 W
WSinging is the act of producing musical sounds with the voice. A person who sings is called a singer or vocalist. Singers perform music that can be sung with or without accompaniment by musical instruments. Singing is often done in an ensemble of musicians, such as a choir of singers or a band of instrumentalists. Singers may perform as soloists or accompanied by anything from a single instrument up to a symphony orchestra or big band. Different singing styles include art music such as opera and Chinese opera, Indian music and religious music styles such as gospel, traditional music styles, world music, jazz, blues, ghazal and popular music styles such as pop, rock and electronic dance music.
 W
WA cappella music is a performance by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment, or a piece intended to be performed in this way. The term a cappella was originally intended to differentiate between Renaissance polyphony and Baroque concertato musical styles. In the 19th century, a renewed interest in Renaissance polyphony coupled with an ignorance of the fact that vocal parts were often doubled by instrumentalists led to the term coming to mean unaccompanied vocal music. The term is also used, rarely, as a synonym for alla breve.
 W
WAnyeint is a traditional Burmese entertainment form that combines dance with instrumental music, song, and comedy routines, in theatrical performances. It is a form of pwe, the Burmese word for traditional entertainment. While classical pwe can be quite formal and almost ritualistic, anyeint is considered light entertainment.
 W
WBacking vocalists or backup singers are singers who provide vocal harmony with the lead vocalist or other backing vocalists. A backing vocalist may also sing alone as a lead-in to the main vocalist's entry or to sing a counter-melody. Backing vocalists are used in a broad range of popular music, traditional music, and world music styles.
 W
WCollegiate a cappella ensembles are college-affiliated singing groups, primarily in the United States, and, increasingly, the United Kingdom and Ireland, that perform entirely without musical instruments. The groups are typically composed of, operated by, and directed by students. In the context of collegiate a cappella, the term a cappella typically also refers to the music genre performed by pop-centric student singing groups. Consequently, an ensemble that sings unaccompanied classical music may not be considered an a cappella group, even though technically it is performing a cappella.
 W
WCrooner is a term used to describe primarily male singers who performed using a smooth style made possible by better microphones which picked up quieter sounds and a wider range of frequencies, allowing the singer to utilize more dynamic range and perform in a more intimate manner. It is derived from the old verb "to croon". This suggestion of intimacy was supposedly wildly attractive to women, especially younger ones such as teenage girls, known at the time as "bobby soxers". The crooning style developed out of singers who performed with big bands, and reached its height in the 1940s to late 60s.
 W
WGerong is the Javanese verb meaning "to sing in a chorus." Penggerong is the proper name of a member of the chorus, but often the word gerong is used to refer to the unison male chorus that sings with the gamelan. The chorus or the melody may also be called the gerongan.
 W
WKaraoke is a type of interactive entertainment usually offered in clubs and bars, where people sing along to recorded music using a microphone. The music is an instrumental version of a well-known popular song. Lyrics are usually displayed on a video screen, along with a moving symbol, changing colour, or music video images, to guide the singer. In Chinese-speaking countries and regions such as mainland China, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Singapore, a karaoke box is called a KTV. The global karaoke market has been estimated to be worth nearly $10 billion.
 W
WThe lead vocalist in popular music is typically the member of a group or band whose voice is the most prominent melody in a performance where multiple voices may be heard. The lead singer sets their voice against the accompaniment parts of the ensemble as the dominant sound. In vocal group performances, notably in soul and gospel music, and early rock and roll, the lead singer takes the main vocal melody, with a chorus or harmony vocals provided by other band members as backing vocalists. Lead vocalists typically incorporate some movement or gestures into their performance, and some may participate in dance routines during the show, particularly in pop music. Some lead vocalists also play an instrument during the show, either in an accompaniment role, or playing a lead instrument/instrumental solo role when they are not singing.
 W
WA lip dub is a type of music video that combines lip synching and audio dubbing to make a music video. It is made by filming individuals or a group of people lip synching while listening to a song or any recorded audio then dubbing over it in post editing with the original audio of the song. There is often some form of mobile audio device used such as an MP3 player. Often they look like simple music videos, although many involve much preparation and production. Lip dubs are usually done in a single unedited shot that often travel through different rooms and situations within a building. They have become popular with the advent of mass participatory video content sites like YouTube.
 W
WLip sync or lip synch is a technical term for matching a speaking or singing person's lip movements with sung or spoken vocals.
 W
WA Meistersinger was a member of a German guild for lyric poetry, composition and unaccompanied art song of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. The Meistersingers were drawn from middle class males for the most part.
 W
WA minstrel was a medieval European entertainer. Originally describing any type of entertainer such as a musician, juggler, acrobat, singer or fool, the term later, from the sixteenth century, came to mean a specialist entertainer who sang songs and played musical instruments.
 W
WMusical theatre is a form of theatrical performance that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance. The story and emotional content of a musical – humor, pathos, love, anger – are communicated through words, music, movement and technical aspects of the entertainment as an integrated whole. Although musical theatre overlaps with other theatrical forms like opera and dance, it may be distinguished by the equal importance given to the music as compared with the dialogue, movement and other elements. Since the early 20th century, musical theatre stage works have generally been called, simply, musicals.
 W
WThe New York Singing Teachers' Association (NYSTA) is an international educational association of singing teachers and affiliated voice professionals based in New York City. It was founded in 1906, and is the oldest such group based in the United States. The association provides worldwide training in the teaching of singing through local events, as well as educational media archives and a highly regarded professional development program available to members worldwide via its website, www.nyst.org
 W
WOffstage musicians and singers are performers who play instruments and/or sing backstage, out of sight of the audience, during a live popular music concert at which the main band is visible playing and singing onstage. The sound from the offstage musicians or singers is captured by a microphone or from the output of their instrument, and this signal is mixed in with the singing and playing of the onstage performers using an audio console and a sound reinforcement system. Offstage backup singers are also used in some Broadway musicals, as have offstage instrumentalists, in cases where an onstage actor needs to appear to play an instrument.
 W
WOpera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers, but is distinct from musical theatre. Such a "work" is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor.
 W
WA pasindhèn is a female solo singer who sings with a gamelan. They may perform in dance, wayang or klenèngan performances.
 W
WQuan họ singing is a Vietnamese folk music style characterized both by its antiphonal nature, with alternating groups of female and male singers issuing musical challenges and responses. Quan họ is common in rituals and festivals, and a common theme in many songs is love and sentimentality as experienced by young adults. Quan họ was recognised as a UNESCO Intanginble Cultural Heritage practice in 2009.
 W
WA Red Envelope Club is a form of Cabaret in Taiwan that originated in Taipei in the 1960s as an imitation of Shanghai Cabaret. In these cabarets, female singers sing old Chinese songs from the 1920s to 1950s to mostly older men, many of whom were soldiers in General Chiang Kai-shek's Kuomintang army that fled Mainland China after the Chinese Civil War. The cabarets get their name from the fact that the audience gives the singers, who they appreciate, money in red envelopes. The remaining clubs are mostly located in the Ximending District of Taipei on Hankou Street, Emei Street, and Xining South Road.
 W
WSign singing or Karaoke signing is singing using sign language. Typically a song is played, and the performer expressively performs a sign language version of the lyrics. Whereas vocal singing uses pitch and tone to convey expressions, sign singing relies on the performer's hands, body, and facial expressions.
 W
WA vocal coach, also known as a voice coach, is a music teacher, usually a piano accompanist, who helps singers prepare for a performance, often also helping them to improve their singing technique and take care of and develop their voice, but is not the same as a singing teacher. Vocal coaches may give private music lessons or group workshops or masterclasses to singers. They may also coach singers who are rehearsing on stage, or who are singing during a recording session. Vocal coaches are used in both Classical music and in popular music styles such as rock and gospel. While some vocal coaches provide a range of instruction on singing techniques, others specialize in areas such as breathing techniques or diction and pronunciation.
 W
WVocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished.
 W
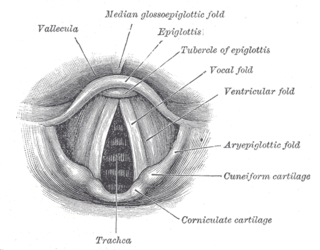
WA vocal register is a range of tones in the human voice produced by a particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds. These registers include modal voice, vocal fry, falsetto, and the whistle register. Registers originate in laryngeal function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches and produces certain characteristic sounds.
 W
WA vocal warm-up is a series of exercises meant to prepare the voice for singing, acting, or other use.