 W
WA national myth is an inspiring narrative or anecdote about a nation's past. Such myths often serve as an important national symbol and affirm a set of national values. A national myth may sometimes take the form of a national epic or be incorporated into a civil religion. A group of related myths about a nation may be referred to as the national mythos, from μῦθος, the original Greek word for "myth".
 W
WThe Afroasiatic Urheimat is the hypothetical place where speakers of the proto-Afroasiatic language lived in a single linguistic community, or complex of communities, before this original language dispersed geographically and divided into separate distinct languages. This speech area is known as the Urheimat. Afroasiatic languages are today distributed in parts of Africa and Western Asia.
 W
WThe Armenian hypothesis of the Proto-Indo-European homeland, proposed by Georgian Tamaz V. Gamkrelidze and Russian linguist Vyacheslav Ivanov in the early 1980s, suggests that Proto-Indo-European was spoken during the 5th–4th millennia BC in “eastern Anatolia, the southern Caucasus, and northern Mesopotamia”.
 W
WIndigenous Aryanism, also known as the Indigenous Aryans theory (IAT) and the Out of India theory (OIT), is the conviction that the Aryans are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages radiated out from a homeland in India into their present locations. It is a "religio-nationalistic" view on Indian history, and propagated as an alternative to the established migration model, which considers the Pontic steppe to be the area of origin of the Indo-European languages.
 W
WAssyrian continuity is the theory—supported by a number of scholars and modern Assyrians—that today's modern Assyrians descend from the ancient Assyrians, a Semitic people native to ancient Assyria, that originally spoke ancient Assyrian language, a dialect of Akkadian language, and Aramaic later. Notions of Assyrian continuity are based on both ethnic, genetic, linguistic and historical claims, and the asserted continuity of Assyria's historical and cultural heritage after the fall of the ancient Assyrian Empire.
 W
WThe beech argument is a now mostly outdated argument in Indo-European studies that is in favour of placing the Indo-European urheimat in an area west of a line connecting Kaliningrad and the Black Sea, based on the current distribution of beech trees. The argument, as summarised by Friedrich and Mallory goes that the Indo-European term *bʰāg(ó) most probably refers to the beech tree. Hence the presence of descendants of the term *bʰāg(ó) in Italic, Germanic, Albanian, Greek and (Indo-)Iranian, and potentially Celtic, Slavic, and Baltic, indicates that this word belonged to the most widely-spoken Indo-European language. And thirdly that since the beech tree distribution was limited historically to the regions west of the Eurasian Steppe, this is where this language was spoken.
 W
WIn antiquity, several theses were elaborated on the origin of the Etruscans that can be summarized into three main hypotheses. The first is the autochthonous development in situ out of the Villanovan culture, as claimed by the Greek historian Dionysius of Halicarnassus who described the Etruscans as indigenous people who had always lived in Etruria. The second is a migration from the Aegean sea, as claimed by two Greek historians: Herodotus, who described them as a group of immigrants from Lydia in Anatolia, and Hellanicus of Lesbos who claimed that the Tyrrhenians were the Pelasgians originally from Thessaly, Greece, who entered Italy at the head of the Adriatic sea. The third hypotheses was reported by Livy and Pliny the Elder, and puts the Etruscans in the context of the Rhaetian people to the north and other populations living in the Alps.
 W
WGothicism or Gothism was a cultural movement in Sweden, centered on the belief in the glory of the Swedish Geats, who were identified with the Goths. The founders of the movement were Nicolaus Ragvaldi and the brothers Johannes and Olaus Magnus. The belief continued to hold power in the 17th century, when Sweden was a great power following the Thirty Years' War, but lost most of its sway in the 18th. It was renewed by the Viking revival and Romantic nationalism in the early 19th century, this time with the Vikings as heroic figures.
 W
WThe Anatolian hypothesis, also known as the Anatolian theory or the sedentary farmer theory, first developed by British archaeologist Colin Renfrew in 1987, proposes that the dispersal of Proto-Indo-Europeans originated in Neolithic Anatolia. It is the main competitor to the Kurgan hypothesis, or steppe theory, which enjoys more academic favor.
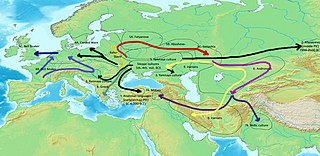 W
WThe Kurgan hypothesis or Steppe theory is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian kurgan (курга́н), meaning tumulus or burial mound.
 W
WThe Proto-Indo-European homeland was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of the different branches of the Indo-European language family.
 W
WScholars have suggested different theories for the origin of the name Kurd. According to the English Orientalist Godfrey Rolles Driver, the term Kurd is related to the Sumerian Karda which was found from Sumerian clay tablets of the third millennium B.C, while according to other scholars, it predates the Islamic period, as a Middle Persian word for "nomad", and may ultimately be derived from an ancient toponym or tribal name, either that of the Cyrtii or of Corduene.
 W
WThe theory on immigration to Norway refers to a theory on the origin of the Norwegian people. The theory is mainly associated with Rudolf Keyser, and developed by Peter Andreas Munch.
 W
WOlmec alternative origin speculations are non-mainstream theories that have been suggested for the formation of Olmec civilization which contradict generally accepted scholarly consensus. These origin theories typically involve contact with Old World societies. Although these speculations have become somewhat well-known within popular culture, particularly the idea of an African connection to the Olmec, they are not regarded as credible by mainstream researchers of Mesoamerica and are considered fringe theories.
 W
WHyksos is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The seat of power of these kings was the city of Avaris in the Nile delta, from where they ruled over Lower and Middle Egypt up to Cusae. In the Aegyptiaca, a history of Egypt written by the Greco-Egyptian priest and historian Manetho in the 3rd century BC, the term Hyksos is used ethnically to designate people of probable West Semitic, Levantine origin. While Manetho portrayed the Hyksos as invaders and oppressors, this interpretation is questioned in modern Egyptology. Instead, Hyksos rule might have been preceded by groups of Canaanite peoples who gradually settled in the Nile delta from the end of the Twelfth Dynasty onwards and who may have seceded from the crumbling and unstable Egyptian control at some point during the Thirteenth Dynasty.
 W
WThe Paleolithic continuity paradigm, before 2010 also Paleolithic continuity theory or PCT), is a hypothesis suggesting that the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) can be traced back to the Upper Paleolithic, several millennia earlier than the Chalcolithic or at the most Neolithic estimates in other scenarios of Proto-Indo-European origins.
 W
WAnti-Normanism is a movement of historical revisionism in opposition to the mainstream narrative of the Viking Age in Eastern Europe, and concerns the origin of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and their historic predecessor, Kievan Rus'. At the centre of the disagreement is the Rus' people, a people generally considered to be of Scandinavian origin and who arrived in Eastern Europe in the 8th and 9th centuries, but who during the 10th and 11th centuries merged with Fenno-Ugrics, Balts and East Slavs, and together with them formed Kievan Rus' with Old East Slavic as a common language, and with the name Rus' as a common marker of identity.
 W
WThe Rus' people were an ethnos in early medieval eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally Norse people, mainly originating from Sweden, settling and ruling along the river-routes between the Baltic and the Black Seas from around the 8th to 11th centuries AD. They formed a state known in modern historiography as Kievan Rus', which was initially a multiethnic society where the ruling Norsemen merged and assimilated with Slavic, Baltic and Finnic tribes, ending up with Old East Slavic as their common language. The elite of Kievan Rus' was still familiar with Old Norse until their assimilation by the second half of the 11th century, and in rural areas vestiges of Norse culture lingered as long as the 14th and early 15th centuries.
 W
WIn Indo-European studies, the salmon problem or salmon argument is an outdated argument in favour of placing the Indo-European urheimat in the Baltic region, as opposed to the Eurasian Steppe, based on the cognate etymology of the respective words for salmon in Germanic and Balto-Slavic languages.
 W
WSarmatism was an ethno-cultural ideology within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was the dominant Baroque culture and ideology of the nobility that existed in times of the Renaissance to the 18th centuries. Together with the concept of "Golden Liberty", it formed a central aspect of the Commonwealth's culture and society. At its core was the unifying belief that the people of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth descended from the ancient Iranian Sarmatians, the legendary invaders of contemporary Polish lands in antiquity.
 W
WThe Nakh peoples, today partly also known as Vainakh peoples, are a group of Caucasian peoples identified by their use of the Nakh languages and other cultural similarities. These are chiefly the ethnic Chechen, Ingush and Bats peoples of the North Caucasus, including closely related minor or historical groups.