 W
WAdobe Fonts is an online service that provides its subscribers with access to its font library, under a single licensing agreement. The fonts may be used directly on websites, or synced via Adobe Creative Cloud to applications on the subscriber's computers.
 W
WApple Inc. uses a large variety of typefaces in its marketing, operating systems, and industrial design with each product cycle. These change throughout the years with Apple's change of style in their products. This is evident in the design and marketing of the company.
 W
WBoston line letter was a tactile writing system created by Dr. Samuel Gridley Howe in 1835, a popular precursor to the now-standardized Braille.
 W
WBraille is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired. It is traditionally written with embossed paper. Braille users can read computer screens and other electronic supports using refreshable braille displays. They can write braille with the original slate and stylus or type it on a braille writer, such as a portable braille notetaker or computer that prints with a braille embosser.
 W
WEmigre Fonts is a digital type foundry based in Berkeley, California, that was founded in 1985 by husband-and-wife team Rudy VanderLans and Zuzana Licko. The type foundry grew out of Emigre magazine, a publication founded by VanderLans and two Dutch friends who met in San Francisco, CA in 1984. Note that unlike the word émigré, Emigre is officially spelled without accents.
 W
WFont hinting is the use of mathematical instructions to adjust the display of an outline font so that it lines up with a rasterized grid. At low screen resolutions, hinting is critical for producing clear, legible text. It can be accompanied by antialiasing and subpixel rendering for further clarity.
 W
WIBM in atoms was a demonstration by IBM scientists in 1989 of a technology capable of manipulating individual atoms. A scanning tunneling microscope was used to arrange 35 individual xenon atoms on a substrate of chilled crystal of nickel to spell out the three letter company initialism. It was the first time atoms had been precisely positioned on a flat surface.
 W
WIn digital typography, the Medieval Unicode Font Initiative (MUFI) is a project which aims to coordinate the encoding and display of special characters in medieval texts written in the Latin alphabet, which are not encoded as part of Unicode.
 W
WMultiple master fonts are an extension to Adobe Systems' Type 1 PostScript fonts, now superseded by the advent of OpenType and, in particular, the introduction of OpenType Font Variations in OpenType 1.8, also called variable fonts.
 W
WFont rasterization is the process of converting text from a vector description to a raster or bitmap description. This often involves some anti-aliasing on screen text to make it smoother and easier to read. It may also involve hinting—information embedded in the font data that optimizes rendering details for particular character sizes.
 W
WThe topic of seven-segment display character representations revolves around the various shapes of numerical digits, letters, and punctuation devisable on seven-segment displays. Such representation of characters is not standardized by any relevant entity. Unicode provides encoding codepoint for segmented digits in Unicode 13.0 in Symbols for Legacy Computing block.
 W
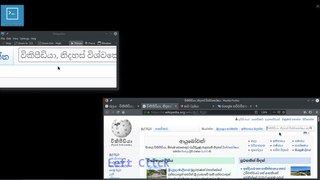
WSinhala input methods are ways of writing the Sinhala language, spoken primarily in Sri Lanka, using a computer. Sinhala input methods can be broadly classified into two main groups: ones based on typewriter keyboard layouts, and ones that are meant to be typed on QWERTY keyboards using an input method, known as "Singlish".
 W
WUnicode, formally the Unicode Standard, is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines 144,697 characters covering 159 modern and historic scripts, as well as symbols, emoji, and non-visual control and formatting codes.
 W
WWeb typography refers to the use of fonts on the World Wide Web. When HTML was first created, font faces and styles were controlled exclusively by the settings of each web browser. There was no mechanism for individual Web pages to control font display until Netscape introduced the font element in 1995, which was then standardized in the HTML 3.2 specification. However, the font specified by the font element had to be installed on the user's computer or a fallback font, such as a browser's default sans-serif or monospace font, would be used. The first Cascading Style Sheets specification was published in 1996 and provided the same capabilities.
 W
WXeTeX is a TeX typesetting engine using Unicode and supporting modern font technologies such as OpenType, Graphite and Apple Advanced Typography (AAT). It was originally written by Jonathan Kew and is distributed under the X11 free software license.