 W
WA transmission is a machine in a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of power. Often the term 5-speed transmission refers simply to the gearbox, that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque block conversions from a rotating power source to another device.
 W
WA belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel.
 W
WBraking choppers, sometimes also referred to as braking units, are used in the DC voltage intermediate circuits of frequency converters to control voltage when the load feeds energy back to the intermediate circuit. This arises, for example, when a magnetized motor is being rotated by an overhauling load and so functions as a generator feeding power to the DC voltage intermediate circuit. They are an application of the chopper principle, using on-off control of a switching device.
 W
WA chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A chain may consist of two or more links. Chains can be classified by their design, which can be dictated by their use:Those designed for lifting, such as when used with a hoist; for pulling; or for securing, such as with a bicycle lock, have links that are torus shaped, which make the chain flexible in two dimensions. Small chains serving as jewellery are a mostly decorative analogue of such types. Those designed for transferring power in machines have links designed to mesh with the teeth of the sprockets of the machine, and are flexible in only one dimension. They are known as roller chains, though there are also non-roller chains such as block chain.
 W
WA chain conveyor is a type of conveyor system for moving material through production lines.
 W
WChain drive is a way of transmitting mechanical power from one place to another. It is often used to convey power to the wheels of a vehicle, particularly bicycles and motorcycles. It is also used in a wide variety of machines besides vehicles.
 W
WDC injection braking is a method of slowing AC electric motors. A DC voltage is injected into the winding of the AC motor after the AC voltage is disconnected, providing braking force to the rotor.
 W
WA drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.
 W
WA belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel.
 W
WFlat chain is a form of chain used chiefly in agricultural machinery. Early machinery made extensive use of flat chain. It has been gradually replaced in most applications by roller chain, which is quieter, lasts longer, and requires less frequent retensioning.
 W
WA flexible shaft is a device for transmitting rotary motion between two objects which are not fixed relative to one another. It consists of a rotating wire rope or coil which is flexible but has some torsional stiffness. It may or may not have a covering, which also bends but does not rotate. It may transmit considerable power, or only motion, with negligible power.
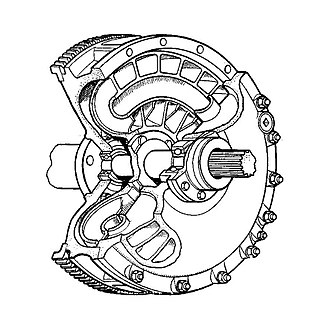 W
WA fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power. It has been used in automobile transmissions as an alternative to a mechanical clutch. It also has widespread application in marine and industrial machine drives, where variable speed operation and controlled start-up without shock loading of the power transmission system is essential.
 W
WA high-tensile chain, also referred to as a transport chain, is a link chain with a high tensile strength used for drawing or securing loads. This type of chain usually consist of broad (thick/heavy) metal, oblong torus-shaped links for high strength. All the links of the chain are usually identical, and on the ends are usually two hooks of the appropriate size and strength to slide easily over one chain link but small enough not let the links slip by. When the ability to grasp the load is required, a slip hook is used.
 W
WA jackshaft is an intermediate shaft used to transfer power from a powered shaft such as the output shaft of an engine or motor to driven shafts such as the drive axles of a locomotive. As applied to railroad locomotives in the 19th and 20th centuries, jackshafts were typically in line with the drive axles of locomotives and connected to them by side rods. In general, each drive axle on a locomotive is free to move about one inch (2.5 cm) vertically relative to the frame, with the locomotive weight carried on springs. This means that if the engine, motor or transmission is rigidly attached to the locomotive frame, it cannot be rigidly connected to the axle. This problem can be solved by mounting the jackshaft on unsprung bearings and using side-rods or chain drives.
 W
WA line shaft is a power-driven rotating shaft for power transmission that was used extensively from the Industrial Revolution until the early 20th century. Prior to the widespread use of electric motors small enough to be connected directly to each piece of machinery, line shafting was used to distribute power from a large central power source to machinery throughout a workshop or an industrial complex. The central power source could be a water wheel, turbine, windmill, animal power or a steam engine. Power was distributed from the shaft to the machinery by a system of belts, pulleys and gears known as millwork.
 W
WMotor drive, or simply known as drive, describes equipment used to control the speed of machinery. Many industrial processes such as assembly lines must operate at different speeds for different products. Where process conditions demand adjustment of flow from a pump or fan, varying the speed of the drive may save energy compared with other techniques for flow control.
 W
WThe o-ring chain is a specialized type of roller chain used in the transmission of mechanical power from one sprocket to another.
 W
WA belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel.
 W
WA power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is any of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate machine.
 W
WA pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that does not transfer power to a shaft, but is used to guide the cable or exert a force, the supporting shell is called a block, and the pulley may be called a sheave.
 W
WA quick return mechanism is an apparatus to produce a reciprocating motion in which the time taken for travel in return stroke is less than in the forward stroke. It is driven by a circular motion source and uses a system of links with three turning pairs and a sliding pair. A quick-return mechanism is a subclass of a slider-crank linkage, with an offset crank.
 W
WRoller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficient means of power transmission.
 W
WA rope drive is a form of belt drive, used for mechanical power transmission.
 W
WA belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel.
 W
WA sheave or pulley wheel is a grooved wheel often used for holding a belt, wire rope, or rope and incorporated into a pulley. The sheave spins on an axle or bearing inside the frame of the pulley. This allows the wire or rope to move freely, minimizing friction and wear on the cable. Sheaves can be used to redirect a cable or rope, lift loads, and transmit power. The words sheave and pulley are sometimes used interchangeably.
 W
WA sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passing over it. It is distinguished from a gear in that sprockets are never meshed together directly, and differs from a pulley in that sprockets have teeth and pulleys are smooth except for timing pulleys used with toothed belts.
 W
WA timing belt, timing chain, or cambelt is a part of an internal combustion engine that synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and the camshaft(s) so that the engine's valves open and close at the proper times during each cylinder's intake and exhaust strokes. In an interference engine the timing belt or chain is also critical to preventing the piston from striking the valves. A timing belt is usually a toothed belt—a drive belt with teeth on the inside surface. A timing chain is a roller chain.
 W
WA torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power source to the load. It is usually located between the engine's flexplate and the transmission. The equivalent location in a manual transmission would be the mechanical clutch.
 W
WA variable-frequency drive (VFD) or adjustable-frequency drive (AFD), variable-voltage/variable-frequency (VVVF) drive, variable speed drive (VSD), AC drive, micro drive or inverter drive is a type of motor drive used in electro-mechanical drive systems to control AC motor speed and torque by varying motor input frequency and voltage.
 W
WA belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel.
 W
WWire rope is several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix forming a composite rope, in a pattern known as laid rope. Larger diameter wire rope consists of multiple strands of such laid rope in a pattern known as cable laid.