 W
WThe Conductor Pipe is a large diameter pipe that is set into the ground to provide the initial stable structural foundation for a borehole or oil well. The Conductor pipe is the first string of casing and is the largest diameter casing to be installed in a well. It can also be referred to as a drive pipe because it is often driven into the ground with a pile driver.
 W
WA crown block is the stationary section of a block and tackle that contains a set of pulleys or sheaves through which the drill line is threaded or reeved and is opposite and above the traveling block.
 W
WA derrickhand or derrickman is the person who sits atop the derrick on a drilling rig. Though the exact duties vary from rig to rig, they almost always report directly to the driller. Their job is to guide the stands of the drill pipe into the fingers at the top of the derrick. Other duties might include monitoring pH and calcium levels, viscosity and the mud weight (density), adding chemicals and oil based fluids, and being responsible for the shale shakers and mud pump.
 W
WDesanders and desilters are solid control equipment with a set of hydrocyclones that separate sand and silt from the drilling fluids in drilling rigs. Desanders are installed on top of the mud tank following the shale shaker and the degasser, but before the desilter. Desander removes the abrasive solids from the drilling fluids which cannot be removed by shakers. Normally the solids diameter for desander to be separated would be 45~74μm, and 15~44μm for desilter.
 W
WA directional well is an oil industry term for an oil well with a borehole that deviates from a vertically straight line. This is normally done with the intention of hitting several target sands, for instance.
 W
WThe drill floor is the heart of any drilling rig. This is the area where the drill string begins its trip into the earth. It is traditionally where joints of pipe are assembled, as well as the BHA, drilling bit, and various other tools. This is the primary work location for roughnecks and the driller. The drill floor is located directly under the derrick.
 W
WIn a drilling rig, the drill line is a multi-thread, twisted wire rope that is threaded or reeved through in typically 6 to 12 parts between the traveling block and crown block to facilitate the lowering and lifting of the drill string into and out of the wellbore.
 W
WA drill string on a drilling rig is a column, or string, of drill pipe that transmits drilling fluid and torque to the drill bit. The term is loosely applied to the assembled collection of the smuggler pool, drill collars, tools and drill bit. The drill string is hollow so that drilling fluid can be pumped down through it and circulated back up the annulus.
 W
WThe Driller is a team leader in charge during the process of well drilling. The term is commonly used in the context of an oil well drilling rig. Driller comes after the Toolpusher in the Rig crew hierarchy. Toolpusher takes the operation orders from the Company-man. Toolpusher then supervises these order to the driller and the rest of the drilling crew and gets the job done. While Toolpusher, driller and the drilling crew generally belong to the Drilling contractor company, Company-man is the employee of the operator company.
 W
WA drilling rig is an integrated system that drills wells, such as oil or water wells, in the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person and such are called augers. Drilling rigs can sample subsurface mineral deposits, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, and also can be used to install sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be mobile equipment mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures. The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex equipment that is used to penetrate the surface of the Earth's crust.
 W
WThe International Drillers is the name given to the more than 500 drillers from Lambton County who worked in oil fields across the world between December 1873 to the mid-1940s. Many of the International Drillers grew up learning the oil business in Enniskillen County and provided the skilled labour, expertise and technology necessary for the development of the global petroleum industry.
 W
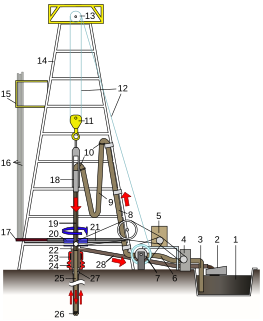
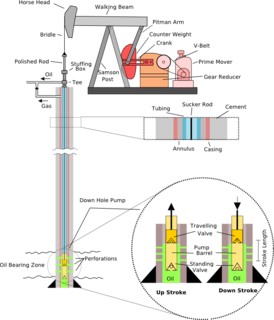
WSee List of components of oil drilling rigs to view a diagram.
 W
WAn oil well dug house is the steel-sided room adjacent to an oil rig floor, usually having an access door close to the driller's controls. This general-purpose shelter is a combination tool shed, office, communications center, coffee room, lunchroom, and general meeting place for the driller and his crew. It is at the same elevation as the rig floor, usually cantilevered out from the main substructure supporting the rig.
 W
WOil well fires are oil or gas wells that have caught on fire and burn. They can be the result of accidents, arson, or natural events, such as lightning. They can exist on a small scale, such as an oil field spill catching fire, or on a huge scale, as in geyser-like jets of flames from ignited high pressure wells. A frequent cause of a well fire is a high-pressure blowout during drilling operations.
 W
WPetrology is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together because they both contain heavy use of chemistry, chemical methods, and phase diagrams. Sedimentary petrology is, on the other hand, commonly taught together with stratigraphy because it deals with the processes that form sedimentary rock.
 W
WA rotary table is a mechanical device on a drilling rig that provides clockwise rotational force to the drill string to facilitate the process of drilling a borehole. Rotary speed is the number of times the rotary table makes one full revolution in one minute (rpm).
 W
WRoughneck is a term for a person whose occupation is hard manual labor. The term applies across a number of industries, but is most commonly associated with the workers on a drilling rig. The ideal of the hard-working, tough roughneck has been adopted by several sports teams who use the phrase as part of their name or logo.
A stripper well or marginal well is an oil or gas well that is nearing the end of its economically useful life. In the United States a "stripper" gas well is defined by the Interstate Oil and Gas Compact Commission as one that produces 60,000 cubic feet (1,700 m3) or less of gas per day at its maximum flow rate; the Internal Revenue Service, for tax purposes, uses a threshold of 90,000 cubic feet (2,500 m3) per day. Oil wells are generally classified as stripper wells when they produce 10-15 barrels per day or less for any twelve-month period.
 W
WA sucker rod is a steel rod, typically between 25 and 30 feet in length, and threaded at both ends, used in the oil industry to join together the surface and downhole components of a reciprocating piston pump installed in an oil well. The pumpjack is the visible above-ground drive for the well pump, and is connected to the downhole pump at the bottom of the well by a series of interconnected sucker rods. Sucker rods are also commonly available made of fiberglass in 37 1/2 foot lengths and diameters of 3/4, 7/8, 1, and 1 1/4 inch. These are terminated in metallic threaded ends, female at one end and male at the other.
 W
WA Swivel is a mechanical device used on a drilling rig that hangs directly under the traveling block and directly above the kelly drive, that provides the ability for the kelly to rotate while allowing the traveling block to remain in a stationary rotational position while simultaneously allowing the introduction of drilling fluid into the drill string.
 W
WA traveling block is the freely moving section of a block and tackle that contains a set of pulleys or sheaves through which the drill line is threaded or reeved and is opposite the crown block.
 W
WTripping pipe is the physical act of pulling the drill string out of the wellbore and then running it back in. This is done by physically breaking out or disconnecting every other 2 or 3 joints of drill pipe at a time and racking them vertically in the derrick. When feasible the driller will start each successive trip on a different "break" so that after several trips fresh pipe dope will have been applied to every segment of the drill string.
 W
WTrue vertical depth is the measurement of a straight line perpendicularly downwards from a horizontal plane.
 W
WA wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment.