 W
WImmigration to the United States is the international movement of non-United States nationals to reside permanently in the country. Immigration has been a major source of population growth and cultural change throughout much of the United States. history. All Americans, except for Native Americans, can trace their ancestry to immigrants from other nations around the world.
 W
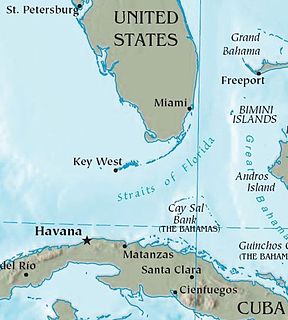
WThe 1994 Cuban rafter crisis which is also known as the 1994 Cuban raft exodus or the Balsero crisis was the emigration of more than 35,000 Cubans to the United States via makeshift rafts. The exodus occurred over five weeks following rioting in Cuba; Fidel Castro announced in response that anyone who wished to leave the country could do so without any hindrance. Fearing a major exodus, the Clinton administration would mandate that all rafters captured at sea be detained at the Guantanamo Bay Naval Base.
 W
WIn 2006-2007, millions of people participated in protests over a proposed change to U.S. immigration policy. These large scale mobilizations are widely seen as a historic turn point in Latino politics, especially Latino immigrant civic participation and political influence, as noted in a range of scholarly publications in this field. The protests began in response to proposed legislation known as H.R. 4437, which would raise penalties for illegal immigration and classify illegal aliens and anyone who helped them enter or remain in the US as felons. As part of the wider immigration debate, most of the protests not only sought a rejection of this bill, but also a comprehensive reform of the country's immigration laws that included a path to citizenship for all illegal immigrants.
 W
WU.S. citizens and permanent residents entering Canada by land are required to possess the requisite documentation, and to meet other criteria before they are allowed entry into Canada. Consequently, travelers must also meet the requirements for re-entering the U.S. at the end of their visit.
 W
WAmericans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America. Although citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates and permanent residents could also legally claim American nationality. The United States is home to people of many ethnic origins. As a result, American culture and law does not equate nationality with race or ethnicity, but with bona fide citizenship and an oath of permanent allegiance.
 W
WA green card, known officially as a permanent resident card, is an identity document which shows that a person has permanent residency in the United States. Green card holders are formally known as lawful permanent residents (LPRs). As of 2019, there are an estimated 13.9 million green card holders of whom 9.1 million are eligible to become United States citizens. Approximately 65,000 of them serve in the U.S. Armed Forces.
 W
WThe Assistant Secretary of State for Consular Affairs is the head of the Bureau of Consular Affairs within the United States Department of State. The Assistant Secretary of State for Consular Affairs reports to the Under Secretary of State for Management. From 1953 to 1977, the position was called Administrator of the Bureau of Security and Consular Affairs. The bureau is "responsible for the welfare and protection of U.S. citizens abroad, for the issuance of passports and other documentation to citizens and nationals, and for the protection of U.S. border security and the facilitation of legitimate travel to the United States" as described by the bureau's website.
 W
WThe United States recognizes the right of asylum for individuals as specified by international and federal law. A specified number of legally defined refugees who are granted refugee status outside the United States are annually admitted under 8 U.S.C. § 1157 for firm resettlement. Other aliens enter the United States either lawfully or unlawfully and apply for asylum under section 1158.
 W
WBalseros was the name given to boat people who emigrated without formal documentation in self constructed or precarious vessels from Cuba to neighboring states including The Bahamas, Jamaica, the Cayman Islands and, most commonly, the United States since the 1994 Balsero crisis and during the wet feet, dry feet policy.
 W
WThe Canada–United States Safe Third Country Agreement (STCA) is a treaty, entered into force on 29 December 2004, between the governments of Canada and the United States to better manage the flow of refugee claimants at the shared land border.
 W
WCasa San Diego is a holding facility located in El Cajon, California for minors who are either unaccompanied at the United States border or who have been separated from their families. Currently, around 10 percent of children housed in Casa San Diego were separated from their parents on entry at the border. Casa San Diego currently houses boys and girls between the ages of 6 and 17.
 W
WCircassian Americans are Americans of ethnic Circassian origin. The term "Circassian Americans" can refer to ethnic Circassian immigrants to the United States, as well as their American-born descendants. The majority trace their roots to the Republic of Turkey, however, there are also those who descend from Circassians in Jordan, Circassians in Syria, and other areas of the Circassian diaspora. They mostly live in Upstate New York, California, and New Jersey and number around 25,000. There is also a Circassian community in Canada.
 W
WCitizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constitution and laws of the United States, such as freedom of expression, due process, the rights to vote, live and work in the United States, and to receive federal assistance. The implementation of citizenship requires attitudes including pledging allegiance to the United States and swearing an oath to support and defend the constitution thereof.
 W
WA commuter worker, also known as a cross-border commuter or alien commuter is a worker who is resident in a different country to that in which they work, and crosses a national border as part of their regular commute. The term is commonly used with reference to workers who live in Mexico and cross the Mexico–United States border to work in the United States. However, it can also refer to workers who cross the Canada–United States border or other national borders.
 W
WCourage to Resist (CTR) is an organization in the San Francisco, CA area and beyond formed during the early part of the Iraq War which began in 2003. CTR's mission is to support U.S military war resisters, including helping them with legal fees such as well-known resisters Chelsea Manning and Reality Winner. In 2018, CTR began encouraging soldiers to resist at detention camps and other immigrant operations of the U.S. military. CTR's principle slogans are “Supporting the troops who refuse to fight!” and "Towards a World Without War!" They support those “who face consequences for acting on conscience, in opposition to illegal wars, occupations, [and] the policies of empire”.
 W
WCuban immigration to the United States, for the most part, occurred in two periods: the first series of immigration of Cuban Americans to the United States resulted from Cubans establishing cigar factories in Tampa and from attempts to overthrow Spanish colonial rule by the movement led by José Martí, the second to escape from Communist rule under Fidel Castro following the Cuban Revolution. Massive Cuban migration to Miami during the second series led to major demographic and cultural changes in Miami. There was also economic emigration, particularly during the Great Depression in the 1930s. As of 2019, there were 1,359,990 Cubans in the United States.
 W
WDepartures is a 2011 Turkish short film directed by Ali Y. Akarçeşme. The film is twelve minutes long and is about immigration to the United States from Turkey. In order to raise funds for the film, Akarçeşme held a successful Kickstarter campaign that raised $2,665. Departures was named Best Drama at the Brownfish Short Film Festival in New York City in 2011. And he won the Best Director Award at NY ITN Distribution Film Festival. These awards were the first Akarçeşme received while living in the United States. In 2012, the film was screened at New York's Rushes Soho Shorts Film Festival and the Love Your Shorts Film Festival and competed in the Boston Turkish Film Festival. The film also had official selections in various festivals such as NY Soho International, New Hope, Spain's Renderyard, Buffalo Niagara, NJ's Garden State and more.
 W
WThe Dima Yakovlev Law, Dima Yakovlev Bill, Dima Yakovlev Act, anti-Magnitsky law, or Law of Scoundrels is a law in Russia that defines sanctions against U.S. citizens involved in "violations of the human rights and freedoms of Russian citizens". It creates a list of citizens who are banned from entering Russia, and also allows the government to freeze their assets and investments. The law suspends the activity of politically active non-profit organisations which receive money from American citizens or organisations. It also bans citizens of the United States from adopting children from Russia. The law was signed by Russian President Vladimir Putin on 28 December 2012 and took effect on 1 January 2013. The law is informally named after a Russian orphan adopted by a family from Purcellville, Virginia, who died of heat stroke after being left in a parked car for nine hours. The law is described as a response to the Magnitsky Act in the United States, which places sanctions on Russian officials who were involved in a tax scandal exposed by Russian lawyer Sergei Magnitsky against Russian officials; Magnitsky was later found to have been handcuffed and tortured while in jail.
 W
WImmigrants make up about 13% of the US population, about 42 million out of a total population of 318.9 million citizens in 2017. First and second generation immigrant children have become the fastest-growing segment of the United States population. Compared to the native-born population, young adults aged 15–34 are significantly over-represented in new immigrants. Children and immigrants ages 35–44 are in similar proportion to native-born Americans, but older people are under-represented in new immigrants.
 W
WA Form I-766 employment authorization document or EAD card, known popularly as a work permit, is a document issued by the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) that provides temporary employment authorization to noncitizens in the United States.
 W
WThe Executive Office for Immigration Review (EOIR) is a sub-agency of the United States Department of Justice whose chief function is to conduct removal proceedings in immigration courts and adjudicate appeals arising from the proceedings. These administrative proceedings determine the removability and admissibility of individuals in the United States. As of February 20, 2020, there were sixty-nine immigration courts throughout the United States.
 W
WFamilies Belong Together refers both to an advocacy campaign devoted to reuniting immigrant families that were separated at the US-Mexico border by a Trump Administration policy introduced in spring 2018, and also specifically to a series of protests on June 30, 2018 in Washington, D.C., New York City, and 700 other cities and towns in the United States. Very large crowds turned out to those events despite heat waves in many areas, including in Washington, D.C.
 W
WFreedom University is a modern-day Freedom School in Atlanta, Georgia. Freedom U provides tuition-free college classes to undocumented youth unable to access higher education in Georgia due to the state's out-of-state tuition requirement. The school formed in 2011 in response to the University System of Georgia's passage of a policy banning undocumented students from the state's top public universities.
 W
WThe Galveston Movement, also known as the Galveston Plan, was a U.S. immigration assistance program operated by several Jewish organizations between 1907 and 1914. The program diverted Jewish immigrants, fleeing Russia and eastern Europe, away from East Coast cities, particularly New York, which was already crowded with these poverty-stricken immigrants. During its operation, ten thousand Jewish immigrants passed through the port of Galveston, Texas, about a third the number that emigrated to Palestine during the same period. New York financier and philanthropist Jacob Schiff was the driving force behind the effort, which he supported with nearly $500,000 of his personal fortune. B'nai Israel's Rabbi Henry Cohen was the humanitarian face of the movement, meeting ships at the Galveston docks and helping guide the immigrants through the cumbersome arrival and distribution process, and on into the countryside.
 W
WHaiti has a sizeable diaspora, present majoritarily in the United States, Dominican Republic, Cuba, Canada, France, the Bahamas, Brazil and Chile. They also live in other countries like Belgium, Turks and Caicos, Mexico, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, among others.
 W
WThe Hebrew Emigrant Aid Society (HEAS) was a late 19th-century American charitable organization. It is distinct from the later Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society, but was involved in some of the same areas of charitable work.
 W
WHomestead Temporary Shelter for Unaccompanied Children is a 3,200-bed migrant children's detention center in Homestead, Florida. Until August 3, 2019, the center had been operated by Comprehensive Health Services, Inc. (CHSi), which is a subsidiary of the homeland security operator Caliburn International. It was believed to be the only remaining for-profit child detention center for migrants. The organization has faced severe criticism concerning immigration. Senator Elizabeth Warren had demanded that the detention facility be "closed down", and calls for investigation and oversight grew stronger when it was revealed that the federal government had paid $33 million in just 46 days for 1,200 of the empty beds.
 W
WImmigrant health care in the United States refers to the collective systems in the United States that deliver health care services to immigrants. The term "immigrant" is often used to encompass non-citizens of varying status; this includes permanent legal residents, refugees, and undocumented residents.
 W
WThe immigrant paradox is that recent immigrants often outperform more established immigrants and non-immigrants on a number of health-, education-, and conduct- or crime-related outcomes, despite the numerous barriers they face to successful social integration.
 W
WThe United States Immigration and Naturalization Service (INS) was an agency of the U.S. Department of Labor from 1933 to 1940 and the U.S. Department of Justice from 1940 to 2003.
 W
WThe Immigration Reform and Control Act was passed by the 99th United States Congress and signed into law by U.S. President Ronald Reagan on November 6, 1986.
 W
WReview of the Department of Justice’s Planning and Implementation of Its Zero Tolerance Policy and Its Coordination with the Department of Homeland Security and Health and Human Services is a report by the United States Department of Justice Office of the Inspector General which was released on December 9, 2020 by Inspector General Michael E. Horowitz. The report reviewed the Trump administration's family separation policy, and in particular the "zero-tolerance" policy that was espoused by then U.S. Attorney General Jeff Sessions and how DOJ planned, implemented, and coordinated the policy with DHS and DHHS.
 W
WThe International Entrepreneur Rule is a regulation by U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) to increase the presence of foreign entrepreneurship in the U.S. Under this rule, qualified foreign entrepreneurs are granted temporary parole to the U.S. in order to build and scale their businesses. Foreign entrepreneurs wishing to enter or remain in the country to build their business operations must meet certain criteria that are reviewed on a case-by-case basis by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Unlike the Startup Visa, this rule does not need to be approved by Congress. The American public was allowed to comment on the proposed rule for 45 days, and the final rule was published in January 2017 and implemented in December 2017 after a federal court order. The Department of Homeland Security estimates that 2,940 entrepreneurs will be granted parole to the U.S. each year.
 W
WIsraeli Americans are Americans who have Israeli citizenship either by descent or Aliyah, or are Americans of Israeli national origin. Reflecting Israel's population, while the vast majority are Jewish, they also include the faiths of the Arab-Israeli minorities: Christians, Druze, and Muslims; as well as other Jewish and non-Jewish ethnic groups of Israel.
 W
WThe student walkouts of Friday, March 24, 2006 in Los Angeles, California commenced protests that spanned several days. That day, hundreds of students representing all ages walked out of at least five high schools in the Los Angeles Unified School District. Over 40,000 students staged walkouts in Los Angeles on the 27th. The protests were against the Border Protection, Anti-terrorism, and Illegal Immigration Control Act of 2005. This act would make it even harder than ever for immigrants to attain residency status and would criminalize undocumented immigrants as well as individuals and organizations that aid them. Both Southern California immigrants and residents worked together to create a community response to legislative proposals that would scale back immigrant rights. Hundreds of thousands of people gathered at Los Angeles City Hall to demand a stop to H.R. 4437.
 W
WThe March for America was a protest march in Washington, DC, United States. On March 21, 2010, over 200,000 marched by the Capitol in Washington, DC, to call for comprehensive immigration reform in that year. The event was organized by Reform Immigration FOR America and many more groups.
 W
WBruce Andrew Morrison is a former Congressman from Connecticut and candidate for Governor of Connecticut. He is a lobbyist and immigration lawyer. He is a member of the Democratic Party, and an officer of the National Democratic Ethnic Coordinating Committee.
 W
WMVM is a company headquartered in Ashburn, Virginia, United States. It is a private security contractor that provides security contractors, staffing, training, translation and related services to U.S. Government clients including being a contractor for detaining children who are subject to immigration proceedings.
 W
WThe New Way Forward Act is a proposed legislation introduced in the U.S. Senate and House on December 10, 2019 by Jesús "Chuy" García, which focuses on immigration reform. The bill would repeal sections 1325 and 1326 of the immigration law to decriminalize unauthorized border crossing whilst maintaining civil deportation procedures. The bill intends to give immigration judges discretion when deciding immigration claims for immigrants with criminal records in the United States, changes immigration enforcement by ending mandatory detention in specific cases and intends to remove private detention centers for immigrants.
 W
WAlexander Nowrasteh is an American analyst of immigration policy currently working at the Center for Global Liberty and Prosperity of the Cato Institute, a libertarian think tank located in Washington D.C. Nowrasteh is an advocate of freer migration to the United States. He previously worked as the immigration policy analyst at the Competitive Enterprise Institute, another libertarian think tank. Nowrasteh is a self-described "radical" advocate for open borders to and from the United States. He has published a number of peer-reviewed studies on immigration.
 W
WOperation New Life was the care and processing on Guam of Vietnamese refugees evacuated before and after the Fall of Saigon, the closing day of the Vietnam War. More than 111,000 of the evacuated 130,000 Vietnamese refugees were transported to Guam where they were housed in tent cities for a few weeks while being processed for resettlement. The great majority of the refugees were resettled in the United States. A few thousand were resettled in other countries or chose to return to Vietnam on the vessel Thuong Tin.
 W
WOperation Streamline is a joint initiative of the Department of Homeland Security and Department of Justice in the United States, started in 2005, that adopts a "zero-tolerance" approach to unauthorized border-crossing by criminally prosecuting those perpetrating it. Up to 70 people are tried at the same time, sometimes wearing shackles in the courtroom. Entering without inspection is a misdemeanor, and re-entering after deportation is a felony.
 W
WPaper sons or paper daughters is a term used to refer to Chinese people who were born in China and illegally immigrated to the United States by purchasing documentation which stated that they were blood relatives to Chinese Americans who had already received U.S. citizenship. Typically it would be relation by being a son or a daughter. Many fled China because of constant war and poverty that occurred in China due to the corrupt Qing Dynasty. Several historical events such as the Chinese Exclusion Act and San Francisco earthquake of 1906 caused the illegal documents to be produced.
 W
WThe RAISE Act is a bill first introduced in the United States Senate in 2017. Co-sponsored by Republican senators Tom Cotton and David Perdue, the bill seeks to reduce levels of legal immigration to the United States by 50% by halving the number of green cards issued. The bill would also dramatically reduce family-based immigration pathways; impose a cap of 50,000 refugee admissions a year; end the visa diversity lottery; and eliminate the current demand-driven model of employment-based immigration and replace it with a points system. The bill received the support of President Donald Trump, who promoted a revised version of the bill in August 2017, and was opposed by Democrats, immigrant rights groups, and some Republicans.
 W
WThe Reconquista ("reconquest") is a term to describe an irredentist vision by different individuals, groups, and/or nations that the Southwestern United States should be politically or culturally returned to Mexico. Such opinions are often formed on the basis that those territories were claimed by Spain for centuries and then by Mexico from 1821 until they were ceded to the United States during the Texas Annexation (1845) and the Mexican Cession (1848) because of the Mexican–American War.
 W
WThe Remote Video Inspection System (RVIS) was deployed by United States in the late 1990s at select low-traffic border entry points from Canada. The system allowed passport and customs inspections to be conducted remotely, so that low-risk travelers could enter the country during hours that the border station did not have on-site staff. The system was successfully deployed at a number of entry points, in six different states. RVIS was discontinued following the September 11 attacks.
 W
WThe Swedish Emigration Commission, was a commission that existed between 1907 and 1913 that was mandated by the Swedish Riksdag to try to reduce Swedish emigration to the United States. In the 19th century, Sweden had had one of the highest rates of emigration to North America in all of Europe, the third highest after Ireland and Norway. By 1910, one fifth of all Swedes had their homes in America. The situation alarmed conservative Swedes, who regarded emigration as a challenge to national solidarity and to the very nation state itself, already seemingly under threat from trade unionism and the international socialist movement. The liberal interest, which had in the 19th century favored emigration as a practical necessity, by now also saw it as a net drain, depriving Sweden of the labor necessary for economic development. Both camps shared a perception, disturbing in a Europe where the forces of war were gathering, that young, male Swedes were fleeing to America to escape military service.
 W
WSystematic Alien Verification for Entitlements (SAVE) is a program managed by United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), a branch of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS). SAVE facilitates lookups on the immigration and nationality status of individuals in the United States. It is an intergovernmental initiative designed to help federal, state, tribal, and local government agencies, or by a contractor acting on the agency's behalf, to determine eligibility for benefits, licenses or grants, government credentials, or to conduct background investigations. It is one of two programs that uses the Verification Information System (VIS). The other program is the Electronic Employment Eligibility Verification Program, also known as E-Verify, and is used by employers to verify the immigration status of employees. For additional verification, SAVE relies on the Person Centric Query System (PCQS).
 W
WThe Trump travel ban denotes a series of executive actions enacted by Donald Trump as President of the United States in 2017. First, Executive Order 13769 placed stringent restrictions on travel to the United States for citizens of Iran, Iraq, Libya, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, and Yemen. Following protests and legal challenges, a second order, Executive Order 13780, amended some provisions of the first order, and removed Iraq from the list. Finally, Presidential Proclamation 9645 added restrictions on Chad, North Korea, and Venezuela, while Sudan was removed.
 W
WUnaccompanied Alien Children is a United States government classification for children in immigration custody and the name of a program operated by the Office of Refugee Resettlement to house and care for them. The term designates unaccompanied minors who are aliens, typically those who have been apprehended outside of a legal port of entry or judged inadmissible upon their entry.
 W
WThe United States Immigration Station is a government building located at 333 Mount Elliott Street in Detroit, Michigan. It is currently known as the Rosa Parks Federal Building, and houses the Detroit Field Office of Immigration and Customs Enforcement. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2013.
 W
WUrsula is the colloquial name for the Central Processing Center, the largest U.S. Customs and Border Protection detention center for undocumented immigrants. The facility is a retrofitted warehouse that can hold more than 1,000 people. It was opened in 2014 on W. Ursula Avenue in McAllen, Texas. In June 2018, it gained notoriety for the practice of keeping children in large cages made of chain-link fencing.
 W
WState of Washington and State of Minnesota v. Trump, 847 F.3d 1151, was a lawsuit that challenged the lawfulness and constitutionality of Executive Order 13769, an executive order signed by U.S. President Donald Trump.
 W
WThe wet feet, dry feet policy or wet foot, dry foot policy was the name given to a former interpretation of the 1995 revision of the application of the Cuban Adjustment Act of 1966 that essentially says that anyone who emigrated from Cuba and entered the United States would be allowed to pursue residency a year later. Prior to 1995, the U.S. government allowed all Cubans who reached U.S. territorial waters to remain in the U.S. After talks with the Cuban government, the Clinton administration came to an agreement with Cuba that it would stop admitting people intercepted in U.S. waters. For two decades thereafter, any Cuban caught on the waters between the two nations would summarily be returned to Cuba or sent to a third country, while one who made it to shore got a chance to remain in the United States, and later would qualify for expedited "legal permanent resident" status in accordance with the 1966 Act and eventually U.S. citizenship. On January 12, 2017, Barack Obama announced the immediate end of the policy.