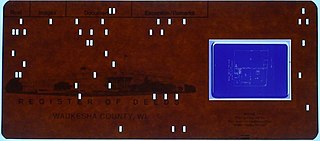
 W
WAn aperture card is a type of punched card with a cut-out window into which a chip of microfilm is mounted. Such a card is used for archiving or for making multiple inexpensive copies of a document for ease of distribution. The card is typically punched with machine-readable metadata associated with the microfilm image, and printed across the top of the card for visual identification; it may also be punched by hand in the form of an edge-notched card. The microfilm chip is most commonly 35mm in height, and contains an optically reduced image, usually of some type of reference document, such as an engineering drawing, that is the focus of the archiving process. Machinery exists to automatically store, retrieve, sort, duplicate, create, and digitize cards with a high level of automation.
 W
WAn Archival Resource Key (ARK) is a multi-purpose URL suited to being a persistent identifier for information objects of any type. It is widely used by libraries, data centers, archives, museums, publishers, and government agencies to provide reliable references to scholarly, scientific, and cultural objects. In 2019 it was registered as a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
 W
WComputable Document Format (CDF) is an electronic document format designed to allow authoring dynamically generated, interactive content. CDF was created by Wolfram Research, and CDF files can be created using Mathematica. As of 2021, the Wolfram Research website lists CDF as a "legacy" format.
 W
WDataCite is an international not-for-profit organization which aims to improve data citation in order to:establish easier access to research data on the Internet increase acceptance of research data as legitimate, citable contributions to the scholarly record support data archiving that will permit results to be verified and re-purposed for future study.
 W
WA digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to identify objects uniquely, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications. DOIs have also been used, however, to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.
 W
WGoogle Wave, later known as Apache Wave, was a software framework for real-time collaborative editing online. Originally developed by Google and announced on 28 May 2009, it was renamed to Apache Wave when the project was adopted by the Apache Software Foundation as an incubator project in 2010.
 W
WThe International Image Interoperability Framework defines several application programming interfaces that provide a standardised method of describing and delivering images over the web, as well as "presentation based metadata" about structured sequences of images. If institutions holding artworks, books, newspapers, manuscripts, maps, scrolls, single sheet collections, and archival materials provide IIIF endpoints for their content, any IIIF-compliant viewer or application can consume and display both the images and their structural and presentation metadata.
 W
Wlettrs is a global mobile application and social network that allows users to compose and send mobile messages privately or publicly. The lettrs app converts mobile voice, data and pictures to digital personal and public messages via its text and mobile delivery inventions.
 W
WElectronic mail is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email entered limited use in the 1960s, but users could only send to users of the same computer. Some systems also supported a form of instant messaging, where sender and receiver needed to be online simultaneously. Ray Tomlinson is credited as the inventor of networked email; in 1971, he developed the first system able to send mail between users on different hosts across the ARPANET, using the @ sign to link the user name with a destination server. By the mid-1970s, this was the form recognized as email.
 W
WA quick start guide or quickstart guide (QSG) is in essence a shortened version of a manual, meant to make a buyer familiar with his or her product as soon as possible. This implies the use of a concise step-based approach that allows the buyer to use a product without any delay, if necessary including the relevant steps needed for installation. A quick start guide, or QSG for short, focuses on the most common instructions, often accompanying such instructions with easy-to-understand illustrations. The appearance of a QSG can vary significantly from product to product and from manufacturer to manufacturer. For example, it could be a single A4 sheet, a folded card or a booklet consisting of only a few pages.
 W
WTheSwizzle was a webmail tool that worked with existing email and enabled consumers to manage email subscriptions, primarily from commercial vendors. It was acquired by Mailstrom of 410 Labs in September 2014, and TheSwizzle.com subsequently shut down.
 W
WZathura is a free, plugin-based document viewer. Plugins are available for PDF, PostScript and DjVu. It was written to be lightweight and controlled with vi-like keybindings. Zathura's customizability makes it well-liked by many Linux users.