 W
WBautil is a fundamental Swedish runological work by the priest, runologist and archaeologist Johan Göransson, published in 1750.
 W
WViking art, also known commonly as Norse art, is a term widely accepted for the art of Scandinavian Norsemen and Viking settlements further afield—particularly in the British Isles and Iceland—during the Viking Age of the 8th-11th centuries CE. Viking art has many design elements in common with Celtic, Germanic, the later Romanesque and Eastern European art, sharing many influences with each of these traditions.
 W
WThe East Germanic languages, also called the Oder–Vistula Germanic languages, are a group of extinct Germanic languages spoken by East Germanic peoples. East Germanic is one of the primary branches of Germanic languages, along with North Germanic and West Germanic.
 W
WThe francisca is a throwing axe used as a weapon during the Early Middle Ages by the Franks, among whom it was a characteristic national weapon at the time of the Merovingians from about 500 to 750 and is known to have been used during the reign of Charlemagne (768–814). Although generally associated with the Franks, it was also used by other Germanic peoples of the period, including the Anglo-Saxons; several examples have been found in England.
 W
WViking art, also known commonly as Norse art, is a term widely accepted for the art of Scandinavian Norsemen and Viking settlements further afield—particularly in the British Isles and Iceland—during the Viking Age of the 8th-11th centuries CE. Viking art has many design elements in common with Celtic, Germanic, the later Romanesque and Eastern European art, sharing many influences with each of these traditions.
 W
WThe Nordwestblock is a hypothetical Northwestern European cultural region that some scholars propose as a prehistoric culture in the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, northern France, and northwestern Germany, in an area approximately bounded by the Somme, Oise, Meuse and Elbe rivers, possibly extending to the eastern part of what is now England, during the Bronze and Iron Ages from the 3rd to the 1st millennia BCE, up to the onset of historical sources, in the 1st century BCE.
 W
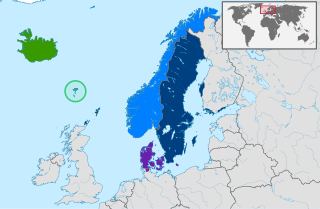
WThe North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the "Nordic languages", a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish scholars and people.
 W
WNorth Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic, is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants.
 W
WViking art, also known commonly as Norse art, is a term widely accepted for the art of Scandinavian Norsemen and Viking settlements further afield—particularly in the British Isles and Iceland—during the Viking Age of the 8th-11th centuries CE. Viking art has many design elements in common with Celtic, Germanic, the later Romanesque and Eastern European art, sharing many influences with each of these traditions.
 W
WA picture stone, image stone or figure stone is an ornate slab of stone, usually limestone, which was raised in Germanic Iron Age or Viking Age Scandinavia, and in the greatest number on Gotland. More than four hundred picture stones are known today. All of the stones were probably erected as memorial stones, but only rarely beside graves. Some of them have been positioned where many people could see them at bridges and on roads.
 W
WA runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but most of the runestones date from the late Viking Age. Most runestones are located in Scandinavia, but there are also scattered runestones in locations that were visited by Norsemen during the Viking Age. Runestones are often memorials to dead men. Runestones were usually brightly coloured when erected, though this is no longer evident as the colour has worn off. Most runestones are found in present-day Sweden.
 W
WA sceat was a small, thick silver coin minted in England, Frisia, and Jutland during the Anglo-Saxon period that normally weighed 0.8–1.3 grams.
 W
WThe Suebian knot is a historical male hairstyle ascribed to the tribe of the Germanic Suebi. The knot is attested by Tacitus in his 1st century AD work Germania, found on contemporary depictions of Germanic peoples, their art, and bog bodies.