 W
WThe ATA Carnet, often referred to as the "Passport for goods", is an international customs document that permits the tax-free and duty-free temporary export and import of nonperishable goods for up to one year. It consists of unified customs declaration forms which are prepared ready to use at every border crossing point. It is a globally accepted guarantee for customs duties and taxes which can replace the security deposit required by each customs authority. It can be used in multiple countries in multiple trips up to its one-year validity. The acronym ATA is a combination of French and English terms "Admission Temporaire/Temporary Admission." The ATA carnet is now the document most widely used by the business community for international operations involving temporary admission of goods.
 W
WThe Carnet de Passages en Douane is a customs document that identifies a traveller's motor vehicle or other valuable equipment or baggage. It is required in order to take a motor vehicle into a significant but diminishing number of countries around the world.
 W
WCountervailing duties (CVDs), also known as anti-subsidy duties, are trade import duties imposed under World Trade Organization (WTO) rules to neutralize the negative effects of subsidies. They are imposed after an investigation finds that a foreign country subsidizes its exports, injuring domestic producers in the importing country. According to World Trade Organization rules, a country can launch its own investigation and decide to charge extra duties, provided such additional duties are in accordance with the GATT Article VI and the GATT Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures.
 W
WThe Court of Exchequer was formerly a distinct part of the court system of Scotland, with responsibility for administration of government revenue and jurisdiction of adjudicate on cases relating to customs and excise, revenue, stamp duty and probate. In 1856 the Court of Session was designated as the Exchequer Court, which now carries out its judicial functions.
 W
WCustoms is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs has been considered as the fiscal subject that charges customs duties and other taxes on import and export. In recent decades, the views on the functions of customs have considerably expanded and now covers three basic issues: taxation, security, and trade facilitation.
 W
WA duty-free shop is a retail outlet whose goods are exempt from the payment of certain local or national taxes and duties, on the requirement that the goods sold will be sold to travelers who will take them out of the country. Which products can be sold duty-free vary by jurisdiction, as well as how they can be sold, and the process of calculating the duty or refunding the duty component.
 W
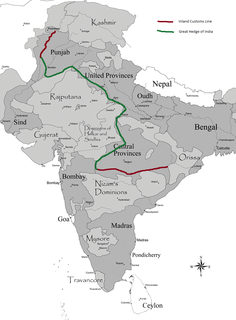
WThe Inland Customs Line, incorporating the Great Hedge of India, was a customs barrier built by the British colonial rulers of India to prevent smuggling of salt from coastal regions in order to avoid the substantial salt tax.
 W
WThe Lotteries Act 1710 was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain. As enacted, it specified duties on exports of certain commodities, coal, and candles and regulated the state lottery. Section 57, the last to be repealed, reinforced the Suppression of Lotteries Act 1698 and specified a £100 fine for offenders, to be distributed one third each to the Crown, the parish poor, and the informant.
 W
WThe offshore off-licence is the name coined by the media to describe a 2004 venture to bring "tax- and duty-free" alcohol and cigarettes to Teesside, England, by selling the imported goods from a boat anchored just outside the UK's 12-mile limit. Two businessmen, Phil Berriman and Trevor Lyons, a maritime law expert, used the latter's 72-foot staysail schooner Rich Harvest to transport large quantities of cigarettes and spirits from Heligoland to Hartlepool. The vessel was anchored a little more than 12 miles offshore, and people from Hartlepool came out in private boats to buy the untaxed goods. Customers would then ostensibly be allowed to bring their purchases into the UK using their duty-free allowance.
 W
WTrinity House, 99 Kirkgate, is a building in Leith, Edinburgh, Scotland, which was a guild hall, customs house, and centre for maritime administration and poor relief. In the Late Middle Ages and Early Modern Era it also served as an almshouse and hospital. Now in state care, it houses a maritime museum. It is a category A listed building.
 W
WA trade war is an economic conflict resulting from extreme protectionism in which states raise or create tariffs or other trade barriers against each other in response to trade barriers created by the other party. If tariffs are the exclusive mechanism, then such conflicts are known as Customs wars, toll wars or tariff wars; as a reprisal, the latter state may also increase the tariffs. Increased protection causes both nations' output compositions to move towards their autarky position.
 W
WThe Trump tariffs are a series of United States tariffs imposed during the presidency of Donald Trump as part of his "America First" economic policy to reduce the United States trade deficit by shifting American trade policy from multilateral free trade agreements to bilateral trade deals. In January 2018, Trump imposed tariffs on solar panels and washing machines of 30 to 50 percent. In March 2018, he imposed tariffs on steel (25%) and aluminum (10%) from most countries, which, according to Morgan Stanley, covered an estimated 4.1 percent of U.S. imports. In June 2018, this was extended to the European Union, Canada, and Mexico. In separate moves, the Trump administration has set and escalated tariffs on goods imported from China, leading to a trade war.
 W
WThe World Customs Organization (WCO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. The WCO works on customs-related matters including the development of international conventions, instruments, and tools on topics such as commodity classification, valuation, rules of origin, collection of customs revenue, supply chain security, international trade facilitation, customs enforcement activities, combating counterfeiting in support of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), illegal drug enforcement, combating counterfeiting of medicinal drugs, illegal weapons trading, integrity promotion, and delivering sustainable capacity building to assist with customs reforms and modernization. The WCO maintains the international Harmonized System (HS) goods nomenclature, and administers the technical aspects of the World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreements on Customs Valuation and Rules of Origin.