 W
WA boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
 W
WIn classical antiquity, an authepsa or autepsa was a vessel used for water heating. Basically, it was a vase with a central tube used to keep coals.
 W
WBoiler blowdown is water intentionally wasted from a boiler to avoid concentration of impurities during continuing evaporation of steam. The water is blown out of the boiler with some force by steam pressure within the boiler. Bottom blowdown used with early boilers caused abrupt downward adjustment of boiler water level and was customarily expelled downward to avoid the safety hazard of showering hot water on nearby individuals.
 W
WBoiler design is the process of designing boilers used for various purposes. The main function of a boiler is to heat water to generate steam. Steam produced in a boiler can be used for a variety of purposes including space heating, sterilisation, drying, humidification and power generation. The temperature or condition of steam required for these applications is different, so boiler designs vary accordingly.
 W
WA boiler explosion is a catastrophic failure of a boiler. There are two types of boiler explosions. One type is a failure of the pressure parts of the steam and water sides. There can be many different causes, such as failure of the safety valve, corrosion of critical parts of the boiler, or low water level. Corrosion along the edges of lap joints was a common cause of early boiler explosions.
 W
WBoiler feedwater is an essential part of boiler operations. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used it is then dumped to the main condenser. From the condenser it is then pumped to the deaerated feed tank. From this tank it then goes back to the steam drum to complete its cycle. The feed water is never open to the atmosphere. This cycle is known as a closed system or Rankine cycle.
 W
WBoiler water is liquid water within a boiler, or in associated piping, pumps and other equipment, that is intended for evaporation into steam. The term may also be applied to raw water intended for use in boilers, treated boiler feedwater, steam condensate being returned to a boiler, or boiler blowdown being removed from a boiler.
 W
WClarke Chapman is a British engineering firm based in Gateshead, which was formerly listed on the London Stock Exchange.
 W
WA couscoussier is a traditional double-chambered food steamer used in Berber cuisine to cook couscous.
 W
WAn electric steam boiler is a type of boiler where the steam is generated using electricity, rather than through the combustion of a fuel source. Such boilers are used to generate steam for process purposes in many locations, for example laundries, food processing factories and hospitals. Although they are more expensive to run than gas-fired or oil-fired boilers they are popular because of their simplicity and ease of use. Because of the large currents required, they are normally run from a three-phase electricity supply. They convert electrical energy into thermal energy with almost 100% efficiency but the overall thermal efficiency is variable, depending on the efficiency with which the electricity is generated.
 W
WA flash boiler is a type of water-tube boiler. The tubes are close together and water is pumped through them. A flash boiler differs from the type of monotube steam generator in which the tube is permanently filled with water. In a flash boiler, the tube is kept so hot that the water feed is quickly flashed into steam and superheated. Flash boilers had some use in automobiles in the 19th century and this use continued into the early 20th century.
 W
WA forced circulation boiler is a boiler where a pump is used to circulate water inside the boiler. This differs from a natural circulation boiler which relies on current density to circulate water inside the boiler. In some forced circulation boilers, the water is circulated twenty times the rate of evaporation.
 W
WGreenwood Clean Energy, Inc. is a privately held company located in Redmond, Washington that manufactures wood and biomass central heating systems. In 2009, a team of entrepreneurs and industry veterans to develop and distribute woody-biomass fueled heating appliances for home and light commercial use.
 W
WA heating plant, also called a physical plant, or steam plant, generates thermal energy in the form of steam for use in district heating applications. Unlike combined heat and power installations which produce thermal energy as a by-product of electricity generation, heating plants are dedicated to generating heat for use in various processes.
 W
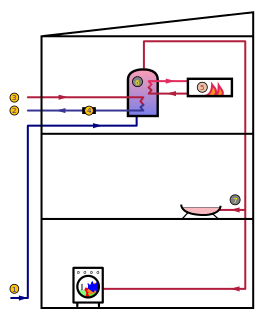
WHydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and steam systems. Historically, in large-scale commercial buildings such as high-rise and campus facilities, a hydronic system may include both a chilled and a heated water loop, to provide for both heating and air conditioning. Chillers and cooling towers are used either separately or together as means to provide water cooling, while boilers heat water. A recent innovation is the chiller boiler system, which provides an efficient form of HVAC for homes and smaller commercial spaces.
 W
WA kier or keeve is a large circular boiler or vat used in bleaching or scouring cotton fabric. They were also used for processing paper pulp.
 W
WA LaMont boiler is a type of forced circulation water-tube boiler in which the boiler water is circulated through an external pump through long closely spaced tubes of small diameter. The mechanical pump is employed in order to have an adequate and positive circulation in steam and hot water boilers.
 W
WA fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam.
 W
WA multi-fuel stove is similar to a wood-burning stove in appearance and design. Multifuel refers to the capability of the stove to burn wood and also coal, wood pellets, or peat. Stoves that have a grate for the fire to burn on and a removable ash pan are generally considered multi-fuel stoves. If the fire simply burns on a bed of ash, it is a wood-only fuelled appliance, and cannot be used for coal or peat.
 W
WIn a natural circulation boiler the circulation is achieved by the difference in density when the water in the boiler is heated. In natural circulation steam boilers the circulation of water is by convection currents, which are set up during the heating of water. In most of the boilers there is a natural circulation of water the fundamental principle of which is based on the principle of Thermosiphon.
 W
WThe outdoor wood boiler is a variant of the classic wood stove adapted for set-up outdoors while still transferring the heat to interior buildings.
 W
WA pop-pop boat is a toy with a very simple steam engine without moving parts, typically powered by a candle or vegetable oil burner. The name comes from the noise made by some versions of the boats. Other names are putt-putt boat, crazy boat, flash-steamer, hot-air-boat, pulsating water engine boat. Around the world they may be called Can-Can-boot, Knatterboot, toc-toc, Puf-Puf boat, Poof Poof craft, Phut-Phut, or Pouet-Pouet.
 W
WRecovery boiler is the part of Kraft process of pulping where chemicals for white liquor are recovered and reformed from black liquor, which contains lignin from previously processed wood. The black liquor is burned, generating heat, which is usually used in the process of making electricity, much as in a conventional steam power plant. The invention of the recovery boiler by G.H. Tomlinson in the early 1930s was a milestone in the advancement of the kraft process.
 W
WA round-topped boiler is a type of boiler used for some designs of steam locomotive and portable engine. It was an early form of locomotive boiler, although continuing to be used for new locomotives through to the end of steam locomotive manufacture in the 1960s.
 W
WSoil steam sterilization is a farming technique that sterilizes soil with steam in open fields or greenhouses. Pests of plant cultures such as weeds, bacteria, fungi and viruses are killed through induced hot steam which causes vital cellular proteins to unfold. Biologically, the method is considered a partial disinfection. Important heat-resistant, spore-forming bacteria can survive and revitalize the soil after cooling down. Soil fatigue can be cured through the release of nutritive substances blocked within the soil. Steaming leads to a better starting position, quicker growth and strengthened resistance against plant disease and pests. Today, the application of hot steam is considered the best and most effective way to disinfect sick soil, potting soil and compost. It is being used as an alternative to bromomethane, whose production and use was curtailed by the Montreal Protocol. "Steam effectively kills pathogens by heating the soil to levels that cause protein coagulation or enzyme inactivation."
 W
WA steam accumulator is an insulated steel pressure tank containing hot water and steam under pressure. It is a type of energy storage device. It can be used to smooth out peaks and troughs in demand for steam. Steam accumulators may take on a significance for energy storage in solar thermal energy projects. An example is the PS10 solar power tower plant near Seville, Spain and one planned for the "solar steam train" project in Sacramento, California.
 W
WA steam drum is a standard feature of a water-tube boiler. It is a reservoir of water/steam at the top end of the water tubes. The drum stores the steam generated in the water tubes and acts as a phase-separator for the steam/water mixture. The difference in densities between hot and cold water helps in the accumulation of the "hotter"-water/and saturated-steam into the steam-drum.
 W
WA steam generator is a form of low water-content boiler, similar to a flash steam boiler. The usual construction is as a spiral coil of water-tube, arranged as a single, or monotube, coil. Circulation is once-through and pumped under pressure, as a forced-circulation boiler. The narrow-tube construction, without any large-diameter drums or tanks, means that they are safe from the effects of explosion, even if worked at high pressures. The pump flowrate is adjustable, according to the quantity of steam required at that time. The burner output is throttled to maintain a constant working temperature. The burner output required varies according to the quantity of water being evaporated: this can be either adjusted by open-loop control according to the pump throughput, or by a closed-loop control to maintain the measured temperature.
 W
WSteam generators are heat exchangers used to convert water into steam from heat produced in a nuclear reactor core. They are used in pressurized water reactors (PWR) between the primary and secondary coolant loops.
 W
WA steam generator is a type of boiler used to produce steam for climate control and potable water heating in railroad passenger cars. The output of a railroad steam generator is low pressure, saturated steam that is passed through a system of pipes and conduits throughout the length of the train.
 W
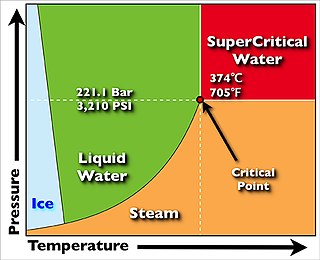
WA supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure, frequently used in the production of electric power.
 W
WThermic siphons are heat-exchanging elements in the firebox or combustion chamber of some steam boiler and steam locomotive designs. As they are directly exposed to the radiant heat of combustion, they have a high evaporative capacity relative to their size. By arranging them near-vertically, they also have good water circulation by means of the thermosyphon effect.
 W
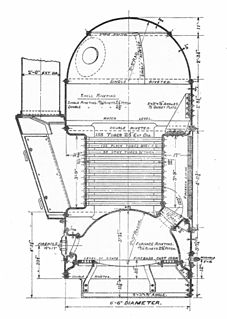
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WA vertical boiler is a type of fire-tube or water-tube boiler where the boiler barrel is oriented vertically instead of the more common horizontal orientation. Vertical boilers were used for a variety of steam-powered vehicles and other mobile machines, including early steam locomotives.
 W
WA vertical boiler with horizontal fire-tubes is a type of small vertical boiler, used to generate steam for small machinery. It is characterised by having many narrow fire-tubes, running horizontally.
 W
WAn electric water boiler, also called a thermo pot, is a consumer electronics small appliance used for boiling water and maintaining it at a constant temperature. It is typically used to provide an immediate source of hot water for making tea, hot chocolate, coffee, instant noodles, or baby formula, or for any other household use where clean hot water is required. They are a common component of Japanese kitchens and the kitchens of many East Asian countries but are found in varying use globally. Some thermo pots are designed with a feature that can purify water.
 W
WWater heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.
 W
WA high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.
 W
WA wood-burning stove is a heating appliance capable of burning wood fuel and wood-derived biomass fuel, such as sawdust bricks. Generally the appliance consists of a solid metal closed firebox, often lined by fire brick, and one or more air controls. The first wood-burning stove was patented in Strasbourg in 1557, two centuries before the Industrial Revolution, which would make iron an inexpensive and common material, so such stoves were high end consumer items and only gradually spread in use.