 W
WFinno-Ugric or Finno-Ugrian (Fenno-Ugrian), is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages. Its formerly commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th century and is criticized by some contemporary linguists such as Tapani Salminen and Ante Aikio as inaccurate and misleading. The three most-spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric, although linguistic roots common to both branches of the traditional Finno-Ugric language tree are distant.
 W
WThe two main official languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. There are also several official minority languages: three variants of Sami, Romani, Finnish Sign Language and Karelian.
 W
WÅland dialects are dialects of Swedish spoken in the Åland Islands, an autonomous province of Finland. The Åland dialects have similarities to both Finland Swedish and the historical dialects of Uppland, but are generally considered to be part of Eastern Swedish.
Estonian is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch spoken in Estonia. It is the official language of Estonia, spoken natively by about 1.1 million people; 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 outside Estonia. It is a Southern Finnic language and is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages.
 W
WFinnish is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent.
 W
WFinnish Sign Language is the sign language most commonly used in Finland. There are 3,000 (2012 estimate) Finnish deaf who have Finnish Sign Language as a first language. As the Finnish system records users by their written language, not their spoken alone, nearly all deaf people who sign are assigned this way and may be subsumed into the overall Finnish language figures. Historically the aim was oralism, whereby deaf people were taught to speak oral Finnish, even if they could not hear it; thus older people are recorded under these figures. In 2014, only 500 people registered Finnish Sign Language as their first language. There are several sign languages that come under this label; FSL for those that can see; Signed Finnish, which does not follow the same grammatical rules, and a version for those who are blind and deaf. Thus, there are around 8,000 people that use a Finnish Sign Language linguistically. Many estimates say 5,000, but these are exaggerations derived from the 14,000 deaf people in Finland. Finnish Sign Language is derived from Swedish Sign Language, which is a different language from Finnish Swedish Sign Language, from which it began to separate as an independent language in the middle of the 19th century.
 W
WInari Sami is a Sami language spoken by the Inari Sami of Finland. It has approximately 300 speakers, the majority of whom are middle-aged or older and live in the municipality of Inari. According to the Sami Parliament of Finland, 269 persons used Inari Sami as their first language. It is the only Sami language that is spoken exclusively in Finland. The language is classified as being seriously endangered, as few children learn it; however, more and more children are learning it in language nests. In 2018, Inari Sami had about 400 speakers; due to revival efforts, the language had gained speakers.
 W
WKarelian is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as karjalaismurteet in Finland.
 W
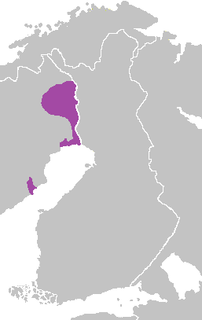
WÅland, an autonomous region of Finland, has the largest Swedish-speaking majority in Finland, with about 88% of the province, or about 25,500 people, speaking Swedish as their first language. Swedish is also the sole official language of the province. Finnish also has a presence, although it is small; only about 5% of Ålanders are Finnish-speaking.
 W
WThere are 53 municipalities of Finland in which Finnish is not the sole official language. In Finland, as of December 31, 2013, 89.3% of the population speak Finnish, 5.3% Swedish and 0.04% Sami languages. Both Finnish and Swedish are official languages of Finland. Officially, a municipality is bilingual if the minority language group consists of at least 8% of the population, or at least 3,000 speakers. A previously bilingual municipality remains so if the linguistic minority proportion drops below 8%, up to 6%. If it drops below 6%, it is possible for the municipality to remain bilingual by government decree, on the recommendation of the municipal council, for a further ten years. Municipalities that make use of the 3,000-speaker rule include the national capital Helsinki and the cultural center of Swedish Finns, Turku. On the Åland archipelago, where Finnish is almost absent from daily life, the language law does not apply. On the mainland, the highest proportion of Swedish-speakers is found on the western coast, in Ostrobothnia.
 W
WMeänkieli is a Finnic language or a group of distinct Finnish dialects spoken in the northernmost part of Sweden along the valley of the Torne River. Its status as an independent language is disputed, but in Sweden it is recognized as one of the country's five minority languages.
 W
WFinland has two official languages, Finnish and Swedish. Many places in the country have different names in Finnish and Swedish, both being official endonyms.
 W
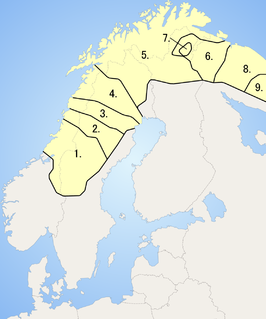
WNorthern or North Sami is the most widely spoken of all Sami languages. The area where Northern Sami is spoken covers the northern parts of Norway, Sweden and Finland. The number of Northern Sami speakers is estimated to be somewhere between 15,000 and 25,000. About 2,000 of these live in Finland and between 5,000 and 6,000 in Sweden.
 W
WThe orthography used to write Northern Sámi has experienced numerous changes since the first writing systems for the language were developed. Traditionally, Norway, Sweden, and Finland — the three countries where Northern Sámi is spoken — used separate orthographies for teaching the Sámi within their borders. This changed in 1979 when a Saami Council-led effort to standardize a pan-Scandinavian orthography for Northern Sámi.
 W
WLivvi-Karelian is a dialect of the Karelian language, which is a Finnic language of the Uralic family, spoken by Olonets Karelians, traditionally inhabiting the area between Ladoga and Onega lakes, northward of Svir River. The name "Olonets Karelians" is derived from the territory inhabited, Olonets Krai, named after the town of Olonets, named after the Olonka River.
 W
WRomani is an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities. According to Ethnologue, seven varieties of Romani are divergent enough to be considered languages of their own. The largest of these are Vlax Romani, Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself.
 W
WSámi languages, in English also rendered as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.
 W
WSkolt Sami is a Uralic, Sami language that is spoken by the Skolts, with approximately 300 speakers in Finland, mainly in Sevettijärvi and approximately 20–30 speakers of the Njuõʹttjäuʹrr (Notozero) dialect in an area surrounding Lake Lovozero in Russia. Skolt Sami also used to be spoken in the Neiden area of Norway. It is written using a modified Roman orthography which was made official in 1973.
 W
WFinland Swedish or Fenno-Swedish is a general term for the variety of the Swedish language and a closely related group of Swedish dialects spoken in Finland by the Swedish-speaking population as their first language.
 W
WSwedish is a North Germanic language spoken natively by at least 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and in parts of Finland, where it has equal legal standing with Finnish. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is largely dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Written Norwegian and Danish are usually more easily understood by Swedish speakers than the spoken languages, due to the differences in tone, accent, and intonation. Swedish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. It has more speakers than any other North Germanic language.
 W
WThe Tatar language is a Turkic language spoken by Tatars mainly located in modern Tatarstan, as well as Siberia. It should not be confused with the Crimean Tatar or Siberian Tatar, which are closely related but belong to different subgroups of the Kipchak languages.
 W
WThe Uralic languages form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25 million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian; while other significant languages are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt, Sami, and Komi, spoken in northern regions of Scandinavia and the Russian Federation.