 W
WA druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.
 W
WAn adder stone is a type of stone, usually glassy, with a naturally occurring hole through it. Such stones, which usually consist of flint, have been discovered by archaeologists in both Britain and Egypt. Commonly, they are found in Northern Germany at the coasts of the North and Baltic Seas.
 W
WThe Bard. A Pindaric Ode (1757) is a poem by Thomas Gray, set at the time of Edward I's conquest of Wales. Inspired partly by his researches into medieval history and literature, partly by his discovery of Welsh harp music, it was itself a potent influence on future generations of poets and painters, seen by many as the first creative work of the Celtic Revival and as lying at the root of the Romantic movement in Britain.
 W
WBarddas is a book of material compiled and written by the Welsh writer and literary forger Iolo Morganwg. Though purported to be an authentic compilation of ancient Welsh bardic and druidic theology and lore, its contents are largely Iolo's own invention. The work was published by John Williams for the Welsh Manuscripts Society in two volumes, 1862 and 1874.
 W
WBenie Hoose, also Bunyie Hoose, is a Neolithic site in the parish of Nesting, northeastern Whalsay, in the Shetland Islands of Scotland. It is located approximately 100 yards (91 m) to the northwest of the Standing Stones of Yoxie, and about 140 metres (460 ft) southeast of the Pettigarths Field Cairns. Benie Hoose and Yoxie demonstrate characteristics of 'paired houses'. It was excavated in 1954–1955 by Charles S. T. Calder who gave the items to the National Museum of Antiquities of Scotland in 1955–1956. Furthermore, its close proximity to Yoxie indicates that Druid priests probably lived in the house and performed ceremonies at the stones. OS (NKB) visited the site on 30 May 1968. The one-room site measures 24.4 by 12.8 metres, and features a horned forecourt.
 W
WThe Druid Network is a British druidic (neo-pagan) organisation providing a source of information and inspiration about modern Druidic traditions, practices and their histories. It was founded in February 2003 by Emma Restall Orr, and approved as a religious charity in the United Kingdom in 2010.
 W
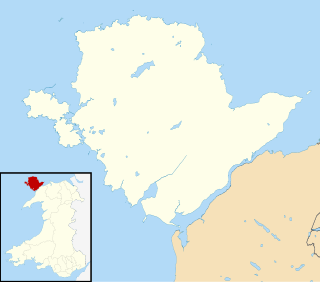
WIlton is a village in North Yorkshire, England, 3 miles south-west of Masham. It is the principal settlement in the civil parish of Ilton cum Pott, in Harrogate district. The parish includes Roundhill Reservoir. The population of the parish was estimated at 50 in 2015.
 W
WGorsedd Cymru, or simply the Gorsedd or the Orsedd, is a society of Welsh-language poets, writers, musicians and others who have contributed to the Welsh language and to public life in Wales. Its aim is to honour such individuals and help develop and promote their fields in addition to maintaining relationships with other Celtic nations and Y Wladfa. The Gorsedd is most prominent at the National Eisteddfod of Wales where it is responsible for the main ceremonies held.
 W
WGorsedd Stones are groups of standing stones constructed for the National Eisteddfod of Wales. They form an integral part of the druidic Gorsedd ceremonies of the Eisteddfod. The stones can be found as commemorative structures throughout Wales and are the hallmark of the National Eisteddfod having visited a community.
 W
WHuman sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors, as a retainer sacrifice when a king's servants are killed in order for them to continue to serve their master in the next life. Closely related practices found in some tribal societies are cannibalism and headhunting.
 W
WHuman sacrifice in the ancient Iberian Peninsula is recorded in classical sources, which give it as a custom of Lusitanians and other Celtic peoples from the northern area of the peninsula. Its most complete mention comes from the work of Greek chronicler Strabo, in which those ceremonies have a divinatory utility. Modern authors have seen in this phenomenon hints of a possible priestly class among the mentioned peoples, similar to but differentiated from European Celtic druids.
 W
WA nemeton was a sacred space of ancient Celtic religion. Nemeta appear to have been primarily situated in natural areas, and, as they often utilized trees, they are often interpreted as sacred groves. However, other evidence suggests that the word implied a wider variety of ritual spaces, such as shrines and temples. Evidence for nemeta consists chiefly of inscriptions and toponymy or place-names, which occur all across the Celtic world. Toponyms related to the word nemeton occur as far west as Galicia in the Iberian peninsula, as far north as Scotland, and as far east as central Turkey. The word is related to the name of the Nemetes tribe living by the Rhine between the Palatinate and Lake Constance in what is now Germany, and their goddess Nemetona.
 W
WThe Romans invaded north-west Wales in 60/61 CE after subjugating much of southern Britain. Anglesey, recorded in Latin as Mona and still the island of Môn in modern Welsh, at the north-west corner of Wales, was a centre of resistance to Rome.
 W
WThe Standing Stones of Yoxie is a Neolithic site in the parish of Nesting on the northeastern coast of Whalsay, in the Shetland islands of Scotland. It is located approximately 100 yards (91 m) to the southeast of Benie Hoose, not far from the steep cliffs of Yoxie Geo. The site is also known as "Yoxie Biggins". The structure is the remains of a building in a neolithic settlement called Pettigarths Field, about 4,000 years old, which also includes a megalithic tomb and Benie Hoose. The site has been compared to that of Hal Tarxien.
 W
WIn modern English, the nouns vates and ovate (, ), are used as technical terms for ancient Celtic bards, prophets and philosophers. The terms correspond to a Proto-Celtic word which can be reconstructed as *wātis. They are sometimes also used as English equivalents to later Celtic terms such as Irish fáith "prophet, seer".
 W
WA wicker man was a large wicker statue reportedly used by the ancient Druids for sacrifice by burning it in effigy.