take the revenues of the post and deputise somebody else to carry out any teaching work involved.
 W
WStudium generale is the old customary name for a medieval university in medieval Europe.
 W
WThe trivium is the lower division of the seven liberal arts and comprises grammar, logic, and rhetoric.