 W
WThe term baroque horse describes a group of horse breeds, usually descended from and retaining the distinctive characteristics of a particular type of horse that rose to prominence in Europe during the Baroque era, after significant development throughout the Middle Ages. It describes the type of agile but strong-bodied descendants of horses in the Middle Ages such as the destrier. Specific ancestors of this type include the Neapolitan horse, and the Iberian horse of Barb ancestry known in the Middle Ages as the Spanish Jennet. They are characterized by powerful hindquarters, a muscular, arched neck, a straight or slightly convex profile, and usually a full, thick mane and tail. These horses are particularly well suited for the haute ecole discipline of classical dressage.
 W
WCahirmee Horse Fair is held on 12 July every year in the town of Buttevant, County Cork, Ireland.
 W
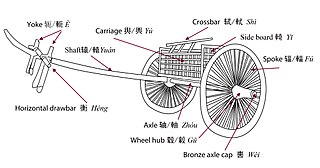
WThe ancient Chinese chariot was used as an attack and pursuit vehicle on the open fields and plains of ancient China from around 1200 BCE. Chariots also allowed military commanders a mobile platform from which to control troops while providing archers and soldiers armed with dagger-axes increased mobility. They reached a peak of importance during the Spring and Autumn period, but were largely superseded by cavalry during the Han Dynasty.
 W
WA courser is a swift and strong horse, frequently used during the Middle Ages as a warhorse. It was ridden by knights and men-at-arms.
 W
WThe destrier is the best-known war horse of the medieval era. It carried knights in battles, tournaments, and jousts. It was described by contemporary sources as the Great Horse, due to its significance.
 W
WThere have been five equine recipients of the Dickin Medal since its creation in 1943. The first three were British horses Regal, Olga, and Upstart, followed by the Canadian Corps Cavalry horse Warrior and the American Sergeant Reckless. The first three received their awards at a ceremony on 11 April 1947 at Hyde Park in recognition of the courage they exhibited during World War II. These three were mounts used by members of the Metropolitan Police Service during official duties and to aid civilians during the Blitz and later bombings from September 1940 to late 1944. Warrior served on the Western Front during World War I and was awarded an honorary posthumous medal in September 2014. Another posthumous award was given in 2016 to Sergeant Reckless, a mare who served during the Korean War with the United States Marine Corps and was given the rank of staff sergeant. Of the recipients, three were honoured for courage during active duty, one for remaining calm when his stable was bombed on two occasions and one to commemorate the actions of animals during the First World War. The first three horses were selected primarily as a way to honour the entire mounted police force instead of singling out any particular deed. Olga, Upstart and Regal are buried at the Metropolitan Police Mounted Training Establishment at Thames Ditton which also displays their medals in a museum.
 W
WThe hippika gymnasia were ritual tournaments performed by the cavalry of the Roman Empire to both practice their skills and display their expertise. They took place on a parade ground situated outside a fort and involved the cavalry practicing manoeuvring and the handling of weapons such as javelins and spears. The riders and their mounts wore highly elaborate armour and helmets specially made for display purposes, decorated with images from classical mythology. Such tournaments served several purposes, improving the riders' skills, helping to build unit morale and impressing dignitaries and conquered peoples.
 W
WThe Horse Memorial is a provincial heritage site in Port Elizabeth in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa, in memory of the horses that served and died during the Second Boer War, where Britain brought a large number of horses to South Africa. Designed by Joseph Whitehead, the life-sized bronze memorial features a kneeling soldier presenting a bucket of water to a service horse.
 W
WMaeda Toshimasu , better known as Maeda Keiji (前田慶次) or Keijirō (慶次郎), was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period through early Edo period. He was famously the nephew of Maeda Toshiie and Maeda Matsu. In legends and fictions, he is one of the most celebrated kabukimono of the time period who is known for his monstrous height and his peerless strength. Toshimasu's horse and companion, Matsukaze, was one of the most famous warhorses in Japan.
 W
WA horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, for protecting the herds, and for war. It was a defining characteristic of the Eurasian nomads during antiquity and the medieval period, as well as the Iranian peoples, and Indians in antiquity, and by the Hungarians, Mongols, Chinese, and the Turkic peoples during the Middle Ages. By the expansion of these peoples, the practice also spread to Eastern Europe, Mesopotamia, and East Asia. In East Asia, horse archery came to be particularly honored in the samurai tradition of Japan, where horse archery is called Yabusame.
 W
WThe term rouncey was used during the Middle Ages to refer to an ordinary, all-purpose horse. They were used for riding, but could also be trained for war. It was not unknown for them to be used as pack horses. The horse, which was also referred to as runcinus, is believed to be a harrowing animal on account of its proportions found in the demesne stock listing before it became an exclusively riding animal.
 W
WThe south-pointing chariot was an ancient Chinese two-wheeled vehicle that carried a movable pointer to indicate the south, no matter how the chariot turned. Usually, the pointer took the form of a doll or figure with an outstretched arm. The chariot was supposedly used as a compass for navigation and may also have had other purposes.
 W
WA part of the Quartermaster Corps, the U.S. Army Remount Service provided horses as remounts to U.S. Army units. Evolving from both the Remount Service of the Quartermaster Corps and a general horse-breeding program under the control of the Department of Agriculture, the Remount Service began systematically breeding horses for the United States Cavalry in 1918. It remained in operation until 1948, when all animal-breeding programs returned to Department of Agriculture control.
 W
WHorses in East Asian warfare are inextricably linked with the strategic and tactical evolution of armed conflict. A warrior on horseback or horse-drawn chariot changed the balance of power between civilizations.
 W
WHorses were widely used during the Napoleonic Wars for combat, patrol and reconnaissance, and for logistical support. Vast numbers were used throughout the wars. During the War of the Sixth Coalition, depletion of the French cavalry arm through attrition and loss of horse-producing allies to provide remounts contributed significantly to the gradual French defeat and downfall of the French Empire. During the Waterloo Campaign, the Armee du Nord had 47,000 horses: 25,000 cavalry, 12,000 for artillery, 10,000 for infantry and supply columns.
 W
WThe first evidence of horses in warfare dates from Eurasia between 4000 and 3000 BC. A Sumerian illustration of warfare from 2500 BC depicts some type of equine pulling wagons. By 1600 BC, improved harness and chariot designs made chariot warfare common throughout the Ancient Near East, and the earliest written training manual for war horses was a guide for training chariot horses written about 1350 BC. As formal cavalry tactics replaced the chariot, so did new training methods, and by 360 BC, the Greek cavalry officer Xenophon had written an extensive treatise on horsemanship. The effectiveness of horses in battle was also revolutionized by improvements in technology, such as the invention of the saddle, the stirrup, and the horse collar.
 W
WThe use of horses in World War I marked a transitional period in the evolution of armed conflict. Cavalry units were initially considered essential offensive elements of a military force, but over the course of the war, the vulnerability of horses to modern machine gun, mortar, and artillery fire reduced their utility on the battlefield. This paralleled the development of tanks, which ultimately replaces cavalry in shock tactics. While the perceived value of the horse in war changed dramatically, horses still played a significant role throughout the war.
 W
WHorses in World War II were used by the belligerent nations for transportation of troops, artillery, materiel, and, to a lesser extent, in mobile cavalry troops. The role of horses for each nation depended on its military strategy and state of economy and was most pronounced in the German and Soviet Armies. Over the course of the war, both Germany and the Soviet Union employed more than six million horses.