 W
WA carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis, the formation of cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise in both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious.
 W
WAcetoxyacetylaminofluorene is a derivative of 2-acetylaminofluorene used as a biochemical tool in the study of carcinogenesis. It forms adducts with DNA by reacting with guanine at its C-8 position.; This results in breaks in one strand of the DNA.
 W
W2-Acetylaminofluorene is a carcinogenic and mutagenic derivative of fluorene. It is used as a biochemical tool in the study of carcinogenesis. It induces tumors in a number of species in the liver, bladder and kidney. The metabolism of this compound in the body by means of biotransformation reactions is the key to its carcinogenicity. 2-AAF is a substrate for cytochrome P-450 (CYP) enzyme, which is a part of a super family found in almost all organisms. This reaction results in the formation of hydroxyacetylaminofluorene which is a proximal carcinogen and is more potent than the parent molecule. The N-hydroxy metabolite undergoes several enzymatic and non-enzymatic rearrangements. It can be O-acetylated by cytosolic N-acetyltransferase enzyme to yield N-acetyl-N-acetoxyaminofluorene. This intermediate can spontaneously rearrange to form the arylamidonium ion and a carbonium ion which can interact directly with DNA to produce DNA adducts. In addition to esterification by acetylation, the N-hydroxy derivative can be O-sulfated by cytosolic sulfur transferase enzyme giving rise to the N-acetyl-N-sulfoxy product.
 W
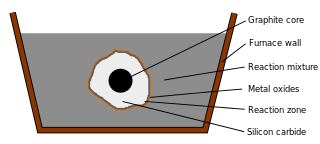
WThe Acheson process was invented by Edward Goodrich Acheson to synthesize silicon carbide (SiC) and graphite.
 W
WAgent Orange is a herbicide and defoliant chemical, one of the "tactical use" Rainbow Herbicides. It is widely known for its use by the U.S. military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. It is a mixture of equal parts of two herbicides, 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D. In addition to its damaging environmental effects, traces of dioxin found in the mixture have caused major health problems for many individuals who were exposed, and their offspring.
 W
WAlcoholic beverages are classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as a Group 1 carcinogen. IARC classifies alcoholic beverage consumption as a cause of female breast, colorectal, larynx, liver, esophagus, oral cavity, and pharynx cancers; and as a probable cause of pancreatic cancer.
 W
WAmericium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after the Americas.
 W
WArsenic tribromide is the inorganic compound with the formula AsBr3. This pyramidal molecule is the only known binary arsenic bromide. AsBr3 is noteworthy for its very high refractive index of approximately 2.3. It also has a very high diamagnetic susceptibility. The compound exists as colourless deliquescent crystals that fume in moist air.
 W
WAsbestos is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere by abrasion and other processes. Inhalation of asbestos fibres can lead to various serious lung conditions, including mesothelioma, asbestosis, and lung cancer, so it is now notorious as a health and safety hazard.
 W
WAzoxymethane (AOM) is a carcinogenic and neurotoxic chemical compound used in biological research. It is the oxide of azomethane and is particularly effective for the induction of a colon carcinoma.
 W
WBenzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
 W
WA benzopyrene is an organic compound with the formula C20H12. Structurally speaking, the colorless isomers of benzopyrene are pentacyclic hydrocarbons and are fusion products of pyrene and a phenylene group. Two isomeric species of benzopyrene are benzo[a]pyrene and the less common benzo[e]pyrene. They belong to the chemical class of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
 W
WThe bromate anion, BrO−3, is a bromine-based oxoanion. A bromate is a chemical compound that contains this ion. Examples of bromates include sodium bromate,, and potassium bromate,.
 W
WCalcium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3(AsO4)2. A colourless salt, it was originally used as a pesticide and as a germicide. It is highly soluble in water, as compared with lead arsenate, which makes it more toxic. The minerals rauenthalite Ca3(AsO4)2·10H2O and phaunouxite Ca3(AsO4)2·11H2O are hydrates of calcium arsenate.
 W
WCantonese Salted Fish is a traditional Chinese food originating from Guangdong province. It is a fish preserved or cured with salt, and was a staple food in Guangdong. It historically earned the nickname of the "poor man's food", as its extreme saltiness is useful in adding variety to the simpler rice-based dinners. Cantonese salted fish was revealed to be on the list of Group 1 known carcinogens, but was suspected and studied for its links to cancer as early as the 1960s due to the high incidence of nasopharyngeal cancer, an extremely rare type of nose and head cancer now understood to be linked to a high consumption of this dish.
 W
WChlordecone, better known under the brand name Kepone in the United States, is an organochlorine compound and a colourless solid. This compound is an obsolete insecticide related to Mirex and DDT. Its use was so disastrous that it is now prohibited in the western world, but only after many thousands of tonnes had been produced. Chlordecone is a known persistent organic pollutant (POP) that was banned globally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2009.
 W
W4-Chloro-o-toluidine (4-COT, 4-chloro-2-methylaniline) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3Cl(NH2). It is a colorless solid. The compound is produced as an intermediate to the pesticide chlordimeform and a precursor to some azo dyes. Production has declined after it was shown to be highly carcinogenic.
 W
WChromyl chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal complexes.
 W
WDiepoxybutane is a chemical compound with two epoxide functional groups. It is used as a chemical intermediate, as a curing agent for polymers, as a cross-linking agent for textiles, and as a preservative.
 W
W7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) is an immunosuppressor and a powerful organ-specific laboratory carcinogen. DMBA is widely used in many research laboratories studying cancer. DMBA serves as a tumor initiator. Tumor promotion can be induced with treatments of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) in some models of two-stage carcinogenesis. This allows for a greatly accelerated rate of tumor growth, making many cancer studies possible.
 W
WWhen the parade season ended in 2014, the New Orleans city government spent $1.5 million to pick up about 1,500 tons of Mardi Gras-induced waste, consisting mostly of beads. This is a recurring problem every year for the city. In addition, the city must also deal with the environmental repercussions endured after Mardi Gras. Because they are not biodegradable and contain high amounts of heavy metals, Mardi Gras beads put the local environment and health of southern Louisianians at risk.
 W
WEthionine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid structurally related to methionine, with an ethyl group in place of the methyl group.
 W
WFurylfuramide is a synthetic nitrofuran derivative which was widely used as a food preservative in Japan since at least 1965, but withdrawn from the market in 1974 when it was observed to be mutagenic to bacteria in vitro and thus suspected of carcinogenicity. This was confirmed later when animal testing found it to cause benign and malignant tumors in the mammary glands, stomachs, esophagi, and lungs of rodents of both sexes, although insufficient evidence exists in human exposure.
 W
WGW501516 is a PPARδ receptor agonist that was invented in a collaboration between Ligand Pharmaceuticals and GlaxoSmithKline in the 1990s. It entered into clinical development as a drug candidate for metabolic and cardiovascular diseases, but was abandoned in 2007 because animal testing showed that the drug caused cancer to develop rapidly in several organs.
 W
WHeterocyclic amines, also sometimes referred to as HCAs, are chemical compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring, which by definition has atoms of at least two different elements, as well as at least one amine (nitrogen-containing) group. Typically it is a nitrogen atom of an amine group that also makes the ring heterocyclic, though compounds exist in which this is not the case. The biological functions of heterocyclic amines vary, including vitamins and carcinogens. Carcinogenic heterocyclic amines are created by high temperature cooking of meat and smoking of plant matter like tobacco. Some well known heterocyclic amines are niacin, nicotine, and the nucleobases that encode genetic information in DNA.
 W
WHeterocyclic amines are a group of chemical compounds, many of which can be formed during cooking. They are found in meats that are cooked to the "well done" stage, in pan drippings and in meat surfaces that show a brown or black crust. Epidemiological studies show associations between intakes of heterocyclic amines and cancers of the colon, rectum, breast, prostate, pancreas, lung, stomach/esophagus and animal feeding experiments support a causal relationship. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service labeled several heterocyclic amines as likely carcinogens in its 13th Report on Carcinogens. Changes in cooking techniques reduce the level of heterocyclic amines.
 W
WHuman papillomavirus infection is an infection caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), a DNA virus from the Papillomaviridae family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. However, in some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV; two strains, HPV16 and HPV18, account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis.
 W
WHydroxyacetylaminofluorene is a derivative of 2-acetylaminofluorene used as a biochemical tool in the study of carcinogenesis.
 W
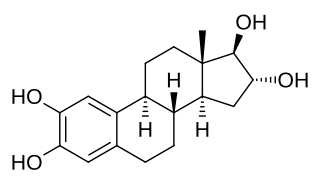
W2-Hydroxyestriol, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,16α,17β-tetrol, is an endogenous catechol estrogen and metabolite of estriol. It is a suspected carcinogen of carcinogenicity category 2.
 W
WMethylcholanthrene is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures. Methylcholanthrene is also known as 3-methylcholanthrene, 20-methylcholanthrene or the IUPAC name 3-methyl-1,2-dyhydrobenzo[j]aceanthrylene. The short notation often used is 3-MC or MCA. This compound forms pale yellow solid crystals when crystallized from benzene and ether. It has a melting point around 180 °C and its boiling point is around 280 °C at a pressure of 80 mmHg. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz[a]anthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.
 W
W4-Methylimidazole is a heterocyclic organic chemical compound with molecular formula H3C–C3H3N2 or C4H6N2. It is formally derived from imidazole through replacement of the hydrogen in position 4 by a methyl group. It is a slightly yellowish solid.
 W
WMezerein is a toxic diterpene ester found in the sap of Daphne mezereum and related plants. Plants of the genera Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae possess a wide variety of different phorbol esters, which share the capacity of mimicking diacylglycerol (DAG) and thus activating different isoforms of protein kinase C. Mezerein was first isolated in 1975. It has antileukemic properties in mice, but it is also defined as a weak promoter of skin cancers in the same species. All parts of the plants contain an acrid and irritant sap that contains mezerein, thought to be the principal poison. The sap is especially prevalent in the bark and berries.
 W
W3-Nitrobenzanthrone (3-nitro-7H-benz[de]anthracen-7-one) is a chemical compound emitted in diesel exhaust; it is a potent carcinogen. It produced the highest score ever reported in the Ames test, a standard measure of the cancer-causing potential of toxic chemicals, far greater than the previous known strongest.
 W
W4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxide is a quinoline derivative and a tumorigenic compound used in the assessment of the efficacy of diets, drugs, and procedures in the prevention and treatment of cancer in animal models. It induces DNA lesions usually corrected by nucleotide excision repair.
 W
WNitrosamines (or more formally N-Nitrosamines) are organic compounds of the chemical structure R2N−N=O, where R is usually an alkyl group. They feature a nitroso group (NO+) bonded to a deprotonated amine. Most nitrosamines are carcinogenic in animals. A recent systematic review supports a "positive association between nitrite and nitrosamine intake and gastric cancer, between meat and processed meat intake and gastric cancer and oesophageal cancer, and between preserved fish, vegetable and smoked food intake and gastric cancer, but is not conclusive".
 W
WPhorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu) is a phorbol ester which is one of the constituents of croton oil. As an activator of protein kinase C, it is a weak tumor promoter compared to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate.
 W
WPlutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous.
 W
WA polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a hydrocarbon—a chemical compound containing only carbon and hydrogen—that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The group is a major subset of the aromatic hydrocarbons. The simplest of such chemicals are naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon are also used for this concept.
 W
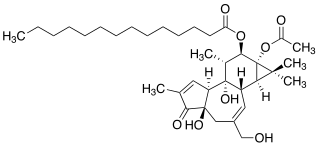
WPtaquiloside is a norsesquiterpene glucoside produced by bracken ferns during metabolism. It is identified to be the main carcinogen of the ferns and to be responsible for their biological effects, such as haemorrhagic disease and bright blindness in livestock and oesophageal, gastric cancer in humans. Ptaquiloside has unstable chemical structure and acts as a DNA alkylating agent under physiological conditions. It was first isolated and characterized by Yamada and co-workers in 1983.
 W
WRadon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains through which thorium and uranium slowly decay into lead and various other short-lived radioactive elements. Radon itself is the immediate decay product of radium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of only 3.8 days, making it one of the rarest elements. Since thorium and uranium are two of the most common radioactive elements on Earth, while also having three isotopes with half-lives on the order of several billion years, radon will be present on Earth long into the future despite its short half-life. The decay of radon produces many other short-lived nuclides, known as radon daughters, ending at stable isotopes of lead.
 W
WSmokeless tobacco is a tobacco product that is used by means other than smoking. Their use involves chewing, sniffing, or placing the product between gum and the cheek or lip. Smokeless tobacco products are produced in various forms, such as chewing tobacco, snuff, snus, and dissolvable tobacco products. Smokeless tobacco products typically contain over 3000 constituents. All smokeless tobacco products contain nicotine and are therefore highly addictive. Quitting smokeless tobacco use is as challenging as smoking cessation.
 W
W12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also commonly known as tetradecanoylphorbol acetate, tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), is a diester of phorbol and a potent tumor promoter often employed in biomedical research to activate the signal transduction enzyme protein kinase C (PKC). The effects of TPA on PKC result from its similarity to one of the natural activators of classic PKC isoforms, diacylglycerol. TPA is a small molecule drug.
 W
WThorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft, malleable, and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided.
 W
WThe chemical compound trichloroethylene is a halocarbon commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is a clear, colourless non-flammable liquid with a chloroform-like sweet smell. It should not be confused with the similar 1,1,1-trichloroethane, which is commonly known as chlorothene.