 W
WAfghans or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry from there. Concurrently the term "Afghan" can refer to someone or something of that country. Afghanistan is made up of various ethnicities, of which the Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras and Uzbeks are the largest; the pre-nation state, historical ethnonym Afghan was used to refer to a member of the Pashtuns, an ethnicity that traditionally resides in the modern Afghanistan-Pakistan border region. Due to the changing political nature of the state, such as the British-drawn border with India in 1893, the term has shifted to be the national identity of people from Afghanistan from all ethnicities. The two main languages spoken by Afghans are Pashto and Dari, and many are bilingual.
 W
WAjam is an Arabic word meaning mute, which today refers to someone whose mother tongue is not Arabic. During the Arab conquest of Persia, the term became a racial pejorative. In many languages — including Persian, Turkish, Urdu, Azerbaijani, Bengali, Hindi, Kurdish, Gujarati, Malay, Punjabi, and Swahili — Ajam and Ajami refer to Iran and Iranians respectively.
 W
WA barbarian is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less civilized or orderly but may also be part of a certain "primitive" cultural group or social class both within and outside one's own nation. Alternatively, they may instead be admired and romanticised as noble savages. In idiomatic or figurative usage, a "barbarian" may also be an individual reference to a brutal, cruel, warlike, and insensitive person.
 W
WBjarmaland was a territory mentioned in Norse sagas since the Viking Age and in geographical accounts until the 16th century. The term is usually seen to have referred to the southern shores of the White Sea and the basin of the Northern Dvina River as well as, presumably, some of the surrounding areas. Today, those territories comprise a part of the Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia, as well as the Kola Peninsula.
 W
WFarang is a Persian word that originally referred to the Franks and later came to refer to Europeans in general. The word "Farang" is a cognate and originates from Old French: "franc".
 W
WGarðaríki or Garðaveldi is the Old Norse term used in medieval times for the states of Rus'.
 W
WGiaour or Gawur meaning "infidel", a slur, historically used in the Ottoman Empire for non-Muslims or more particularly Christians in the Balkans.
 W
WIn modern Hebrew and Yiddish goy is a term for a gentile, a non-Jew. Through Yiddish, the word has been adopted into English also to mean gentile, sometimes with a pejorative sense.
 W
WJuan dela Cruz or Maria dela Cruz for females, is the national personification of the Philippines, often used to represent the "Filipino everyman." He is usually depicted wearing the native salakot hat, Barong Tagalog, long pants, and tsinelas.
 W
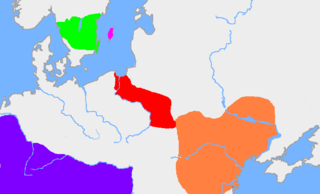
WOstyak is a name formerly used to refer to several indigenous peoples and languages in Siberia, Russia. Both the Khanty people and the Ket people were formerly called Ostyaks, whereas the Selkup people were referred to as Ostyak-Samoyed.
 W
WReidgotaland, Reidgothland, Reidgotland, Hreidgotaland or Hreiðgotaland was a land in Scandinavian sagas as well as in the pre-Viking English Widsith, which usually referred to the land of the Goths.
 W
WRuthenians /ruːˈθiːnɪən/ and Ruthenes are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Western and Central Europe as common designations for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. Latin term Rutheni was initially used, since the 11th century, as an exonymic designation for people of the medieval Kievan Rus', thus including ancestors of the modern Ukrainians, Rusyns and the most of Belarusians. The use of Ruthenian designations was continued throughout the early modern period, acquiring several distinctive meanings, both in terms of their regional scopes and additional religious connotations.
 W
WSaracens were primarily Arab Muslims, but also Turks, Persians or other Muslims as referred to by Christian writers in Europe during the Middle Ages. The term's meaning evolved during its history. In the early centuries of the Christian Era, Greek and Latin writings used the term to refer to the people who lived in desert areas in and near the Roman province of Arabia Petraea, and in Arabia Deserta. In Europe during the Early Middle Ages, the term came to be associated with tribes of Arabia. The oldest known source mentioning Saracens in relation to Islam dates to the 7th century. It was found in Doctrina Jacobi, a commentary that discussed the Muslim conquest of the Levant.
 W
WTartary or Tatary was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China and India at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym can be traced from the 13th to the 19th century. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia in a series of negatively colored names that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main population of which in the past was engaged in animal husbandry.
 W
WZanj was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is also the origin of the place-names Zanzibar and the Sea of Zanj.