 W
WSocial constructionism is a theory of knowledge in sociology and communication theory that examines the development of jointly-constructed understandings of the world that form the basis for shared assumptions about reality. The theory centers on the notion that meanings are developed in coordination with others rather than separately within each individual. It has often been characterised as neo-Marxian or also as a neo-Kantian theory, in that social constructionism replaces the transcendental subject with a concept of society that is at the same time descriptive and normative.
 W
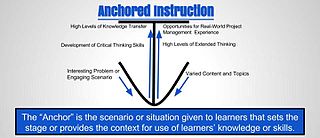
WAnchored Instruction is a technology centered learning approach, which falls under the social constructionism paradigm. It is a form of situated learning that emphasizes problem-solving within an integrated learning context, which can be examined from multiple perspectives. "In other words, the learning is contextualized to provide students with realistic roles that serve to enhance the learning process",. During teaching, activities are designed or tied around an "anchor", such as an adventure or story, with a problem at the end, that needs to be resolved. The connection made between the content and the authentic context is referred to as "anchoring". These models typically embed all the information needed for the problem to be solved, such data and hints. Anchored instruction is akin to problem-based learning (P.B.L.) with the exception of its open-endedness.
 W
WAttention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) controversies include concerns about causes, perceived overdiagnosis, and methods of treatment, especially with the use of stimulant medications in children. While currently the disorder ADHD is widely recognized and accepted, the treatments for the disorder are not. These controversies have surrounded the subject since at least the 1970s. Problems with the treatment of the disorder start with diagnosis, as differences in male and female developments leads to both over and under diagnoses. This has set up controversies in treatment as well. Treatment of ADHD has come into scrutiny due to misuse of stimulants, conflicts of interest and the stigma surrounding mental health diagnoses.
 W
WPeter Ludwig Berger was an Austrian-born American sociologist and Protestant theologian. Berger became known for his work in the sociology of knowledge, the sociology of religion, study of modernization, and theoretical contributions to sociological theory.
 W
WA unit of real estate or immovable property is limited by a legal boundary. The boundary may appear as a discontinuation in the terrain: a ditch, a bank, a hedge, a wall, or similar, but essentially, a legal boundary is a conceptual entity, a social construct, adjunct to the likewise abstract entity of property rights.
 W
WCornelius Castoriadis was a Greek-French philosopher, social critic, economist, psychoanalyst, author of The Imaginary Institution of Society, and co-founder of the Socialisme ou Barbarie group.
 W
WMany causes of autism have been proposed, but understanding of the theory of causation of autism and the other autism spectrum disorders (ASD) is incomplete. ASD is a complex developmental condition marked by persistent challenges to social interaction, speech and nonverbal communication, and restricted/repetitive behaviors. ASD phenotypes vary significantly.
 W
WRaewyn Connell, usually cited as R. W. Connell, is an Australian sociologist. She gained prominence as an intellectual of the Australian New Left. She was appointed University Professor at the University of Sydney in 2004, and retired from her University Chair on July, 2014. She has been Professor Emerita at the University of Sydney since her retirement. She is known for the concept of hegemonic masculinity and her book, Southern Theory.
 W
WConstructivism is a view in the philosophy of science that maintains that scientific knowledge is constructed by the scientific community, which seeks to measure and construct models of the natural world. According to the constructivist, natural science, therefore, consists of mental constructs that aim to explain sensory experience and measurements.
 W
WCourtship is the period of development towards a sexual relationship wherein a couple get to know each other and decide whether there will be an engagement, followed by a marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private matter between two people or may be a public affair, or a formal arrangement with family approval. Traditionally, in the case of a formal engagement, it is the role of a male to actively "court" or "woo" a female, thus encouraging her to understand him and her receptiveness to a marriage proposal.
 W
WCulture is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.
 W
WDisease mongering is a pejorative term for the practice of widening the diagnostic boundaries of illnesses and aggressively promoting their public awareness in order to expand the markets for treatment.
 W
WAn expert is somebody who has a broad and deep competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized as a reliable source of technique or skill whose faculty for judging or deciding rightly, justly, or wisely is accorded authority and status by peers or the public in a specific well-distinguished domain. An expert, more generally, is a person with extensive knowledge or ability based on research, experience, or occupation and in a particular area of study. Experts are called in for advice on their respective subject, but they do not always agree on the particulars of a field of study. An expert can be believed, by virtue of credentials, training, education, profession, publication or experience, to have special knowledge of a subject beyond that of the average person, sufficient that others may officially rely upon the individual's opinion on that topic. Historically, an expert was referred to as a sage. The individual was usually a profound thinker distinguished for wisdom and sound judgment.
 W
WThe feminization of the workplace is the feminization, or the shift in gender roles and sex roles and the incorporation of women into a group or a profession once dominated by men, as it relates to the workplace. It is a set of social theories seeking to explain occupational gender-related discrepancies.
 W
WPaul-Michel Foucault was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic.
 W
WGender polarization is a concept in sociology by American psychologist Sandra Bem which states that societies tend to define femininity and masculinity as polar opposite genders, such that male-acceptable behaviors and attitudes are not seen as appropriate for women, and vice versa. The theory is an extension of the sex and gender distinction in sociology in which sex refers to the biological differences between men and women, while gender refers to the cultural differences between them, such that gender describes the "socially constructed roles, behaviours, activities, and attributes that a given society considers appropriate for men and women". According to Bem, gender polarization begins when natural sex differences are exaggerated in culture; for example, women have less hair than men, and men have more muscles than women, but these physical differences are exaggerated culturally when women remove hair from their faces and legs and armpits, and when men engage in body building exercises to emphasize their muscle mass. She explained that gender polarization goes further, when cultures construct "differences from scratch to make the sexes even more different from one another than they would otherwise be", perhaps by dictating specific hair styles for men and women, which are noticeably distinct, or separate clothing styles for men and women. When genders become polarized, according to the theory, there is no overlap, no shared behaviors or attitudes between men and women; rather, they are distinctly opposite. She argued that these distinctions become so "all-encompassing" that they "pervade virtually every aspect of human existence", not just hairstyles and clothing but how men and women express emotion and experience sexual desire. She argued that male-female differences are "superimposed on so many aspects of the social world that a cultural connection is thereby forged between sex and virtually every other aspect of human experience".
 W
WSally Haslanger is an American philosopher and professor. She is the Ford Professor of Philosophy in the Department of Linguistics and Philosophy at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She held the 2015 Spinoza Chair of Philosophy at the University of Amsterdam.
 W
WHow to Lose Your Virginity is an American documentary film directed by Therese Shechter and distributed by Women Make Movies. The film examines how the concept of virginity shapes the sexual lives of young women and men through the intersecting forces of history, politics, religion and popular culture. It premiered at DOC NYC, a New York City documentary festival, on November 17, 2013.
 W
WNoel Ignatiev was an American author and historian. He was best known for his theories on race and for his call to abolish "whiteness". Ignatiev was the co-founder of the New Abolitionist Society and co-editor of the journal Race Traitor, which promoted the idea that "treason to whiteness is loyalty to humanity". He also wrote a book on antebellum Northern xenophobia against Irish immigrants, How the Irish Became White.
 W
WImagined Communities: Reflections on the Origin and Spread of Nationalism is a book by Benedict Anderson. It introduces a popular concept in political sciences and sociology, that of imagined communities named after it. It was first published in 1983, and reissued with additional chapters in 1991 and a further revised version in 2006.
 W
WIntersectionality is an analytical framework for understanding how aspects of a person's social and political identities combine to create different modes of discrimination and privilege. The term was conceptualized and coined by Kimberlé Williams Crenshaw in a paper in 1989. Intersectionality identifies multiple factors of advantage and disadvantage. Examples of these factors include gender, caste, sex, race, class, sexuality, religion, disability, physical appearance, and height. These intersecting and overlapping social identities may be both empowering and oppressing. For example, a black woman might face discrimination from a business that is not distinctly due to her race nor distinctly due to her gender, but due to a combination of the two factors.
 W
WInvented traditions are cultural practices that are presented or perceived as traditional, arising from the people starting in the distant past, but which in fact are relatively recent and often even consciously invented by identifiable historical actors. The concept was highlighted in the 1983 book The Invention of Tradition, edited by Eric Hobsbawm and Terence Ranger. Hobsbawm's introduction argues that many "traditions" which "appear or claim to be old are often quite recent in origin and sometimes invented." This "invention" is distinguished from "starting" or "initiating" a tradition which does not then claim to be old. The phenomenon is particularly clear in the modern development of the nation and of nationalism, creating a national identity promoting national unity, and legitimising certain institutions or cultural practices.
 W
WJonathan Ned Katz is an American historian of human sexuality who has focused on same-sex attraction and changes in the social organization of sexuality over time. His works focus on the idea, rooted in social constructionism, that the categories with which society describes and defines human sexuality are historically and culturally specific, along with the social organization of sexual activity, desire, relationships, and sexual identities.
 W
WAnnette Kolodny was an American feminist literary critic and activist, held the position of College of Humanities Professor Emerita of American Literature and Culture at the University of Arizona in Tucson. Her major scholarly writings examined the experiences of women on the American frontiers and the projection of female imagery onto the American landscape. Her other writings examined some aspects of feminism after the 1960s; the revision of dominant themes in American studies; and the problems faced by women and minorities in the American academy.
 W
WBruno Latour is a French philosopher, anthropologist and sociologist. He is especially known for his work in the field of science and technology studies (STS). After teaching at the École des Mines de Paris from 1982 to 2006, he became Professor at Sciences Po Paris (2006–2017), where he was the scientific director of the Sciences Po Medialab. He retired from several university activities in 2017. He was also a Centennial Professor at the London School of Economics.
 W
WMasculinity is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles associated with men and boys. Although sociologists think of masculinity as socially constructed, there is also widespread recognition that some behaviors considered masculine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent masculinity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is distinct from the definition of the biological male sex, as both males and females can exhibit masculine traits.
 W
WMary Susan McIntosh was a British sociologist, feminist, political activist and campaigner for lesbian and gay rights in the UK.
 W
WSheila McNamee is an American academic known for her work in human communication and social constructionism theory and practice. She is a Professor of Communication at the University of New Hampshire and founding member, Vice President and board member of the Taos Institute. She has authored numerous, books, chapters, and journal articles. Her work focuses on appreciative dialogic transformation within a variety of social and institutional contexts including psychotherapy, organizations, education, healthcare, and local communities. She engages constructionist practices in a variety of contexts to bring communities of participants with diametrically opposing viewpoints together to create livable futures.
 W
WMental health is "a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community", according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others. From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health".Some early signs related health problems are sleep irritation, lack of energy and suicidal thinking.
 W
WNabawiyya Mohamed Musa Badawia(Arabic: نبوية موسى محمد بدوية; December 17, 1886 – April 30, 1951) was an Egyptian Nationalist and Feminist and is recognized as one of the founding feminists of the 20th century in Egypt. Her career and life is often discussed alongside figures such as Huda Sharawi and Malak Hifni Nasif, as all three of these women gave lectures and put on other events to further education, promote health, and reduce sexual exploitation for women, among other things. She grew up in Alexandria and was part of the Egyptian middle-class. Along with being an avid educator, she was a prolific writer. She wrote and published articles such as "al-Ayat al–badyyina fi tarbiya al-banat" in 1902, "al-Mar’a wa-l-‘amal" in 1920 as well as editing a woman's page for al-Balagh al-usbui. She is known as the first Egyptian woman to obtain a baccalaureate secondary degree, and her writings are considered important historical documents reflecting the periods of Egyptian history her life spanned, especially Egyptian life under rule of the British protectorate.
 W
WThe National Emergency Concerning the Southern Border of the United States was declared on February 15, 2019, by President of the United States Donald Trump. Citing the National Emergencies Act, it ordered the diversion of billions of dollars of funds that had been appropriated to the U.S. Department of Defense for military construction. Trump declared the emergency after he signed, but derided, a bipartisan funding bill containing border security funding without funding for the border wall that Trump demanded.
 W
WIn sociology, nomos is a habit or custom of social and political behavior that is socially constructed and historically specific. It refers not only to explicit laws but to all of the normal rules and forms people take for granted in their daily activities. Because it represents order that is validated by and binding on those who fall under its jurisdiction, it is a social construct with ethical dimensions.
 W
WOld age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms include old people, the elderly, OAPs, seniors, senior citizens, older adults, and the elders.
 W
WTrevor J. Pinch, is a British sociologist, part-time musician and former chair of the Science and Technology Studies department at Cornell University. In 2018, he won the J.D. Bernal Prize from the Society for Social Studies of Science for "distinguished contributions to Science and Technology Studies over the course of [a] career".
 W
WSocial constructionism is a theory of knowledge in sociology and communication theory that examines the development of jointly-constructed understandings of the world that form the basis for shared assumptions about reality. The theory centers on the notion that meanings are developed in coordination with others rather than separately within each individual. It has often been characterised as neo-Marxian or also as a neo-Kantian theory, in that social constructionism replaces the transcendental subject with a concept of society that is at the same time descriptive and normative.
 W
WSocial reality is distinct from biological reality or individual cognitive reality, representing as it does a phenomenological level created through social interaction and thereby transcending individual motives and actions. The product of human dialogue, social reality may be considered as consisting of the accepted social tenets of a community, involving thereby relatively stable laws and social representations. Radical constructivism would cautiously describe social reality as the product of uniformities among observers.
 W
WAlfred Schutz was an Austrian philosopher and social phenomenologist whose work bridged sociological and phenomenological traditions. Schutz is gradually being recognized as one of the 20th century's leading philosophers of social science. He related Edmund Husserl's work to the social sciences, using it to develop the philosophical foundations of Max Weber's sociology, in his major work Phenomenology of the Social World.
 W
WThe sociology of scientific knowledge (SSK) is the study of science as a social activity, especially dealing with "the social conditions and effects of science, and with the social structures and processes of scientific activity." The sociology of scientific ignorance (SSI) is complementary to the sociology of scientific knowledge. For comparison, the sociology of knowledge studies the impact of human knowledge and the prevailing ideas on societies and relations between knowledge and the social context within which it arises.
 W
WThe social model of disability identifies systemic barriers, derogatory attitudes, and social exclusion, which make it difficult or impossible for individuals with impairments to attain their valued functionings. The social model of disability diverges from the dominant medical model of disability, which is a functional analysis of the body as a machine to be fixed in order to conform with normative values. While physical, sensory, intellectual, or psychological variations may cause individual functional limitation or impairments, these do not necessarily have to lead to disability unless society fails to take account of and include people regardless of their individual differences.
 W
WIn sociology, social psychology studies the relationship between the individual and society. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of psychology, sociological social psychology places relatively more emphasis on the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Researchers broadly focus on higher levels of analysis, directing attention mainly to groups and the arrangement of relationships among people. This subfield of sociology is broadly recognized as having three major perspectives: Symbolic interactionism, social structure and personality, and structural social psychology.
 W
WAccording to Robin A. Williams and David Edge (1996), "Central to social shaping of technology (SST) is the concept that there are choices inherent in both the design of individual artifacts and systems, and in the direction or trajectory of innovation programs."
 W
WSociology of gender is a prominent subfield of sociology. Social interaction directly correlated with sociology regarding social structure. One of the most important social structures is status. This is determined based on position that an individual possesses which effects how they will be treated by society. One of the most important statuses an individual claims is gender. Public discourse and the academic literature generally use the term gender for the perceived or projected (self-identified) masculinity or femininity of a person.
 W
WSomatocentrism is a cultural value system in which biological determinism is the basis for social organization. The phenotypical variation of an individual in this system determines the individual's social identity and social relations, although it does not necessarily denote their social position.
 W
WSocial construction of technology (SCOT) is a theory within the field of science and technology studies. Advocates of SCOT—that is, social constructivists—argue that technology does not determine human action, but that rather, human action shapes technology. They also argue that the ways a technology is used cannot be understood without understanding how that technology is embedded in its social context. SCOT is a response to technological determinism and is sometimes known as technological constructivism.
 W
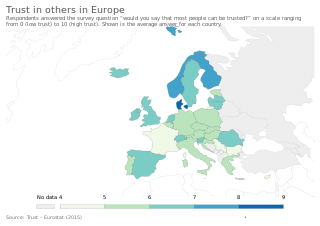
WTrust exists in interpersonal relationships. Humans have a natural disposition to trust and to judge trustworthiness. This can be traced to the neurobiological structure and activity of a human brain. Some studies indicate that trust can be altered e.g. by the application of oxytocin.
 W
WTsvia Walden is an Israeli psycholinguist. She is a professor at the Ben Gurion University of the Negev and previously a senior lecturer at Beit Berl Academic College and Ben-Gurion University. Walden specializes in social constructionism through language, language and gender, language acquisition, literacy, digital literacy and research of Jewish texts. She is the creator and presenter of a filmed lecture series about language instruction and language acquisition.
 W
WWildness, in its literal sense, is the quality of being wild or untamed. Beyond this, it has been defined as a quality produced in nature, as that which emerges from a forest, and as a level of achievement in nature. More recently, it has been defined as "a quality of interactive processing between organism and nature where the realities of base natures are met, allowing the construction of durable systems". A wilderness is a place where wildness occurs.
 W
WStephen William Woolgar is a British sociologist. He has worked closely with Bruno Latour, with whom he wrote Laboratory Life: The Construction of Scientific Facts (1979).
 W
WWorld religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the five—and in some cases more—largest and most internationally widespread religious movements. Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Hinduism, and Buddhism are always included in the list, being known as the "Big Five". Some scholars also include other religions, such as Sikhism, Zoroastrianism, or the Baháʼí Faith, in the category. These are often juxtaposed against other categories, such as indigenous religions and new religious movements, which are also used by scholars in this field of research.
 W
WYouth is the time of life when one is young, and often means the time between childhood and adulthood (maturity). It is also defined as "the appearance, freshness, vigor, spirit, etc., characteristic of one who is young". Its definitions of a specific age range varies, as youth is not defined chronologically as a stage that can be tied to specific age ranges; nor can its end point be linked to specific activities, such as taking unpaid work or having sexual relations.