 W
WLudwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein was an Austrian-British philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language. He is considered to be one of the greatest philosophers of the modern era.
 W
WThe Austrian Ludwig Wittgenstein Society was first established in 1974 to promote philosophical conferences, workshops, summer schools, and research that are inspired by the work of Ludwig Wittgenstein and the Vienna Circle. It is an international society, which also has a publication series.
 W
WFamily resemblance is a philosophical idea made popular by Ludwig Wittgenstein, with the best known exposition given in his posthumously published book Philosophical Investigations (1953). It argues that things which could be thought to be connected by one essential common feature may in fact be connected by a series of overlapping similarities, where no one feature is common to all of the things. Games, which Wittgenstein used as an example to explain the notion, have become the paradigmatic example of a group that is related by family resemblances. It has been suggested that Wittgenstein picked up the idea and the term from Friedrich Nietzsche, who had been using it, as did many nineteenth century philologists, when discussing language families.
 W
WForm of life is a term used sparingly by Ludwig Wittgenstein in posthumously published works Philosophical Investigations, On Certainty and in parts of his Nachlass. The term itself is ambiguously understood, giving grounds for both a universal and/or relativistic understanding of Wittgenstein's philosophy and as such should not be presented here as either the one or the other.
 W
WThe Haidbauer incident, known in Austria as Der Vorfall Haidbauer, took place in April 1926 when Josef Haidbauer, an 11-year-old schoolboy in Otterthal, Austria, reportedly collapsed unconscious after being hit on the head during class by the Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein.
 W
WA language-game is a philosophical concept developed by Ludwig Wittgenstein, referring to simple examples of language use and the actions into which the language is woven. Wittgenstein argued that a word or even a sentence has meaning only as a result of the "rule" of the "game" being played. Depending on the context, for example, the utterance "Water!" could be an order, the answer to a question, or some other form of communication.
 W
WLudwig Wittgenstein considered his chief contribution to be in the philosophy of mathematics, a topic to which he devoted much of his work between 1929 and 1944. As with his philosophy of language, Wittgenstein's views on mathematics evolved from the period of the Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus: with him changing from logicism towards a general anti-foundationalism and constructivism that was not readily accepted by the mathematical community. The success of Wittgenstein's general philosophy has tended to displace the real debates on more technical issues.
 W
WDavid Hume Pinsent was a collaborator of the Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein. Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus (1922) is dedicated to Pinsent's memory.
 W
WThe private language argument argues that a language understandable by only a single individual is incoherent, and was introduced by Ludwig Wittgenstein in his later work, especially in the Philosophical Investigations. The argument was central to philosophical discussion in the second half of the 20th century.
Frank Plumpton Ramsey was a British philosopher, mathematician, and economist who made major contributions to all three fields before his death at the age of 26. He was a close friend of Ludwig Wittgenstein and, as an undergraduate, translated Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus into English. He was also influential in persuading Wittgenstein to return to philosophy and Cambridge. Like Wittgenstein, he was a member of the Cambridge Apostles, the secret intellectual society, from 1921.
 W
WRemarks on Colour was one of Ludwig Wittgenstein's last works, written in Oxford in 1950, the year before he died.
 W
WRemarks on the Foundations of Mathematics is a book of Ludwig Wittgenstein's notes on the philosophy of mathematics. It has been translated from German to English by G.E.M. Anscombe, edited by G.H. von Wright and Rush Rhees, and published first in 1956. The text has been produced from passages in various sources by selection and editing. The notes have been written during the years 1937–1944 and a few passages are incorporated in the Philosophical Investigations which were composed later. When the book appeared it received many negative reviews mostly from working logicians and mathematicians, among them Michael Dummett, Paul Bernays, and Georg Kreisel. Today Remarks on the Foundations of Mathematics is read mostly by philosophers sympathetic to Wittgenstein and they tend to adopt a more positive stance.
 W
WSidney George Francis Guy Skinner was a friend, collaborator, and lover of the Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein.
 W
WWittgenstein is a 1993 experimental comedy-drama film directed by Derek Jarman and produced by Tariq Ali. An international co-production of the United Kingdom and Japan, the film is loosely based on the life story as well as the philosophical thinking of the philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein. The adult Wittgenstein is played by Karl Johnson.
 W
WWittgenstein's Mistress by David Markson is a highly stylized, experimental novel in the tradition of Samuel Beckett. The novel is mainly a series of statements made in the first person; the protagonist is a woman named Kate who believes herself to be the last human on earth. Though her statements shift quickly from topic to topic, the topics often recur, and often refer to Western cultural icons, ranging from Zeno to Beethoven to Willem de Kooning. Readers familiar with Ludwig Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus will recognize stylistic similarities to that work.
 W
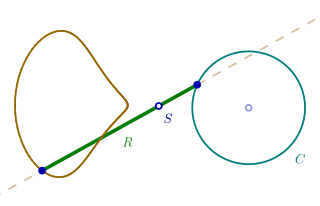
WWittgenstein's rod is a problem in geometry discussed by 20th-century philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein.