 W
WCosmetics ingredients come from a variety of sources but, unlike the ingredients of food, are often not considered by most consumers. Cosmetics often use vibrant colors that are derived from a wide variety of sources, ranging from crushed insects to rust.
 W
WAcetone, or propanone, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colourless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
 W
WAcetyl hexapeptide-3 or acetyl hexapeptide-8 is a synthetic anti-wrinkle cosmetics ingredient. It is a peptide which is a fragment of SNAP-25, a substrate of botulinum toxin (Botox). Acetyl hexapeptide-8 is marketed as Argireline by the Barcelona-based research laboratory Lipotec.
 W
WAllantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid. Allantoin is a major metabolic intermediate in most organisms including animals, plants and bacteria. It is produced from uric acid, which itself is a degradation product of nucleic acids, by action of urate oxidase (uricase).
 W
WAloe, also written Aloë, is a genus containing over 560 species of flowering succulent plants. The most widely known species is Aloe vera, or "true aloe". It is called this because it is cultivated as the standard source for assorted pharmaceutical purposes. Other species, such as Aloe ferox, are also cultivated or harvested from the wild for similar applications.
 W
WArgan oil is a plant oil produced from the kernels of the argan tree that is endemic to Morocco. In Morocco, argan oil is used to dip bread in at breakfast or to drizzle on couscous or pasta. It is also used for cosmetic purposes.
 W
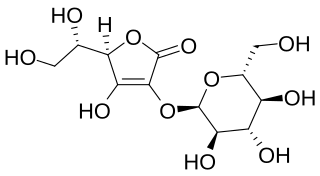
WAscorbyl glucoside (AA-2G) is an ascorbic acid derivative that contains at least one glycosyl group. Ascorbyl glucoside is commonly used in cosmetic products to administer vitamin C topically. Ascorbyl glucoside exhibits superior stability and penetration ability compared to ascorbyl phosphate salts, but the rate of its in vivo conversion to ascorbic acid is not known. Ascorbyl glucosides such as AA-2G, like many other derivatives of the ascorbic acid, show antiscorbutic effects. It is also sometimes used in skin whitening products.
 W
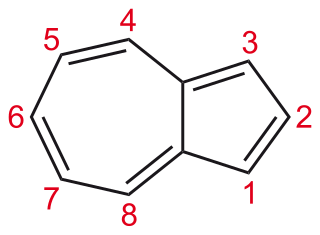
WAzulene is an organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Whereas naphthalene is colourless, azulene is dark blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates.
 W
WBehentrimonium chloride, also known as docosyltrimethylammonium chloride or BTAC-228, is a yellow waxlike organic compound with chemical formula CH3(CH2)21N(Cl)(CH3)3, used as an antistatic agent and, sometimes, a disinfectant. It is commonly found in cosmetics such as conditioners, hair dye, and mousse, and also in detergents. Laboratory tests have indicated that it does not readily biodegrade.
 W
WBimatoprost, sold under the brand name Lumigan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It may also be used to increase the size of the eyelashes. It is used as an eye drop and effects generally occur within four hours.
 W
WBisabolol, or more formally α-(−)-bisabolol or also known as levomenol, is a natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. It is a colorless viscous oil that is the primary constituent of the essential oil from German chamomile and Myoporum crassifolium. It is poorly soluble in water and glycerin, but soluble in ethanol. The enantiomer, α-(+)-bisabolol, is also found naturally but is rare. Synthetic bisabolol is usually a racemic mixture of the two, α-(±)-bisabolol.
 W
WCanthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It has also been found in green algae, bacteria, crustaceans, and bioaccumulates in fish such as carp, golden grey mullet, seabream and trush wrasse.
 W
WCarnauba, also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the carnauba palm Copernicia prunifera, a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Pernambuco, Piauí, Ceará, Maranhão, Bahia, and Rio Grande do Norte. It is known as "queen of waxes" and in its pure state usually comes in the form of hard yellow-brown flakes. It is obtained from the leaves of the carnauba palm by collecting and drying them, beating them to loosen the wax, and then refining and bleaching the wax. As a food additive, its E number is E903.
 W
WCastor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans. It is a colourless to very pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is 313 °C (595 °F) and its density is 0.961 g/cm3. It includes a mixture of triglycerides in which about 90% of fatty acids are ricinoleates. Oleate and linoleates are the other significant components.
 W
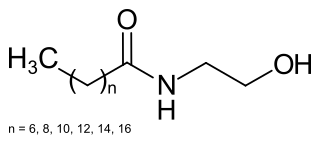
WCocamide DEA, or cocamide diethanolamine, is a diethanolamide made by reacting the mixture of fatty acids from coconut oils with diethanolamine. It is a viscous liquid and is used as a foaming agent in bath products like shampoos and hand soaps, and in cosmetics as an emulsifying agent. See cocamide for the discussion of the lengths of carbon chains in the molecules in the mixture. The chemical formula of individual components is CH3(CH2)nC(=O)N(CH2CH2OH)2, where n typically ranges from 8 to 18.
 W
WCocamide MEA, or cocamide monoethanolamine, is a solid, off-white to tan compound, often sold in flaked form. The solid melts to yield a pale yellow viscous clear liquid. It is a mixture of fatty acid amides which is produced from the fatty acids in coconut oil when reacted with ethanolamine.
 W
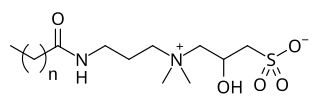
WCocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine (CAHS) is a synthetic amphoteric surfactant from the hydroxysultaine group. It is found in personal care products. It has uses as a foam booster, viscosity builder, and an antistatic agent.
 W
WCocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from the cocoa bean. It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter has a cocoa flavor and aroma. Its melting point is just below human body temperature.
 W
WCarnauba, also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the carnauba palm Copernicia prunifera, a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Pernambuco, Piauí, Ceará, Maranhão, Bahia, and Rio Grande do Norte. It is known as "queen of waxes" and in its pure state usually comes in the form of hard yellow-brown flakes. It is obtained from the leaves of the carnauba palm by collecting and drying them, beating them to loosen the wax, and then refining and bleaching the wax. As a food additive, its E number is E903.
 W
WCopper peptide GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. The tripeptide has strong affinity for copper(II) and was first isolated from human plasma. It can be found also in saliva and urine.
 W
WDecamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5) is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]5. It is a colorless and odorless liquid that is slightly volatile.
 W
WDihydroxyacetone (DHA), also known as glycerone, is a simple saccharide with formula C3H6O3.
 W
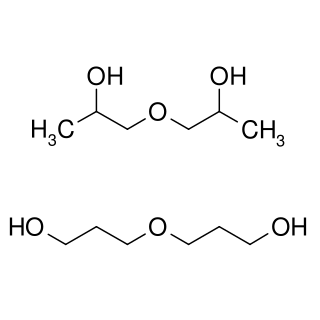
WDipropylene glycol is a mixture of three isomeric chemical compounds, 4-oxa-2,6-heptandiol, 2-(2-hydroxy-propoxy)-propan-1-ol, and 2-(2-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethoxy)-propan-1-ol. It is a colorless, nearly odorless liquid with a high boiling point and low toxicity.
 W
WDisodium cocoamphodiacetate (DSCADA) is a synthetic amphoteric surfactant routinely used in personal care products.
 W
WDMDM hydantoin is an antimicrobial formaldehyde releaser preservative with the trade name Glydant. DMDM hydantoin is an organic compound belonging to a class of compounds known as hydantoins. It is used in the cosmetics industry and found in products like shampoos, hair conditioners, hair gels, and skin care products.
 W
WD-Erythrulose (also known as erythrulose) is a tetrose carbohydrate with the chemical formula C4H8O4. It has one ketone group and so is part of the ketose family. It is used in some self-tanning cosmetics, in general, combined with dihydroxyacetone (DHA).
 W
WEthyl macadamiate is the ester of ethyl alcohol and the fatty acids derived from Macadamia ternifolia seed oil. Ethyl macadamiate is used in some cosmetic formulations.
 W
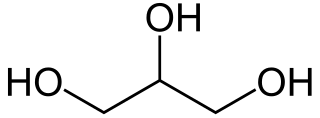
WGlycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Due to having antimicrobial and antiviral properties it is widely used in FDA approved wound and burn treatments. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Owing to the presence of three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature.
 W
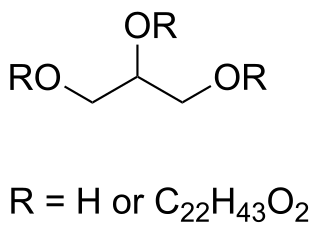
WGlyceryl behenate is a fat used in cosmetics, foods, and oral pharmaceutical formulations. In cosmetics, it is mainly used as a viscosity-increasing agent in emulsions.
 W
WGlycol distearate is the diester of stearic acid and ethylene glycol. It is mostly commonly encountered in personal care products and cosmetics where it is used to produce pearlescent effects as well as a moisturizer.
 W
WGuaiazulene, also azulon or 1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene, is a dark blue crystalline hydrocarbon. A derivative of azulene, guaiazulene is a bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of some essential oils, mainly oil of guaiac and chamomile oil, which also serve as its commercial sources. Various soft corals also contain guaiazulene as a principal pigment. Its low melting point makes guaiazulene difficult to handle, in contrast to the crystalline nature of the parent azulene. The electronic structure of guaiazulene and azulene are very similar.
 W
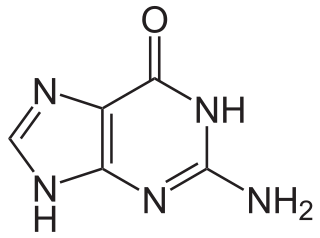
WGuanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine.
 W
WIodopropynyl Butyl Carbamate (IPBC) is a water-soluble preservative used globally in the paints & coatings, wood preservatives, personal care, and cosmetics industries. IPBC is a member of the carbamate family of biocides. IPBC was invented in the 1970s and has a long history of effective use as an antifungal technology.
 W
WJojoba oil is the liquid produced in the seed of the Simmondsia chinensis (jojoba) plant, a shrub, which is native to southern Arizona, southern California, and northwestern Mexico. The oil makes up approximately 50% of the jojoba seed by weight. The terms "jojoba oil" and "jojoba wax" are often used interchangeably because the wax visually appears to be a mobile oil, but as a wax it is composed almost entirely (~97%) of mono-esters of long-chain fatty acids and alcohols (wax ester), accompanied by only a tiny fraction of triglyceride esters. This composition accounts for its extreme shelf-life stability and extraordinary resistance to high temperatures, compared with true vegetable oils.
 W
WMacadamia oil is the non-volatile oil collected from the nuts of the macadamia, a native Australian plant. It is used in food as a frying or salad oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient or fragrance fixative.
 W
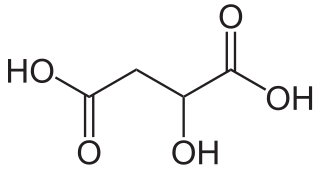
WMalic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H6O5. It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms (L- and D-enantiomers), though only the L-isomer exists naturally. The salts and esters of malic acid are known as malates. The malate anion is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
 W
WMarula oil is extracted from the kernels (nuts) of the fruits of the Marula trees, from the family Anacardiaceae. There are two types of marula oil, the oil extracted from the seeds and the oil extracted from the nut's hard shell. Marula oil is traditionally used in cosmetics, in food as a cooking oil, and as a meat preservative and to treat leather.
 W
WMicrobeads are manufactured solid plastic particles of less than one millimeter in their largest dimension. They are most frequently made of polyethylene but can be of other petrochemical plastics such as polypropylene and polystyrene. They are used in exfoliating personal care products, toothpastes and in biomedical and health-science research.
 W
WMineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils.
 W
WOleyl alcohol, or cis-9-octadecen-1-ol, is an unsaturated fatty alcohol with the molecular formula C18H36O or the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)8OH. It is a colorless oil, mainly used in cosmetics.
 W
WPalmitoyl pentapeptide-4 is a matrikine used in anti-wrinkle cosmetics. It was launched in 2000 as an active ingredient for the personal care industry under the trade name Matrixyl by the French cosmetic active ingredient manufacturer Sederma SAS.
 W
WPanthenol (also called pantothenol) is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), and is thus a provitamin of B5. In organisms, it is quickly oxidized to pantothenic acid. It is a viscous transparent liquid at room temperature. Panthenol is used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic products as a moisturizer and to improve wound healing.
 W
WPetroleum jelly, petrolatum, white petrolatum, soft paraffin, or multi-hydrocarbon, CAS number 8009-03-8, is a semi-solid mixture of hydrocarbons, originally promoted as a topical ointment for its healing properties. The Vaseline brand is a well known American brand of petroleum jelly since 1870.
 W
WPiroctone olamine is a compound sometimes used in the treatment of fungal infections. Piroctone olamine is the ethanolamine salt of the hydroxamic acid derivative piroctone.
 W
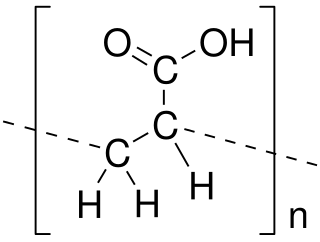
WPoly(acrylic acid) (PAA; trade name Carbomer) is a polymer with the formula (CH2-CHCO2H)n. It is a derivative of acrylic acid (CH2=CHCO2H). In addition to the homopolymers, a variety of copolymers and crosslinked polymers, and partially deprotonated derivatives thereof are known and of commercial value. In a water solution at neutral pH, PAA is an anionic polymer, i.e., many of the side chains of PAA lose their protons and acquire a negative charge. Partially or wholly deprotonaated PAAs are polyelectrolytes, with the ability to absorb and retain water and swell to many times their original volume. These properties - acid-base and water-attracting - are the bases of many applications.
 W
WPolydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, belongs to a group of polymeric organosilicon compounds that are commonly referred to as silicones. PDMS is the most widely used silicon-based organic polymer, as its versatility and properties lead to many applications.
 W
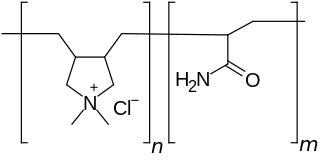
WPolyquaternium-7 is an organic compound in the polyquaternium class of chemicals and used in the personal care industry. It is the copolymer of acrylamide and the quaternary ammonium salt diallyldimethylammonium chloride.
 W
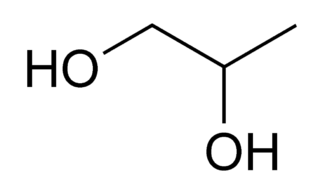
WPropylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. Containing two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
 W
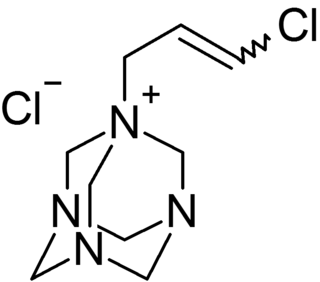
WQuaternium-15 is a quaternary ammonium salt used as a surfactant and preservative in many cosmetics and industrial substances. It acts as an antimicrobial agent because it acts as a formaldehyde releaser, though doing so can also cause contact dermatitis, a symptom of an allergic reaction, especially in those with sensitive skin.
 W
WA silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, and thermal and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk.
 W
WJojoba oil is the liquid produced in the seed of the Simmondsia chinensis (jojoba) plant, a shrub, which is native to southern Arizona, southern California, and northwestern Mexico. The oil makes up approximately 50% of the jojoba seed by weight. The terms "jojoba oil" and "jojoba wax" are often used interchangeably because the wax visually appears to be a mobile oil, but as a wax it is composed almost entirely (~97%) of mono-esters of long-chain fatty acids and alcohols (wax ester), accompanied by only a tiny fraction of triglyceride esters. This composition accounts for its extreme shelf-life stability and extraordinary resistance to high temperatures, compared with true vegetable oils.
 W
WSodium lauroamphoacetate is a zwitterionic surfactant of the amphoacetate class. It is used as a very mild cleaning agent originally used in shampoos and body washes for infants but it now sees broader use in other personal care products.
 W
WSpermaceti is a waxy substance found in the head cavities of the sperm whale. Spermaceti is created in the spermaceti organ inside the whale's head. This organ may contain as much as 1,900 litres (500 US gal) of spermaceti. The whaling industry in the 17th and 18th centuries was developed to find, harvest and refine the contents of the head of a sperm whale. The crews seeking spermaceti routinely left on three year tours on several oceans. Cetaceous lamp oil returned to Nantucket was a commodity that created many maritime fortunes. Measurement of the proportion of wax esters retained by a harvested sperm whale accurately described the age and future life expectancy of a given individual. The light produced by a single pure spermaceti source (candle) became the standard measurement of "Candlepower" for another century.
 W
WSunflower oil is the non-volatile oil pressed from the seeds of sunflower. Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient.
 W
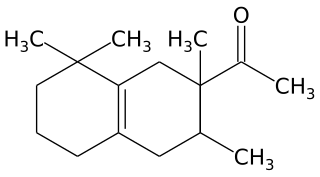
WTetramethyl acetyloctahydronaphthalenes is a synthetic ketone fragrance also known as OTNE and by other commercial trade names such as: Iso E Super, Iso Gamma Super, Anthamber, Amber Fleur, Boisvelone, Iso Ambois, Amberlan, Iso Velvetone, Orbitone, Amberonne. It is a synthetic woody odorant and is used as a fragrance ingredient in perfumes, laundry products and cosmetics.
 W
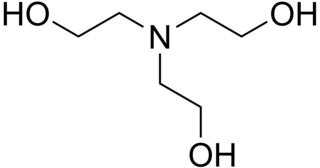
WTriethanolamine, or TEA is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities.
 W
WVitellaria paradoxa, commonly known as shea tree, shi tree, or vitellaria, is a tree of the family Sapotaceae. It is the only species in the genus Vitellaria, and is indigenous to Africa.
 W
WZinc pyrithione is a coordination complex of zinc. It has fungistatic and bacteriostatic properties and is used in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis.
 W
WZinc ricinoleate is the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a major fatty acid found in castor oil. It is used in many deodorants as an odor-adsorbing agent. The mechanism of this activity is unclear.