 W
WPositive psychology is the scientific study of what makes life most worth living, focusing on both individual and societal well-being. It studies "positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions...it aims to improve quality of life." It is a field of study that has been growing steadily throughout the years as individuals and researchers look for common ground on better well-being.
 W
WCharacter Strengths and Virtues (CSV) is a book by Christopher Peterson and Martin Seligman (2004) that attempts to present a measure of humanist ideals of virtue in an empirical, rigorously scientific manner.
 W
WConfidence is a state of being clear-headed either that a hypothesis or prediction is correct or that a chosen course of action is the best or most effective. Confidence comes from a Latin word 'fidere' which means "to trust"; therefore, having self-confidence is having trust in one's self. Arrogance or hubris, in comparison, is the state of having unmerited confidence – believing something or someone is capable or correct when they are not. Overconfidence or presumptuousness is excessive belief in someone succeeding, without any regard for failure. Confidence can be a self-fulfilling prophecy as those without it may fail or not try because they lack it and those with it may succeed because they have it rather than because of an innate ability.
 W
WERG theory is a theory in psychology proposed by Clayton Alderfer.
 W
WFlourishing is "when people experience positive emotions, positive psychological functioning and positive social functioning, most of the time," living "within an optimal range of human functioning." It is a descriptor and measure of positive mental health and overall life well-being, and includes multiple components and concepts, such as cultivating strengths, subjective well-being, "goodness, generativity, growth, and resilience." Flourishing is the opposite of both pathology and languishing, which are described as living a life that feels hollow and empty. It is a central concept in positive psychology, developed by Corey Keyes and Barbara Fredrickson.
 W
WIn positive psychology, a flow state, also known colloquially as being in the zone, is the mental state in which a person performing some activity is fully immersed in a feeling of energized focus, full involvement, and enjoyment in the process of the activity. In essence, flow is characterized by the complete absorption in what one does, and a resulting transformation in one's sense of time.
 W
WGratitude, thankfulness or gratefulness, from the Latin word gratus "pleasing, thankful", is a feeling of appreciation felt by and/or similar positive response shown by the recipient of kindness, gifts, help, favors, or other types of generosity, to the giver of said gifts.
 W
WA gratitude journal is a diary of things for which one is grateful. Gratitude journals are used by individuals who wish to focus their attention on the positive things in their lives.
 W
WHappy is a 2011 feature documentary film directed, written, and co-produced by Roko Belic. It explores human happiness through interviews with people from all walks of life in 14 different countries, weaving in the newest findings of positive psychology.
 W
WIt Gets Better: Coming Out, Overcoming Bullying, and Creating a Life Worth Living is a non-fiction compilation book, edited by Dan Savage and his husband, Terry Miller. It was published March 22, 2011 by Dutton. The book includes selections of essays inspired by the It Gets Better Project, founded by Savage. He decided to start the project after a series of incidents of suicide among LGBT youth. Individuals were encouraged to submit videos with a message of hope and optimism for teenagers who were victims of bullying due to their sexual orientation. Over 100 essays are contained in the book. Contributors include finance advisor Suze Orman; comedic writer David Sedaris; United States Secretary of State Hillary Clinton; and President of the United States Barack Obama.
 W
WJiayou or Gayau is a ubiquitous Chinese expression of encouragement and support. The phrase is commonly used at sporting events and competitions by groups as a rallying cheer and can also be used at a personal level as a motivating phrase to the partner in the conversation.
 W
WThe Life Is Good Company is an American apparel and accessories wholesaler, retailer, and lifestyle brand founded in 1994 and best known for its optimistic T-shirts and hats, many of which feature a smiling stick figure named Jake and the registered trademark "Life is good."
 W
WA philomath is a lover of learning and studying. The term is from Greek philos and manthanein, math-. Philomathy is similar to, but distinguished from, philosophy in that -soph, the latter suffix, specifies "wisdom" or "knowledge", rather than the process of acquisition thereof. Philomath is not synonymous with polymath, as a polymath is someone who possesses great and detailed knowledge and facts from a variety of disciplines, while a philomath is someone who greatly enjoys learning and studying.
 W
WMaslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Review. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. He then created a classification system which reflected the universal needs of society as its base and then proceeding to more acquired emotions. His theories, including the hierarchy, may have been influenced by teachings and philosophy of the Blackfeet tribe, where he spent several weeks prior to writing his influential paper. The hierarchy of needs is split between deficiency needs and growth needs. The theory is usually shown as a triangle in illustrations.
 W
WMental health is "a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community", according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others. From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health".Some early signs related health problems are sleep irritation, lack of energy and suicidal thinking.
 W
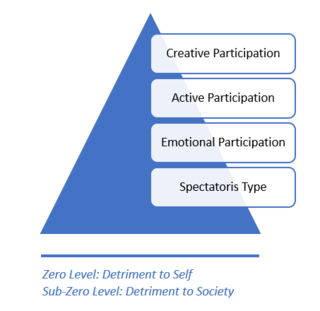
WNash's Pyramid is a framework for ranking leisure activities, developed by Jay B. Nash. Nash was an early leader in the leisure field. His thinking was influenced by the prevalence of 'Spectatoritis' in America which he defines as, "a blanket description to cover all kinds of passive amusement".
 W
WGestalt Practice is a contemporary form of personal exploration and integration developed by Dick Price at the Esalen Institute. The objective of the practice is to become more fully aware of the process of living within a unified field of body, mind, relationship, earth and spirit.
 W
WSelf-determination theory (SDT) is a macro theory of human motivation and personality that concerns people's inherent growth tendencies and innate psychological needs. It is concerned with the motivation behind choices people make without external influence and interference. SDT focuses on the degree to which human behavior is self-motivated and self-determined.
 W
WSubjective well-being (SWB) is a self-reported measure of well-being, typically obtained by questionnaire.
 W
WWell-being, also known as wellness, prudential value or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative to someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good for this person, what is in the self-interest of this person. Well-being can refer to both positive and negative well-being. In its positive sense, it is sometimes contrasted with ill-being as its opposite. The term "subjective well-being" denotes how people experience and evaluate their lives, usually measured in relation to self-reported well-being obtained through questionnaires. Sometimes different types of well-being are distinguished, like mental well-being, physical well-being, economic wellbeing or emotional well-being. The different forms of well-being are often closely interlinked. For example, improved physical well-being is associated with improved emotional well-being. As another example, better economic well-being tends to be associated with better emotional well-being even in adverse situations such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Well-being plays a central role in ethics since what we ought to do depends, at least to some degree, on what would make someone's life go better or worse. According to welfarism, there are no other values besides well-being.
 W
WIn positive psychology, zest is one of the 24 strengths possessed by humanity. As a component of the virtue of courage, zest is defined as living life with a sense of excitement, anticipation, and energy. Approaching life as an adventure; such that one has "motivation in challenging situations or tasks". Zest is essentially a concept of courage, and involves acquiring the motivation to complete challenging situations and tasks. Those who have zest exude enthusiasm, excitement and energy while approaching tasks in life. Hence, the concept of zest involves performing tasks wholeheartedly, whilst also being adventurous, vivacious and energetic. It discourages the focus on the negative views of psychology. It embraces a notion that one must observe people that "live well" in order to truly understand positive psychology. Zestful people simply enjoy things more than people low in zestfulness. Zest is a positive trait reflecting a person's approach to life with anticipation, energy, enthusiasm and excitement.