 W
WMoney is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value and sometimes, a standard of deferred payment. Any item or verifiable record that fulfils these functions can be considered as money.
 W
WBank reserves are a commercial bank's cash holdings physically held by the bank, and deposits held in the bank's account with the central bank. Under the fractional-reserve banking system used in most countries, central banks typically set minimum reserve requirements that require commercial banks under its purview to hold cash or deposits at the central bank equivalent to at least a prescribed percentage of their liabilities, such as customer deposits. Such sums are usually termed required reserves, and any funds above the required amount are called excess reserves. These reserves are prescribed to ensure that, in the normal events, there is sufficient liquidity in the banking system to provide funds to bank customers wishing to withdraw cash. Even when there are no reserve requirements, banks often as a matter of prudent management hold reserves in case of unexpected events, such as unusually large net withdrawals by customers or bank runs. In general, banks do not earn any interest on their reserves. Funds in banks that are not retained as a reserve are available to be lent, at interest.
 W
WBimetallism is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange between them.
 W
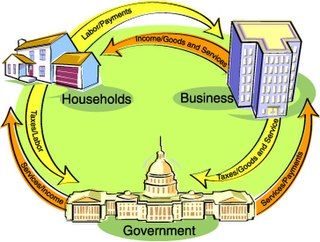
WIn macroeconomics, chartalism is a theory of money that argues that money originated historically with states' attempts to direct economic activity rather than as a spontaneous solution to the problems with barter or as a means with which to tokenize debt, and that fiat currency has value in exchange because of sovereign power to levy taxes on economic activity payable in the currency they issue.
 W
WMonetary circuit theory is a heterodox theory of monetary economics, particularly money creation, often associated with the post-Keynesian school. It holds that money is created endogenously by the banking sector, rather than exogenously by central bank lending; it is a theory of endogenous money. It is also called circuitism and the circulation approach.
 W
WCredit theories of money, also called debt theories of money, are monetary economic theories concerning the relationship between credit and money. Proponents of these theories, such as Alfred Mitchell-Innes, sometimes emphasize that money and credit/debt are the same thing, seen from different points of view. Proponents assert that the essential nature of money is credit (debt), at least in eras where money is not backed by a commodity such as gold. Two common strands of thought within these theories are the idea that money originated as a unit of account for debt, and the position that money creation involves the simultaneous creation of debt. Some proponents of credit theories of money argue that money is best understood as debt even in systems often understood as using commodity money. Others hold that money equates to credit only in a system based on fiat money, where they argue that all forms of money including cash can be considered as forms of credit money.
 W
WThe Death of Money is a 1993 book by Joel Kurtzman, a former editor of Harvard Business Review. Kurtzman uses the "death of money" to refer to a change in the economic nature of money in the United States following Richard Nixon's removal of US dollar from the gold standard, informally referred to as the Nixon shock.
 W
WA debasement of coinage is the practice of lowering the intrinsic value of coins, especially when used in connection with commodity money, such as gold or silver coins. A coin is said to be debased if the quantity of gold, silver, copper or nickel in the coin is reduced.
 W
WIn economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0%. Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate, i.e. when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive.
 W
WDella Moneta is a book written by Ferdinando Galiani, and is considered one of the first specific treatises on economics, especially monetary theory, preceding Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations by twenty-five years.
 W
WEndogenous money is an economy’s supply of money that is determined endogenously—that is, as a result of the interactions of other economic variables, rather than exogenously (autonomously) by an external authority such as a central bank.
 W
WThe South African financial rand was the most visible part of a system of capital controls. Although the financial rand was abolished in March 1995, some capital controls remain in place. These capital controls are locally referred to as "exchange controls", although the system has since 1995 moved towards surveillance — recording and reporting to the authorities of foreign currency transactions — rather than control.
 W
WFractional-reserve banking is the system of banking operating in almost all countries worldwide, under which banks that take deposits from the public are required to hold a proportion of their deposit liabilities in liquid assets as a reserve, and are at liberty to lend the remainder to borrowers. Bank reserves are held as cash in the bank or as balances in the bank's account at the central bank. The country's central bank determines the minimum amount that banks must hold in liquid assets, called the "reserve requirement" or "reserve ratio". Most commercial banks hold more than this minimum amount as excess reserves.
 W
WIdeal Money is a theoretical notion promulgated by John Nash to stabilize international currencies. It is a solution to the Triffin dilemma-the conflict of economic interests between the short-term domestic and long-term international objectives when a currency used in a country is also serving as world reserve currency.
 W
WIn macroeconomic theory, liquidity preference is the demand for money, considered as liquidity. The concept was first developed by John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936) to explain determination of the interest rate by the supply and demand for money. The demand for money as an asset was theorized to depend on the interest foregone by not holding bonds. Interest rates, he argues, cannot be a reward for saving as such because, if a person hoards his savings in cash, keeping it under his mattress say, he will receive no interest, although he has nevertheless refrained from consuming all his current income. Instead of a reward for saving, interest, in the Keynesian analysis, is a reward for parting with liquidity. According to Keynes, money is the most liquid asset. Liquidity is an attribute to an asset. The more quickly an asset is converted into money the more liquid it is said to be.
 W
W"Monetae cudendae ratio" is a paper on coinage by Nicolaus Copernicus. It was written in 1526 at the request of Sigismund I the Old, King of Poland, and presented to the Prussian Diet.
 W
WMonetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price levels over longer periods. Monetarists assert that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply rather than by engaging in discretionary monetary policy.
 W
WIn economics, the monetary base in a country is the total amount of money created by the central bank. This includes:the total currency circulating in the public, plus the currency that is physically held in the vaults of commercial banks, plus the commercial banks' reserves held in the central bank.
 W
WMonetary reform is any movement or theory that proposes a system of supplying money and financing the economy that is different from the current system.
 W
WMoney and Trade Considered: With a Proposal for Supplying the Nation with Money is an early economics text written by John Law of Lauriston, published in 1705. In it, he attempts to compare the prosperity of other countries with that of Scotland, and advocates a "land bank" system of paper money backed by real estate as a commodity instead of gold or silver.
 W
WMoney burning or burning money is the purposeful act of destroying money. In the prototypical example, banknotes are destroyed by setting them on fire. Burning money decreases the wealth of the owner without directly enriching any particular party.
 W
WNominal rigidity, also known as price-stickiness or wage-stickiness, is a situation in which a nominal price is resistant to change. Complete nominal rigidity occurs when a price is fixed in nominal terms for a relevant period of time. For example, the price of a particular good might be fixed at $10 per unit for a year. Partial nominal rigidity occurs when a price may vary in nominal terms, but not as much as it would if perfectly flexible. For example, in a regulated market there might be limits to how much a price can change in a given year.
 W
WOn the Balance of Trade is an economic text on monetary economics, written by David Hume and published in 1752. In this book, Hume examines various mistakes committed by nations regarding trade, and suggests better alternatives. The thought experiments Hume uses in the book are sometimes argued by modern economists to be the first formal economic models.
 W
WThe general price level is a hypothetical measure of overall prices for some set of goods and services, in an economy or monetary union during a given interval, normalized relative to some base set. Typically, the general price level is approximated with a daily price index, normally the Daily CPI. The general price level can change more than once per day during hyperinflation.
 W
WIn macroeconomics, sterilization is action taken by a country's central bank to counter the effects on the money supply caused by a balance of payments surplus or deficit. This can involve open market operations undertaken by the central bank whose aim is to neutralize the impact of associated foreign exchange operations. The opposite is unsterilized intervention, where monetary authorities have not insulated their country's domestic money supply and internal balance against foreign exchange intervention.
 W
WOn the System or Theory of the Trade of the World is an immediate precursor to the first modern economic texts, written by Isaac Gervaise and published in 1720.
 W
WThe Great Debasement (1544–1551) was a currency debasement policy introduced in 1544 England under the order of Henry VIII which saw the amount of precious metal in gold and silver coins reduced and in some cases replaced entirely with cheaper base metals such as copper. Overspending by Henry VIII to pay for his lavish lifestyle and to fund foreign wars with France and Scotland are cited as reasons for the policy's introduction. The main aim of the policy was to increase revenue for the Crown at the cost of taxpayers through savings in currency production with less bullion being required to mint new coins. During debasement gold standards dropped from the previous standard of 23 karat to as low as 20 karat while silver was reduced from 92.5% sterling silver to just 25%. Revoked in 1551 by Edward VI, the policy's economic effects continued for many years until 1560 when all debased currency was removed from circulation.
 W
WTwo Overtures Humbly Offered to his Grace John Duke of Argyll, Her Majesties High Commissioner, and the right Honourable the Estates of Parliament is a pamphlet of economic proposals written by the early eighteenth-century economist John Law of Lauriston which was published in 1705.
 W
WThe velocity of money is a measure of the number of times that the average unit of currency is used to purchase goods and services within a given time period. The concept relates the size of economic activity to a given money supply, and the speed of money exchange is one of the variables that determine inflation. The measure of the velocity of money is usually the ratio of the gross national product (GNP) to a country's money supply.