 W
WComfort women or comfort girls were women and girls forced into sexual slavery by the Imperial Japanese Army in occupied countries and territories before and during World War II. The name "comfort women" is a translation of the Japanese ianfu (慰安婦), a euphemism for "prostitutes".
 W
WThe Bahay na Pula is a former hacienda in San Ildefonso, Bulacan in the Philippines. The site is remembered for the mass rapes and murders committed by the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. The Japanese military murdered all of the men and boys in the adjacent Mapaniqui, Candaba, Pampanga, and forced over 100 women and girls into sexual slavery, confining and raping them in the Red House.
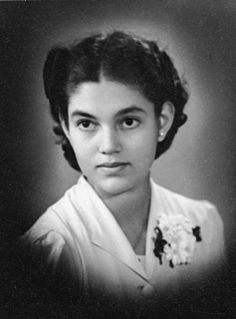 W
WThis is a list of human rights activists who were enslaved by the Japanese Imperial Army as "comfort women" during World War II.
 W
WMaría Rosa Luna Henson or "Lola Rosa" was the first Filipina who made public in 1992 her story as a comfort woman for the Imperial Japanese Army during the Second World War.
 W
WMichael Makoto Honda is an American politician and former educator. A member of the Democratic Party, he served in Congress from 2001 to 2017.
 W
WThe House of Sharing is a nursing home for living comfort women in Seoul, South Korea. The House of Sharing was founded in June 1992 through funds raised by Buddhist organizations and various socio-civic groups. The original location was a dilapidated, more traditional Korean-style rental house in Hyehwa-dong in Seoul. With continued private funding and a notable donation of private land from prominent Buddhist businesswoman Cho Yong-ja, a spacious, modern compound was completed in December 1995. The 'comfort women' were relocated to the new building located in Gwangju, Gyeonggi, on the outskirts of Seoul, in February 1996. The House of Sharing includes “The Museum of Sexual Slavery by Japanese Military” to spread the truth about the Japanese military's brutal abuse of comfort women and to educate descendants and the public.
 W
WIanjo (慰安所) is a military brothel, established by Japanese during World War II. First ianjo was founded in Shanghai, China. Based on these estimates, most international media sources quote about 200,000 young women were kidnapped by Japanese soldiers to serve in military brothels. The BBC quotes "200,000 to 300,000", and the International Commission of Jurists quotes "estimates of historians of 100,000 to 200,000 women."
 W
WKim Bok-dong was among many young women forced into sexual slavery by the Japanese Imperial Army. She later became a Korean human rights activist who campaigned against sexual slavery and war rape. She was one of many young women who were forced into sexual slavery by the Japanese military; a military that systematically recruited girls between the ages of 10 to 18 years of age from colonized and occupied countries from the 1930s until the end of World War II. From age 14, she was imprisoned in comfort stations for eight years across different countries in Asia. Her experiences evoked in her a feminist consciousness and led her to become a strong activist, advocating the end of war-time sexual violence, anti-imperialism, workers' rights, and inter-Korean reconciliation. Along with the other so-called "comfort women", she has made the three-fold demand from the Japanese government: a formal state-level apology, reparations, and correction of Japanese history. In addition, Kim Bok-dong herself also supported other "comfort women" to step forward, and was a leader and spokesperson in the "comfort women" movement. Kim Bok-dong died in Seoul, South Korea, in hospital, on January 28, 2019.
 W
WKim Hak-sun (1924–1997) was a Korean human rights activist who campaigned against sex slavery and wartime sexual violence. Ms. Kim was one of the victims who had been forced into sexual slavery by the Japanese Imperial Army between the early 1930s up until the end of the Pacific War. She is the first woman in Korea to come forward publicly and testify her experience as a comfort woman for the Japanese military. Her testimony was made on 14 August 1991. In December 1991, she filed a class-action lawsuit against the Japanese government for the damages inflicted during the war. She was the first of what would become hundreds of women from Korea, China, Taiwan, the Philippines, Indonesia, and the Netherlands who came forward to tell their stories of their enslavement to the Imperial Japanese military. She was inspired to finally take her story public after 40 years of silence by the growth of the women's rights movement in South Korea. Kim died in 1997 and her court case was still ongoing.
 W
WKisaeng, also called ginyeo, were women from outcast or slave families who were trained to be courtesans, providing artistic entertainment and conversation to men of upper class. First appearing in Goryeo, kisaeng were the government's legal entertainers, required to perform various functions for the state. Many were employed at court, but they were also spread throughout the country. They were carefully trained and frequently accomplished in the fine arts, poetry, and prose, and although they were of low social class, they were respected as educated artists. Aside from entertainment, their roles included medical care and needlework.
 W
WThe Kono Statement refers to a statement released by Chief Cabinet Secretary Yōhei Kōno on August 4, 1993, after the conclusion of the government study that found that the Japanese Imperial Army had forced women, known as comfort women, to work in military-run brothels during World War II. The Japanese government had initially denied that the women had been coerced until this point. In the Kono Statement, the Japanese government acknowledged that:"The then Japanese military was, directly or indirectly, involved in the establishment and management of the comfort stations". "The recruitment of the comfort women was conducted mainly by private recruiters who acted in response to the request of the military." "In many cases they were recruited against their own will, through coaxing, coercion, etc." "At times, administrative/military personnel directly took part in the recruitments." "They lived in misery at comfort stations under a coercive atmosphere."
 W
WLee Yong-soo is a former comfort woman from South Korea. Lee was forced to serve as a sex slave during World War II with the Imperial Japanese Army. She is one of the youngest comfort women still living. However, there is a conflict with the Korean Council for Justice and Remembrance over the distribution of the collected funds. In May 2020, former Korean Council for Justice Yoon Mee-hwan suggested that Lee was not a comfort woman.
 W
WYayori Matsui was a Japanese journalist and women's rights activist noted for her work to raise awareness of sex slaves and sex tourism in post-war Asia. In 1961 she began work as a journalist for the newspaper Asahi Shimbun, retiring in 1994 to work as a full-time social activist, founding numerous women's organizations and writing on gender inequality in Japan and on sex crimes committed by the Japanese Imperial Army, namely against the comfort women of the Second World War. Her work culminated in the 2000 Tokyo Women's War Crimes Tribunal, a tribunal held to gain some form of justice for the victims of Japanese military sexual slavery.
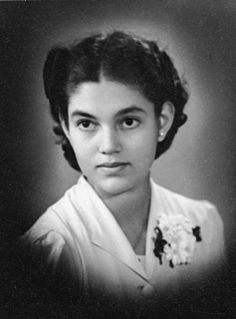 W
WJeanne Alida "Jan" Ruff-O'Herne was a Dutch Australian of Irish ancestry and human rights activist known for campaigning internationally against war rape. During World War II, Ruff-O'Herne was forced into sexual slavery by the Imperial Japanese Army. After remaining silent for fifty years, Ruff-O'Herne spoke out publicly from the 1990s until her death to demand a formal apology from the Japanese government and to highlight the plight of other "comfort women". On her death, the South Australian Attorney-General noted: "her story of survival is a tribute to her strength and courage, and she will be sorely missed not only here in South Australia, but around the world."
 W
WThe Recreation and Amusement Association or RAA, was the largest of the organizations established by Japanese authorities to provide organized prostitution to prevent rapes and sexual violence by Allied occupation troops on the general population, and to create other leisure facilities for occupying Allied troops immediately following World War II. The RAA "recruited" 55,000 women and was short-lived.
 W
WThe San Francisco Comfort Women memorial is a monument dedicated to comfort women before and during World War II. It is built in remembrance of the girls and women that were sexually enslaved by the Imperial Japanese Army through deceit, coercion, and brutal force. It is approximated that there were around 400,000 "comfort women" from South Korea, China, Indonesia, the Philippines and other Asian countries. The site is located near the Saint Mary's Square, at the crossroads of San Francisco Chinatown and the Financial District. The statue "Comfort Women" Column of Strength, by sculptor Steven Whyte, is one of nine and the first sculpture placed in a major U.S. city to commemorate the comfort women.
 W
WWednesday demonstration, officially named Wednesday Demonstration demanding Japan to redress the Comfort Women problems, is a weekly protest in Korea which aims at obtaining justice from the Japanese government regarding the large scale sexual slavery system established under Imperial Japan rule during World War II. The weekly protest is held in the presence of surviving comfort women on every Wednesday at noon in front of the Embassy of Japan in Seoul.