 W
WAltitude3.Net is an electronic business development platform that allows to create web and mobile solutions along with interactive communication strategies. The platform has the same functionalities than a content management system (CMS) and communicates with other systems.
 W
WThe Application Programming Interface Exchange(APIX) is a global fintech marketplace and regulatory sandbox.
 W
WThe Asset Description Metadata Schema (ADMS) is a common metadata vocabulary to describe standards, so-called interoperability assets, on the Web.
 W
WThe Aviation Industry Computer-Based Training Committee (AICC) was an international association of technology-based training professionals that existed from 1988 to 2014. The AICC developed guidelines for aviation industry in the development, delivery, and evaluation of CBT, WBT, and related training technologies.
 W
WIn information science a conceptualization is an abstract simplified view of some selected part of the world, containing the objects, concepts, and other entities that are presumed of interest for some particular purpose and the relationships between them. An explicit specification of a conceptualization is an ontology, and it may occur that a conceptualization can be realized by several distinct ontologies. An ontological commitment in describing ontological comparisons is taken to refer to that subset of elements of an ontology shared with all the others. "An ontology is language-dependent", its objects and interrelations described within the language it uses, while a conceptualization is always the same, more general, its concepts existing "independently of the language used to describe it". The relation between these terms is shown in the figure to the right.
 W
WConfiguration management (CM) is a systems engineering process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. The CM process is widely used by military engineering organizations to manage changes throughout the system lifecycle of complex systems, such as weapon systems, military vehicles, and information systems. Outside the military, the CM process is also used with IT service management as defined by ITIL, and with other domain models in the civil engineering and other industrial engineering segments such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings.
 W
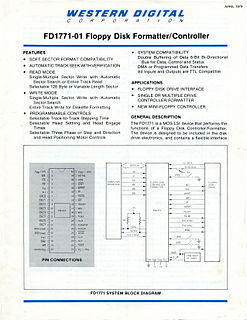
WA data sheet, data-sheet, or spec sheet is a document that summarizes the performance and other characteristics of a product, machine, component, material, subsystem, or software in sufficient detail that allows a buyer to understand what the product is and a design engineer to understand the role of the component in the overall system. Typically, a data sheet is created by the manufacturer and begins with an introductory page describing the rest of the document, followed by listings of specific characteristics, with further information on the connectivity of the devices. In cases where there is relevant source code to include, it is usually attached near the end of the document or separated into another file. Data sheets are created, stored, and distributed via product information management or product data management systems.
 W
WThe Design Manual for Roads and Bridges (DMRB) is a series of 15 volumes that provide standards, advice notes and other documents relating to the design, assessment and operation of trunk roads, including motorways in the United Kingdom, and, with some amendments, the Republic of Ireland. It also forms the basis of the road design standards used in many other countries.
 W
WA flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.
 W
WThe Free On-line Dictionary of Computing (FOLDOC) is an online, searchable, encyclopedic dictionary of computing subjects.
 W
WGrey literature is materials and research produced by organizations outside of the traditional commercial or academic publishing and distribution channels. Common grey literature publication types include reports, working papers, government documents, white papers and evaluations. Organizations that produce grey literature include government departments and agencies, civil society or non-governmental organizations, academic centres and departments, and private companies and consultants.
 W
WJoAnn T. Hackos is a lecturer, consultant, and author of a number of books about technical communication. Now retired, Dr. Hackos is the founder of the Center for Information-Development Management (CIDM) and the president emeritus of Comtech Services in Denver, Colorado. She is also a fellow and past president of the Society for Technical Communication. She is a member of the IEEE Standards Association and active in the ISO SC7 Working Groups that is developing standards for information developers. She is the co-author of the standards on content management and information-development management.
 W
WThe Haynes Owner's Workshop Manuals are a series of practical manuals from the British publisher Haynes Publishing Group. The series primarily focuses upon the maintenance and repair of automotive vehicles, covering a wide range of makes and models ; the manuals are aimed mainly at DIY enthusiasts rather than professional garage mechanics, as they lack the depth of coverage on particular vehicles or problems. The series includes a range of 'practical lifestyle' manuals in the same style for a range of topics, including domestic appliances and personal computers, digital photography, model railways, sport, animal care, men, babies, sex, and women. They also now publish the Bluffer's Guides collection.
 W
WIn computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment.
 W
WA virtual learning environment (VLE) is a system that creates an environment designed to facilitate teachers' management of educational courses for their students, especially a system using computer hardware and software, which involves distance learning. In North America, a virtual learning environment is often referred to as a "learning management system" (LMS).
 W
WRobert E. Horn is an American political scientist who taught at Harvard, Columbia, and Sheffield (U.K.) universities, and has been a visiting scholar at Stanford University's Center for the Study of Language and Information. He is known for the development of information mapping.
 W
WThe HyperText Markup Language, or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.
 W
WInformation Mapping(R) is a research-based method for writing clear and user focused information, based on the audience's needs and the purpose of the information. The method is applied primarily to designing and developing business and technical communications. It is used as a content standard within organizations throughout the world.
 W
WIn computing, internationalization and localization (American) or internationalisation and localisation (BrE), often abbreviated i18n and L10n, are means of adapting computer software to different languages, regional peculiarities and technical requirements of a target locale. Internationalization is the process of designing a software application so that it can be adapted to various languages and regions without engineering changes. Localization is the process of adapting internationalized software for a specific region or language by translating text and adding locale-specific components. Localization uses the infrastructure or flexibility provided by internationalization.
 W
WLearning Object Metadata is a data model, usually encoded in XML, used to describe a learning object and similar digital resources used to support learning. The purpose of learning object metadata is to support the reusability of learning objects, to aid discoverability, and to facilitate their interoperability, usually in the context of online learning management systems (LMS).
 W
WA style guide, or style manual, is a set of standards for the writing and design of documents, either for general use or for a specific publication, organization or field. The implementation of a style guide provides uniformity in style and formatting within a document and across multiple documents. A set of standards for a specific organization is often known as "house style". Style guides are common for general and specialized use, for the general reading and writing audience, and for students and scholars of various academic disciplines, medicine, journalism, the law, government, business, and industry.
 W
WA man page is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs, formal standards and conventions, and even abstract concepts. A user may invoke a man page by issuing the man command.
 W
WMetadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:Descriptive metadata — the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords.Structural metadata — metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships and other characteristics of digital materials.Administrative metadata — the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, permissions, and when and how it was created.Reference metadata — the information about the contents and quality of statistical data.Statistical metadata, also called process data, may describe processes that collect, process, or produce statistical data.Legal metadata — provides information about the creator, copyright holder, and public licensing, if provided.
 W
WNelson rules are a method in process control of determining whether some measured variable is out of control. Rules for detecting "out-of-control" or non-random conditions were first postulated by Walter A. Shewhart in the 1920s. The Nelson rules were first published in the October 1984 issue of the Journal of Quality Technology in an article by Lloyd S Nelson.
The Office Assistant is a discontinued intelligent user interface for Microsoft Office that assisted users by way of an interactive animated character which interfaced with the Office help content. It was included in Microsoft Office for Windows, in Microsoft Publisher and Microsoft Project, Microsoft FrontPage, and Microsoft Office for Mac.
 W
WIn computer science, information science and systems engineering, ontology engineering is a field which studies the methods and methodologies for building ontologies, which encompasses a representation, formal naming and definition of the categories, properties and relations between the concepts, data and entities. In a broader sense, this field also includes a knowledge construction of the domain using formal ontology representations such as OWL/RDF. A large-scale representation of abstract concepts such as actions, time, physical objects and beliefs would be an example of ontological engineering. Ontology engineering is one of the areas of applied ontology, and can be seen as an application of philosophical ontology. Core ideas and objectives of ontology engineering are also central in conceptual modeling.
 W
WThe ORCID is a nonproprietary alphanumeric code to uniquely identify authors and contributors of scholarly communication as well as ORCID's website and services to look up authors and their bibliographic output.
 W
WAn owner's manual is an instructional book or booklet that is supplied with almost all technologically advanced consumer products such as vehicles, home appliances and computer peripherals. Information contained in the owner's manual typically includes:Safety instructions; for liability reasons these can be extensive, often including warnings against performing operations that are ill-advised for product longevity or overall user safety reasons. Assembly instructions; for products that arrive in pieces for easier shipping. Installation instructions; for products that need to be installed in a home or workplace. Setup instructions; for devices that keep track of time or which maintain user accessible state. Instructions for normal or intended operations. Programming instructions; for microprocessor controlled products such as VCRs, programmable calculators, and synthesizers. Maintenance instructions. Troubleshooting instructions; for when the product does not work as expected. Service locations; for when the product requires repair by a factory authorized technician. Regulatory code compliance information; for example with respect to safety or electromagnetic interference. Product technical specifications. Warranty information; sometimes provided as a separate sheet.
 W
WA reference card or reference sheet or crib sheet is a concise bundling of condensed notes about a specific topic, such as mathematical formulas to calculate area/volume, or common syntactic rules and idioms of a particular computer platform, application program, or formal language. It serves as an ad hoc memory aid for an experienced user.
 W
WA run chart, also known as a run-sequence plot is a graph that displays observed data in a time sequence. Often, the data displayed represent some aspect of the output or performance of a manufacturing or other business process. It is therefore a form of line chart.
 W
WIn academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research.
 W
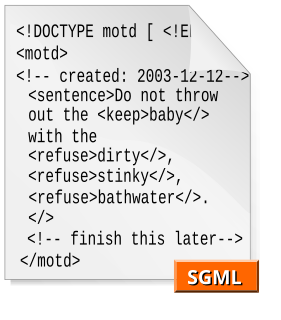
WThe Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":Declarative: Markup should describe a document's structure and other attributes rather than specify the processing that needs to be performed, because it is less likely to conflict with future developments. Rigorous: In order to allow markup to take advantage of the techniques available for processing markup should rigorously define objects like programs and databases.
 W
WStructured writing is a form of technical writing that uses and creates structured documents.
 W
WA style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for general use, or be required usage for an individual publication, a particular organization, or a specific field.
 W
WA table of contents, usually headed simply Contents and abbreviated informally as TOC, is a list, usually found on a page before the start of a written work, of its chapter or section titles or brief descriptions with their commencing page numbers.
 W
WThe Central Technical Construction Archive (AQTN) was established on July 26, 1993 in Tirana, Albania. It gathered technical construction projects of former institutes which belonged to Albania's former Ministry of Construction fund, materials from the Municipality of Tirana and KRRTSH decisions. AQTN's documentary archive has over 45,000 files and 556,000 pages, with the first document dating back to 1911 "Reconstruction of Buna Bridge". The main task of the archive is to preserve, maintain and manage the technical documentation in the field of construction to meet the requirements of private and public entities for technical documentation at its disposal.
 W
WTLDR Pages is a free and open-source collaborative software documentation project that aims to be a simpler, more approachable complement to traditional man pages. It's a collection of community-maintained help pages that covers command-line utilities and other computer programs. A page can be invoked by issuing the tldr command. The name comes from the word TL;DR, which is an abbreviation for "too long; didn't read", referring to man pages that are said to be too long by several users.
A topic map is a standard for the representation and interchange of knowledge, with an emphasis on the findability of information. Topic maps were originally developed in the late 1990s as a way to represent back-of-the-book index structures so that multiple indexes from different sources could be merged. However, the developers quickly realized that with a little additional generalization, they could create a meta-model with potentially far wider application. The ISO standard is formally known as ISO/IEC 13250:2003.
 W
WUnited Media was a large editorial column and comic strip newspaper syndication service based in the United States, owned by the E. W. Scripps Company, that operated from 1978 to 2011. It syndicated 150 comics and editorial columns worldwide. Its core businesses were the United Feature Syndicate and the Newspaper Enterprise Association.
 W
WUsability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use.
 W
WxCHM is a free and open-source GUI front-end for CHMLIB. It compiles and runs on Linux, BSD, Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows. Pre-built binaries for Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows are usually available for download from the project's website.
 W
WExtensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.