 W
WA cobot, or collaborative robot, is a robot intended for direct human robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in close proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industrial robot applications in which robots are isolated from human contact. Cobot safety may rely on lightweight construction materials, rounded edges, and inherent limitation of speed and force, or on sensors and software that ensures safe behavior.
 W
WA social robot is an autonomous robot that interacts and communicates with humans or other autonomous physical agents by following social behaviors and rules attached to its role. Like other robots, a social robot is physically embodied. Some synthetic social agents are designed with a screen to represent the head or 'face' to dynamically communicate with users. In these cases, the status as a social robot depends on the form of the 'body' of the social agent; if the body has and uses some physical motors and sensor abilities, then the system could be considered a robot.
 W
WAISoy1, developed by the Spanish company AISoy Robotics, is a pet-robot considered to be one of the first emotional-learning robots for the consumer market. Its software platform allows it to interpret stimuli from its sensors network, in order to gain information from its environment and take decisions based on logical and emotional criteria. Unlike other previously developed robots, AISoy1 has not a single collection of programmed answers, but its behavior is dynamic and results unpredictable. The dialogue system and the advanced recognition system allow it to interact with humans as well as robots.
 W
WCog was a project at the Humanoid Robotics Group of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was based on the hypothesis that human-level intelligence requires gaining experience from interacting with humans, like human infants do. This in turn required many interactions with humans over a long period. Because Cog's behavior responded to what humans would consider appropriate and socially salient environmental stimuli, the robot was expected to act more human. This behavior also provided the robot with a better context for deciphering and imitating human behavior. This was intended to allow the robot to learn socially, as humans do.
 W
WKismet is a robot head made in the 1990s at Massachusetts Institute of Technology by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal as an experiment in affective computing; a machine that can recognize and simulate emotions. The name Kismet comes from a Turkish word meaning "fate" or sometimes "luck".
 W
WKnightscope, Inc. is an American security camera company that was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in Mountain View, California. The goal of Knightscope is to design, build and deploy robots called Autonomous Data Machines (ADMs) for use in monitoring people in malls, parking lots, and neighborhoods.
 W
WLeonardo is a 2.5 foot social robot, the first created by the Personal Robots Group of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Its development is credited to Cynthia Breazeal. The body is by Stan Winston Studios, leaders in animatronics. Its body was completed in 2002. It was the most complex robot the studio had ever attempted as of 2001. Other contributors to the project include NevenVision, Inc., Toyota, NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, and the Navy Research Lab. It was created to facilitate the study of human–robot interaction and collaboration. A DARPA Mobile Autonomous Robot Software (MARS) grant, Office of Naval Research Young Investigators Program grant, Digital Life, and Things that Think consortia have partially funded the project. The MIT Media Lab Robotic Life Group, who also studied Robonaut 1, set out to create a more sophisticated social-robot in Leonardo. They gave Leonardo a different visual tracking system and programs based on infant psychology that they hope will make for better human-robot collaboration. One of the goals of the project was to make it possible for untrained humans to interact with and teach the robot much more quickly with fewer repetitions. Leonardo was awarded a spot in Wired Magazine’s 50 Best Robots Ever list in 2006.
 W
WManav is India's first humanoid robot which was developed in the laboratory of A-SET Training and Research Institutes by Diwakar Vaish in late December 2014. It debuted at the IIT-Bombay Techfest 2014-15 in Mumbai.
 W
WMusio is a social robot designed by AKA Intelligence, powered by MUSE, a deep learning based AI quantum engine for communication developed by AKA. Using deep learning algorithms, Musio converses with people, recognises objects and also understands people's facial expressions. Additionally, Musio has its own emotional engine, this lets it also express facial expressions when conversing with someone. Different sounds and facial colours are shown with animations. When multiple users are present and registered with Musio, the interaction with each one is different. This is affected based on each person's emotional state when talking to Musio, past discussions and subjects discussed. On May 2015, Musio was first introduced to the world through the global crowdfunding site Indiegogo. It was a success, where AKA Intelligence managed to raise 201% of their needed funding, resulting in a total of just over $100k.
 W
WNadine is a ginoide humanoid social robot that is modelled on Professor Nadia Magnenat Thalmann. The robot has a strong human-likeness with a natural-looking skin and hair and realistic hands. Nadine is a socially intelligent robot which returns a greeting, makes eye contact, and can remember all the conversations had with it. It is able to answer questions autonomously in several languages, simulate emotions both in gestures and facially, depending on the content of the interaction with the user. Nadine can recognise persons it has previously seen, and engage in flowing conversation. Nadine has been programmed with a "personality", in that its demeanour can change according to what is said to it. Nadine has a total of 27 degrees of freedom for facial expressions and upper body movements. With persons it has previously encountered, it remembers facts and events related to each person. It can assist people with special needs by reading stories, showing images, put on Skype sessions, send emails, and communicate with other members of the family. It can play the role of a receptionist in an office or be dedicated to be a personal coach.
 W
WThe PaPeRo which stands for "Partner-type-Personal-Robot", is a personal robot developed by Japanese firm NEC Corporation. It is noted for its cute appearance and facial recognition system. The robot's development began in 1997 with the first prototype, the R100. The name PaPeRo was adopted in 2001.
 W
WPARO is a therapeutic robot baby harp seal, intended to be very cute and to have a calming effect on and elicit emotional responses in patients of hospitals and nursing homes, similar to animal-assisted therapy except using robots.
 W
WQRIO was a bipedal humanoid entertainment robot developed and marketed by Sony to follow up on the success of its AIBO entertainment robot. QRIO stood approximately 0.6 m tall and weighed 7.3 kg. QRIO's slogan was "Makes life fun, makes you happy!"
 W
WRashmi is an realistic Indian humanoid robot developed by Ranjit Shrivastava, a programmer from Ranchi, India.
 W
WRobot Shalu is the world's first homemade artificially intelligent multilingual social and educational humanoid robot, made-up of waste materials, that can speak 47 languages i.e. 9 Indian and 38 foreign languages.
 W
WSophia is a social humanoid robot developed by Hong Kong-based company Hanson Robotics. Sophia was activated on February 14, 2016, and made her first public appearance at South by Southwest Festival (SXSW) in mid-March 2016 in Austin, Texas, United States.
 W
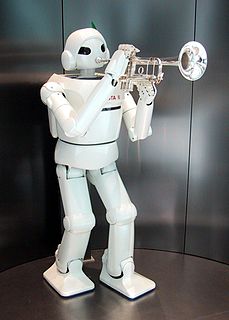
WThe Toyota Partner Robots are a series of humanoid robots developed by Toyota. They debuted playing music on drums and trumpets at the 2005 World EXPO in Aichi, Japan. There are 5 robots in all, most of which have different movement systems. The 5 robots are: Version 1, Version 2, Version 3, Version 4 and the i-Foot . In July 2009, Toyota released a video of the running and standing skills of their partner robot. The robot reaches 7 km/hour, however walking and running can only be achieved on flat surfaces. In 2017, Toyota released its third-generation of humanoid robots, T-HR3, which will be used in space travel.