 W
WA granular material is a conglomeration of discrete solid, macroscopic particles characterized by a loss of energy whenever the particles interact. The constituents that compose granular material are large enough such that they are not subject to thermal motion fluctuations. Thus, the lower size limit for grains in granular material is about 1 μm. On the upper size limit, the physics of granular materials may be applied to ice floes where the individual grains are icebergs and to asteroid belts of the Solar System with individual grains being asteroids.
 W
WAggregate is the component of a composite material that resists compressive stress and provides bulk to the composite material. For efficient filling, aggregate should be much smaller than the finished item, but have a wide variety of sizes. For example, the particles of stone used to make concrete typically include both sand and gravel.
 W
WA cobble is a clast of rock defined on the Udden–Wentworth scale as having a particle size of 64–256 millimeters (2.5–10.1 in), larger than a pebble and smaller than a boulder. Other scales define a cobble's size differently. A rock made predominantly of cobbles is termed a conglomerate. Cobblestone is a building material based on cobbles.
 W
WConstruction aggregate, or simply aggregate, is a broad category of coarse- to medium-grained particulate material used in construction, including sand, gravel, crushed stone, slag, recycled concrete and geosynthetic aggregates. Aggregates are the most mined materials in the world. Aggregates are a component of composite materials such as concrete and asphalt; the aggregate serves as reinforcement to add strength to the overall composite material. Due to the relatively high hydraulic conductivity value as compared to most soils, aggregates are widely used in drainage applications such as foundation and French drains, septic drain fields, retaining wall drains, and roadside edge drains. Aggregates are also used as base material under foundations, roads, and railroads. In other words, aggregates are used as a stable foundation or road/rail base with predictable, uniform properties, or as a low-cost extender that binds with more expensive cement or asphalt to form concrete.
 W
WCrushed stone or angular rock is a form of construction aggregate, typically produced by mining a suitable rock deposit and breaking the removed rock down to the desired size using crushers. It is distinct from gravel which is produced by natural processes of weathering and erosion, and typically has a more rounded shape.
 W
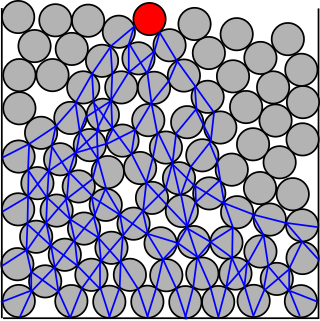
WIn the study of the physics of granular materials, a force chain consists of a set of particles within a compressed granular material that are held together and jammed into place by a network of mutual compressive forces.
 W
WGranular convection is a phenomenon where granular material subjected to shaking or vibration will exhibit circulation patterns similar to types of fluid convection. It is sometimes described as the Brazil nut effect when the largest particles end up on the surface of a granular material containing a mixture of variously sized objects; this derives from the example of a typical container of mixed nuts, where the largest will be Brazil nuts. The phenomenon is also known as the muesli effect since it is seen in packets of breakfast cereal containing particles of different sizes but similar density, such as muesli mix.
 W
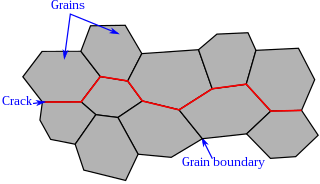
WIntergranular fracture occurs when a crack propagates along the grain boundaries of a material, usually when these grain boundaries are weakened. The more commonly seen transgranular fracture, occurs when the crack grows through the material grains. As an analogy, in a wall of bricks, intergranular fracture would correspond to a fracture that takes place in the mortar that keeps the bricks together.
 W
WLubachevsky-Stillinger (compression) algorithm is a numerical procedure suggested by F. H. Stillinger and B.D. Lubachevsky that simulates or imitates a physical process of compressing an assembly of hard particles. As the LSA may need thousands of arithmetic operations even for a few particles, it is usually carried out on a computer.
 W
WA pebble is a clast of rock with a particle size of 4–64 mm (0.16–2.52 in) based on the Udden-Wentworth scale of sedimentology. Pebbles are generally considered larger than granules and smaller than cobbles. A rock made predominantly of pebbles is termed a conglomerate. Pebble tools are among the earliest known man-made artifacts, dating from the Palaeolithic period of human history.
 W
WA powder is a dry, bulk solid composed of many very fine particles that may flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms powder and granular are sometimes used to distinguish separate classes of material. In particular, powders refer to those granular materials that have the finer grain sizes, and that therefore have a greater tendency to form clumps when flowing. Granulars refers to the coarser granular materials that do not tend to form clumps except when wet.
 W
WSoil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Earth's body of soil, called the pedosphere, has four important functions:as a medium for plant growth as a means of water storage, supply and purification as a modifier of Earth's atmosphere as a habitat for organisms