 W
WAdventive plants or adventitious plants are plants that have established themselves in a place that does not correspond to their area of origin due to anthropogenic influence and, therefore, are all wild species that have only been established with the help of humans, in contrast to the native species.
 W
WAfghanistanism is a term, first recorded in the United States, for the practice of concentrating on problems in distant parts of the world while ignoring controversial local issues. In other contexts, the term has referred to "hopelessly arcane and irrelevant scholarship", "fascination with exotic, faraway lands", or "Railing and shaking your fist at an unseen foe who is quite unaware of your existence, much less your fury".
 W
WBiogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms.
 W
WBiological pollution is the impact of humanity's actions on the quality of aquatic and terrestrial environment. Specifically, biological pollution is the introduction of non-indigenous and invasive species. When the biological pollution is introduced to an aquatic environment, it contributes to water pollution.
 W
WThe biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Biomass can refer to species biomass, which is the mass of one or more species, or to community biomass, which is the mass of all species in the community. It can include microorganisms, plants or animals. The mass can be expressed as the average mass per unit area, or as the total mass in the community.
 W
WBioremediation is a process used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil and subsurface material, by altering environmental conditions to stimulate growth of microorganisms and degrade the target pollutants. Cases where bioremediation is commonly seen is oil spills, soils contaminated with acidic mining drainage, underground pipe leaks, and crime scene cleanups. These toxic compounds are metabolized by enzymes present in microorganisms. Most bioremediation processes involve oxidation-reduction reactions where either an electron acceptor is added to stimulate oxidation of a reduced pollutant or an electron donor is added to reduce oxidized pollutants. Bioremediation is used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic activities, such as industrialization and agricultural processes. In many cases, bioremediation is less expensive and more sustainable than other remediation alternatives. Other remediation techniques include, thermal desorption, vitrification, air stripping, bioleaching, rhizofiltration, and soil washing. Biological treatment, bioremediation, is a similar approach used to treat wastes including wastewater, industrial waste and solid waste. The end goal of bioremediation is to remove or reduce harmful compounds to improve soil and water quality.
 W
WA carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent. Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbon dioxide and methane, can be emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, land clearance and the production and consumption of food, manufactured goods, materials, wood, roads, buildings, transportation and other services. The term was popularized by a $250 million advertising campaign by the oil and gas company BP in an attempt to move public attention away from restricting the activities of fossil fuel companies and onto individual responsibility for solving climate change.
 W
WClimate restoration is the climate change goal and associated actions to restore CO2 to levels humans have survived long-term, below 300 ppm. This would restore the Earth system generally to a safe state, for the well-being of future generations of humanity and nature. Actions include carbon dioxide removal from the Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, which, in combination with emissions reductions, would reduce the level of CO2 in the atmosphere and thereby reduce the global warming produced by the greenhouse effect of an excess of CO2 over its pre-industrial level. Actions also include restoring pre-industrial atmospheric methane levels by accelerating natural methane oxidation.
 W
WIn scientific ecology, climax community or climatic climax community is a historic term for a community of plants, animals, and fungi which, through the process of ecological succession in the development of vegetation in an area over time, have reached a steady state. This equilibrium was thought to occur because the climax community is composed of species best adapted to average conditions in that area. The term is sometimes also applied in soil development. Nevertheless, it has been found that a "steady state" is more apparent than real, particularly across long timescales. Notwithstanding, it remains a useful concept.
 W
WClimax species, also called late seral, late-successional, K-selected or equilibrium species, are plant species that can germinate and grow with limited resources, like they need heat exposure or low water availability. They are the species within forest succession that are more adapted to stable and predictable environments, and will remain essentially unchanged in terms of species composition for as long as a site remains undisturbed.
 W
WIn biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well as gene-culture coevolution.
 W
WIn biology, a colony is composed of two or more conspecific individuals living in close association with, or connected to, one another. This association is usually for mutual benefit such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. It is a cluster of identical cells (clones) on the surface of a solid medium, usually derived from a single parent cell, as in bacterial colony. In contrast, solitary organisms are ones in which all individuals live independently and have all of the functions needed to survive and reproduce.
 W
WThe conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use.
 W
WA constructed wetland (CW) is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a mitigation step for natural areas lost to land development. Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that use natural functions vegetation, soil, and organisms to provide secondary treatment to wastewater. The design of the constructed wetland has to be adjusted according to the type of wastewater to be treated. Constructed wetlands have been used in both centralized and decentralized wastewater systems. Primary treatment is recommended when there is a large amount of suspended solids or soluble organic matter.
 W
WDesakota is a term used in urban geography used to describe areas in the extended surroundings of large cities, in which urban and agricultural forms of land use and settlement coexist and are intensively intermingled.
 W
WIn ecology, a disturbance is a temporary change in environmental conditions that causes a pronounced change in an ecosystem. Disturbances often act quickly and with great effect, to alter the physical structure or arrangement of biotic and abiotic elements. A disturbance can also occur over a long period of time and can impact the biodiversity within an ecosystem.
 W
WDPSIR is a causal framework for describing the interactions between society and the environment: Human impact on the environment and vice versa because of the interdependence of the components.
 W
WEcological engineering uses ecology and engineering to predict, design, construct or restore, and manage ecosystems that integrate "human society with its natural environment for the benefit of both".
 W
WThe ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use for their consumption to the biologically productive area available within a region or the world. In short, it is a measure of human impact on the environment.
 W
WEcological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades, or even millions of years after a mass extinction.
 W
WEcological thinning is a silvicultural technique used in forest management that involves cutting trees to improve functions of a forest other than timber production.
 W
WAn ecosystem model is an abstract, usually mathematical, representation of an ecological system, which is studied to better understand the real system.
 W
WIn ecology, edge effects are changes in population or community structures that occur at the boundary of two or more habitats. Areas with small habitat fragments exhibit especially pronounced edge effects that may extend throughout the range. As the edge effects increase, the boundary habitat allows for greater biodiversity.
 W
WEducation for sustainable development (ESD) is defined as education that encourages changes in knowledge, skills, values and attitudes to enable a more sustainable and just society for all. ESD aims to empower and equip current and future generations to meet their needs using a balanced and integrated approach to the economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development. ESD is the term most used internationally and by the United Nations.
 W
WEnvironmental engineering is a professional engineering discipline that encompasses broad scientific topics like chemistry, biology, ecology, geology, hydraulics, hydrology, microbiology, and mathematics to create solutions that will protect and also improve the health of living organisms and improve the quality of the environment. Environmental engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering and chemical engineering.
 W
WEscaped plants are cultivated plants, usually garden plants, that are not originally native to an area, and due to their dispersal strategies, have escaped from cultivation and have settled in the wild and bred there, whether intentionally or unintentionally. Escaped plants are purposefully introduced plants that have naturalized in the wild and can develop into invasive plants, the settlement of which is to be assessed as problematic. Other commonly used terms include escaped garden plant, garden escapee, escaped ornamental or garden refugee.
 W
WFire ecology is a scientific discipline concerned with natural processes involving fire in an ecosystem and the ecological effects, the interactions between fire and the abiotic and biotic components of an ecosystem, and the role as an ecosystem process. Many ecosystems, particularly prairie, savanna, chaparral and coniferous forests, have evolved with fire as an essential contributor to habitat vitality and renewal. Many plant species in fire-affected environments require fire to germinate, establish, or to reproduce. Wildfire suppression not only eliminates these species, but also the animals that depend upon them.
 W
WA flood-meadow is an area of grassland or pasture beside a river, subject to seasonal flooding. Flood-meadows are distinct from water-meadows in that the latter are artificially created and maintained, with flooding controlled on a seasonal and even daily basis.
 W
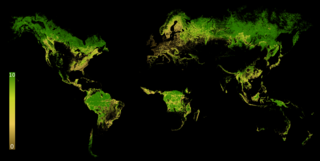
WThe Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe, finds that ~17.4 million km2 of forest has high landscape-level integrity, compared to ~14.6 million with medium integrity (6-9.6) and ~12.2 million km2 with low integrity (0-6).
 W
WA fuel ladder or ladder fuel is a firefighting term for live or dead vegetation that allows a fire to climb up from the landscape or forest floor into the tree canopy. Common ladder fuels include tall grasses, shrubs, and tree branches, both living and dead. The removal of fuel ladders is part of defensible space 'firescaping' practices.
 W
WHemerochory is the distribution of cultivated plants or their seeds and cuttings, consciously or unconsciously, by humans into an area that they could not colonize through their natural mechanisms of spread, but are able to maintain themselves without specific human help in their new habitat.
 W
WAn invasive species is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and negatively alters its new environment. Although their spread can have beneficial aspects, invasive species adversely affect the invaded habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. Sometimes the term is used for native species that become invasive within certain ecosystems due to human alterations of the environment. An example of a native invasive species is the purple sea urchin which has decimated natural kelp forests along the northern California coast due to the historic overhunting of its natural predator, the California sea otter. In the 21st century, invasive species have become a serious economic, social, and environmental threat.
 W
WBiological organisation is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a reductionistic approach. The traditional hierarchy, as detailed below, extends from atoms to biospheres. The higher levels of this scheme are often referred to as an ecological organisation concept, or as the field, hierarchical ecology.
 W
WLimbing or delimbing is the process of removing branches from a standing or fallen tree trunk.
 W
WMinimum viable population (MVP) is a lower bound on the population of a species, such that it can survive in the wild. This term is commonly used in the fields of biology, ecology, and conservation biology. MVP refers to the smallest possible size at which a biological population can exist without facing extinction from natural disasters or demographic, environmental, or genetic stochasticity. The term "population" is defined as a group of interbreeding individuals in similar geographic area that undergo negligible gene flow with other groups of the species. Typically, MVP is used to refer to a wild population, but can also be used for ex-situ conservation.
 W
WA mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types of mires share the common characteristic of being saturated with water at least seasonally with actively forming peat, while having their own ecosystem. Like coral reefs, mires are unusual landforms in that they derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning.
 W
WMycoremediation is a form of bioremediation in which fungi-based remediation methods are used to decontaminate the environment. Fungi have been proven to be a cheap, effective and environmentally sound way for removing a wide array of contaminants from damaged environments or wastewater. These contaminants include heavy metals, organic pollutants, textile dyes, leather tanning chemicals and wastewater, petroleum fuels, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, pharmaceuticals and personal care products, pesticides and herbicides in land, fresh water, and marine environments. The byproducts of the remediation can be valuable materials themselves, such as enzymes, edible or medicinal mushrooms, making the remediation process even more profitable. Some fungi are useful in the biodegradation of contaminants in extremely cold or radioactive environments where traditional remediation methods prove too costly or are unusable due to the extreme conditions. Mycoremediation can even be used for fire management with the encapsulation method. This process consists of using fungal spores coated with agarose in a pellet form. This pellet is introduced to a substrate in the burnt forest, breaking down the toxins in the environment and stimulating growth.
 W
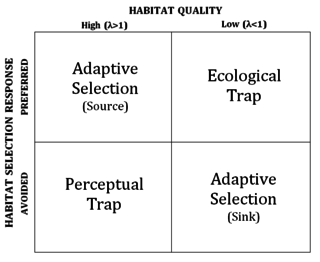
WA perceptual trap is an ecological scenario in which environmental change, typically anthropogenic, leads an organism to avoid an otherwise high-quality habitat. The concept is related to that of an ecological trap, in which environmental change causes preference towards a low-quality habitat.
 W
WPhytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air, and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless". The term is an amalgam of the Greek phyto (plant) and Latin remedium. Although attractive for its cost, phytoremediation has not been demonstrated to redress any significant environmental challenge to the extent that contaminated space has been reclaimed.
 W
WLitterfall, plant litter, leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, or duff, is dead plant material that have fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituent nutrients are added to the top layer of soil, commonly known as the litter layer or O horizon. Litter is an important factor in ecosystem dynamics, as it is indicative of ecological productivity and may be useful in predicting regional nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
 W
WThe politics of climate change results from different perspectives on how to respond to the threat of global warming. Global warming is driven largely by the emissions of greenhouse gases due to human economic activity, especially the burning of fossil fuels, certain industries like cement and steel production, and land use for agriculture and forestry. Since the industrial revolution, fossil fuels have provided the main source of energy for economic and technological development. The centrality of fossil fuels and other carbon intensive industries have resulted in much resistance to climate friendly policy, despite widespread scientific consensus that such policy is necessary.
 W
WA riparian buffer or stream buffer is a vegetated area near a stream, usually forested, which helps shade and partially protect the stream from the impact of adjacent land uses. It plays a key role in increasing water quality in associated streams, rivers, and lakes, thus providing environmental benefits. With the decline of many aquatic ecosystems due to agriculture, riparian buffers have become a very common conservation practice aimed at increasing water quality and reducing pollution.
 W
WThe rural–urban fringe, also known as the outskirts, rurban, peri-urban or the urban hinterland, can be described as the "landscape interface between town and country", or also as the transition zone where urban and rural uses mix and often clash. Alternatively, it can be viewed as a landscape type in its own right, one forged from an interaction of urban and rural land uses.
 W
WSecondary succession is one of the two types ecological succession of a plant's life. As opposed to the first, primary succession, secondary succession is a process started by an event that reduces an already established ecosystem to a smaller population of species, and as such secondary succession occurs on preexisting soil whereas primary succession usually occurs in a place lacking soil. Many factors can affect secondary succession, such as trophic interaction, initial composition, and competition-colonization trade-offs. The factors that control the increase in abundance of a species during succession may be determined mainly by seed production and dispersal, micro climate; landscape structure ; bulk density, pH, and soil texture.
 W
WStream restoration or river restoration, also sometimes referred to as river reclamation, is work conducted to improve the environmental health of a river or stream, in support of biodiversity, recreation, flood management and/or landscape development.
 W
WSurfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined c. 1950.
 W
WSustainability is the capacity to endure in a relatively ongoing way across various domains of life. In the 21st century, it refers generally to the capacity for Earth's biosphere and human civilization to co-exist. Sustainability has also been described as "meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs". For many, sustainability is defined through the interconnected domains of environment, economy and society. Sustainable development, for example, is often discussed through the domains of culture, technology economics and politics.
 W
WUrban sprawl is the unrestricted growth in many urban areas of housing, commercial development, and roads over large expanses of land, with little concern for urban planning. In addition to describing a special form of urbanization, the term also relates to the social and environmental consequences associated with this development. Since the advent of the industrial era, sprawl has entailed no direct disadvantages, such as the loss of protection from medieval city walls. However, its disadvantages and costs include increased travel time, transport costs, pollution, and destruction of countryside. The cost of building the infrastructure needed for new developments is hardly ever recouped through property taxes, amounting to a huge subsidy for the developers and new residents at the expense of existing property taxpayers. In Continental Europe, the term peri-urbanisation is often used to denote similar dynamics and phenomena, but the term urban sprawl is currently being used by the European Environment Agency. There is widespread disagreement about what constitutes sprawl and how to quantify it. For example, some commentators measure sprawl only with the average number of residential units per acre in a given area, but others associate it with decentralization, discontinuity, segregation of uses, and so forth.
 W
WA veteran tree is a tree which, because of its great age, size or condition, is of exceptional cultural, landscape or nature conservation value.
 W
WA water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community, or business is defined as the total volume of fresh water used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business. Water use is measured in water volume consumed (evaporated) and/or polluted per unit of time. A water footprint can be calculated for any well-defined group of consumers or producers, for a single process or for any product or service.
 W
WA water-meadow is an area of grassland subject to controlled irrigation to increase agricultural productivity. Water-meadows were mainly used in Europe from the 16th to the early 20th centuries. Working water-meadows have now largely disappeared, but the field patterns and water channels of derelict water-meadows remain common in areas where they were used, such as parts of Northern Italy, Switzerland and England. Derelict water-meadows are often of importance as wetland wildlife habitats.
 W
WA wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded by water, either permanently or seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of unique plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide.
 W
WWildlife management is the management process influencing interactions among and between wildlife, its habitats and people to achieve predefined impacts. It attempts to balance the needs of wildlife with the needs of people using the best available science. Wildlife management can include wildlife conservation, gamekeeping and pest control. Wildlife management draws on disciplines such as mathematics, chemistry, biology, ecology, climatology and geography to gain the best results.