 W
WMagic, sometimes spelled magick, is the application of beliefs, rituals or actions employed in the belief that they can manipulate natural or supernatural beings and forces. It is a category into which have been placed various beliefs and practices sometimes considered separate from both religion and science.
 W
WBased on Roman Catholic tradition, the Anima Sola or Lonely Soul is an image depicting a soul in purgatory, popular in Latin America, as well as much of Andalusia, Naples and Palermo.
 W
WApotropaic magic is a type of magic intended to turn away harm or evil influences, as in deflecting misfortune or averting the evil eye. Apotropaic observances may also be practiced out of vague superstition or out of tradition, as in good luck charms, amulets, or gestures such as crossed fingers or knocking on wood. The Greeks made offerings to the "averting gods", chthonic deities and heroes who grant safety and deflect evil.
 W
WApuleius was a Numidian Latin-language prose writer, Platonist philosopher and rhetorician. He lived in the Roman province of Numidia, in the Berber city of Madauros, modern-day M'Daourouch, Algeria. He studied Platonism in Athens, travelled to Italy, Asia Minor, and Egypt, and was an initiate in several cults or mysteries. The most famous incident in his life was when he was accused of using magic to gain the attentions of a wealthy widow. He declaimed and then distributed a witty tour de force in his own defense before the proconsul and a court of magistrates convened in Sabratha, near ancient Tripoli, Libya. This is known as the Apologia.
 W
WBlack magic has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for evil and selfish purposes. With respect to the left-hand path and right-hand path dichotomy, black magic is the malicious, left-hand counterpart of the benevolent white magic. In modern times, some find that the definition of black magic has been convoluted by people who define magic or ritualistic practices that they disapprove of as black magic.
 W
WA Bobohizan or Bobolian is a high priestess, a ritual specialist and a spirit medium in Kadazan-Dusun pagan rites. The office of Bobohizan or Bobolian, is also the chief preserver of Momolianism, i.e. the philosophy and way of life of the Kadazan-Dusun people.
 W
WA boli is a fetish of the Bambara or Malinké of Mali.
 W
WA bomoh is a Malay shaman and traditional medicine practitioner. The term is used mainly in Malaysia and parts of Sumatra, whereas most Indonesians use the word dukun. It is often mistranslated into English as medicine man or witch doctor. In colloquial usage, the term bomoh is often interchangeable with another type of shaman or dukun bukan duku, the pawang, but they generally serve different functions. The bomoh is primarily a healer, herbalist, geomancer, and sorcerer. The pawang on the other hand usually specialises in rituals involving weather, nature, animals, and a good harvest. Their roles do overlap however, and both act as an intermediary for the spirits and gods.
 W
WA Book of Shadows is a book containing religious text and instructions for magical rituals found within the Neopagan religion of Wicca. Since its conception in the 1970s, it has made its way into many pagan practices and paths. The most famous Book of Shadows was created by the pioneering Wiccan Gerald Gardner sometime in the late 1940s or early 1950s, and which he utilised first in his Bricket Wood coven and then in other covens which he founded in following decades. The Book of Shadows is also used by other Wiccan traditions, such as Alexandrian Wicca and Mohsianism, and with the rise of books teaching people how to begin following non-initiatory Wicca in the 1970s onward, the idea of the Book of Shadows was then further propagated amongst solitary practitioners unconnected to earlier, initiatory traditions.
 W
WThe bullroarer, rhombus, or turndun, is an ancient ritual musical instrument and a device historically used for communicating over great distances. It dates to the Paleolithic period, being found in Ukraine dating from 18,000 BC. Anthropologist Michael Boyd, a bullroarer expert, documents a number found in Europe, Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Australia.
 W
WSaints Cyprian and Justina are honored in the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Church and Oriental Orthodoxy as Christians of Antioch, who in 304, during the Diocletianic Persecution, suffered martyrdom at Nicomedia on September 26. According to Roman Catholic sources, no Bishop of Antioch bore the name of Cyprian.
 W
WCyprianus is a name given in Scandinavian traditions of folk magic to the "black book" ("Svarteboken"): a grimoire or manuscript collection of spells; and by extension to the magical tradition that these spells form a part of. There is no standard text called "Cyprianus"; it was a general label given to a collection of spells.
 W
WDaemonologie—in full Daemonologie, In Forme of a Dialogue, Divided into three Books: By the High and Mighty Prince, James &c.—was first published in 1597 by King James VI of Scotland as a philosophical dissertation on contemporary necromancy and the historical relationships between the various methods of divination used from ancient black magic. It was reprinted again in 1603 when James took the throne of England.
 W
WDe praestigiis daemonum, translated as On the Tricks of Demons, is a book by medical doctor Johann Weyer, also known as Wier, first published in Basel in 1563. The book argues that witchcraft does not exist and that those who claim to practice it are suffering from delusions, which should be treated as mental illnesses, rather than punished as witchcraft. It was influential in the abolishment of witchcraft trials in the Netherlands.
 W
WDianism is a 19th-century American spiritual sexual practice consisting of "sexual satisfaction from sexual contact" but without ejaculation. The practice was named for Diana, the Roman goddess of chastity, by American court reporter and astronomer Henry M. Parkhurst in his 1882 pamphlet Diana. In the 1890s, sexual mystic Ida Craddock included Dianism as part of her teachings. In the 20th century, the practice found favor with American followers of Aleister Crowley, most notably C.F. Russell.
 W
WA dukun is an Indonesian term for shaman. Their societal role is that of a traditional healer, spirit medium, custom and tradition experts and on occasion sorcerers and masters of black magic. In common usage the dukun is often confused with another type of shaman, the pawang. It is often mistranslated into English as "witch doctor" or "medicine man". Many self-styled dukun in Indonesia are simply scammers and criminals, preying on gullible and superstitious people who were raised to believe in the supernatural.
 W
WElymas, also known as Bar-Jesus, is a Jew described in the Acts of the Apostles, chapter 13, in the New Testament. Acts of the Apostles calls him a magus, which the King James Bible translates as "sorcerer." "Elymas the Sorcerer Struck with Blindness" is the title of a famous cartoon by Raphael, which served as the inspiration for woven tapestries in the Vatican.
 W
WExecration texts, also referred to as proscription lists, are ancient Egyptian hieratic texts, listing enemies of the pharaoh, most often enemies of the Egyptian state or troublesome foreign neighbors. The texts were most often written upon statuettes of bound foreigners, bowls, or blocks of clay or stone, which were subsequently destroyed. The ceremonial process of breaking the names and burying them was intended to be a sort of sympathetic magic that would affect the persons or entities named in the texts. The fragments were usually placed near tombs or ritual sites. This practice was most common during times of conflict with the Asiatic neighbors of Egypt.
 W
WThe Fairy Flag is an heirloom of the chiefs of Clan MacLeod. It is held in Dunvegan Castle along with other notable heirlooms, such as the Dunvegan Cup and Sir Rory Mor's Horn. The Fairy Flag is known for the numerous traditions of celtic fairies, and magical properties associated with it. The flag is made of silk, is yellow or brown in colour, and is a square of side about 18 inches. It has been examined numerous times in the last two centuries, and its condition has somewhat deteriorated. It is ripped and tattered, and is considered to be extremely fragile. The flag is covered in small red "elf dots". In the early part of the 19th century, the flag was also marked with small crosses, but these have since disappeared. The silk of the flag has been stated to have originated in the Far East, and was therefore extremely precious, which led some to believe that the flag may have been an important relic of some sort. Others have attempted to associate the flag with the Crusades or even a raven banner, which was said to have been used by various Viking leaders in the British Isles.
 W
WFaith healing is the practice of prayer and gestures that are believed by some to elicit divine intervention in spiritual and physical healing, especially the Christian practice. Believers assert that the healing of disease and disability can be brought about by religious faith through prayer or other rituals that, according to adherents, can stimulate a divine presence and power. Religious belief in divine intervention does not depend on empirical evidence of an evidence-based outcome achieved via faith healing. Virtually all scientists and philosophers dismiss faith healing as pseudoscience.
 W
WA Fiery Serpent is an evil entity common to Slavic mythology, which presents itself as an anthropomorphic snake demon.
 W
WFilipino witches are the users of black magic and related practices from the Philippines. They include a variety of different kinds of people with differing occupations and cultural connotations which depend on the ethnic group they are associated with. They are completely different from the Western notion of what a witch is, as each ethnic group has their own definition and practices attributed to witches. The curses and other magics of witches are often blocked, countered, cured, or lifted by Filipino shamans associated with the indigenous Philippine folk religions.
 W
WA folk healer, in a contemporary Western perception, is an unlicensed person who practices the art of healing using traditional practices, herbal remedies and the power of suggestion.
 W
WA Garden of Pomegranates is a 160-page book, written by Israel Regardie in 1931. The first edition was published in 1932. The book was printed four times, with a second edition being published in 1970 by Llewellyn Publications. The title pays homage to Moses ben Jacob Cordovero's Pardes Rimonim, or "Pomegranate Orchard."
 W
WCharaktêres are letter-shaped signs lacking both semantic and phonetic correlations which were used as magic signs in ancient literary documents.
 W
WThe study of magic in the Greco-Roman world is a branch of the disciplines of classics, ancient history and religious studies. In classical antiquity, including the Hellenistic world of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, historians and archaeologists view the public and private rituals associated with religion as part of everyday life. Examples of this phenomenon are found in the various state and cult temples, Jewish synagogues, and churches. These were important hubs for ancient peoples, representing a connection between the heavenly realms and the earthly planes. This context of magic has become an academic study, especially in the last twenty years.
 W
WVoces magicae are Ancient Roman magical words, written in either Ancient Greek or Latin.
 W
WA grimoire is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons. In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers, although in many cultures, other sacred texts that are not grimoires have been believed to have supernatural properties intrinsically. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all books on magic could be thought of as grimoires, not all magical books should be thought of as grimoires.
 W
WA Guide to Grand-Jury Men — in full, A Guide to Grand Jury Men, Divided in two books. In the first, is the Author's best advice to them what to do, before they bring in a Billa vera in cases of Witchcraft, with a Christian Direction to such as are too much given upon every cross to think themselves bewitched. In the Second, is a Treatise touching Witches good and bad, how they may be known, evicted, condemned, with many particulars tending thereunto was first published in 1627 and written by a puritan clergyman named Richard Bernard.
 W
WHeka was the deification of magic and medicine in ancient Egypt. The name is the Egyptian word for "magic". According to Egyptian literature, Heka existed "before duality had yet come into being." The term ḥk3 was also used to refer to the practice of magical rituals.
 W
WHenosis is the classical Greek word for mystical "oneness", "union" or "unity". In Platonism, and especially Neoplatonism, the goal of henosis is union with what is fundamental in reality: the One, the Source, or Monad. The Neoplatonic concept has precedents in the Greek mystery religions as well as parallels in Eastern philosophy. It is further developed in the Corpus Hermeticum, in Christian theology, Alevism, soteriology and mysticism, and is an important factor in the historical development of monotheism during Late Antiquity.
 W
WHercules' Club is a Roman Empire and Migration-era artefact type.
 W
WThe Hermetica are texts attributed to the legendary Hellenistic figure Hermes Trismegistus, a syncretic combination of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth. These texts may vary widely in content and purpose, but are usually subdivided into two main categories:The "technical" Hermetica: this category contains a broad variety of treatises dealing with astrology, medicine and pharmacology, alchemy, and magic, the oldest of which were written in Greek and may go back as far as the second or third century BCE. Many of the texts belonging in this category were later translated into Arabic and Latin, often being extensively revised and expanded throughout the centuries. Some of them were also originally written in Arabic, though in many cases their status as an original work or translation remains unclear. These Arabic and Latin Hermetic texts were widely copied throughout the Middle Ages. The "religio-philosophical" Hermetica: this category contains a relatively coherent set of religio-philosophical treatises which were mostly written in the second and third centuries CE, though the very earliest one of them, the Definitions of Hermes Trismegistus to Asclepius, may go back to the first century CE. They are chiefly focused on the relationship between human beings, the cosmos, and God. Many of them are also moral exhortations calling for a way of life leading to spiritual rebirth, and eventually to divinization in the form of a heavenly ascent. The treatises in this category were probably all originally written in Greek, even though some of them only survive in Coptic, Armenian, or Latin translations. During the Middle Ages, most of them were only accessible to Byzantine scholars, until a compilation of Greek Hermetic treatises known as the Corpus Hermeticum was translated into Latin by the Renaissance scholars Marsilio Ficino (1433–1499) and Lodovico Lazzarelli (1447–1500).
 W
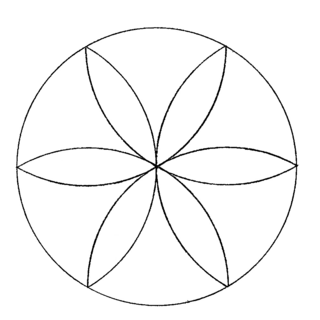
WA hexafoil is a geometric design that is used as a traditional element of Gothic architecture, created by overlapping six circular arcs to form a flower-like image. The hexafoil design is modeled after the six petal lily, for its symbolism of purity and relation to the Trinity. The hexafoil form is created from a series of compound units, and exists as a more complex variation of the same extruded figure. Other forms similar to the hexafoil include the trefoil, quatrefoil, and cinquefoil.
 W
WA kitchen witch, sometimes called a cottage witch or a "Scandinavian" kitchen witch doll, is a poppet or homemade doll resembling a stereotypical witch or crone displayed in residential kitchens as a good luck charm and to ward off bad spirits.
 W
WA mandrake is the root of a plant, historically derived either from plants of the genus Mandragora found in the Mediterranean region, or from other species, such as Bryonia alba, the English mandrake, which have similar properties. The plants from which the root is obtained are also called "mandrakes". Mediterranean mandrakes are perennial herbaceous plants with ovate leaves arranged in a rosette, a thick upright root, often branched, and bell-shaped flowers followed by yellow or orange berries. They have been placed in different species by different authors. They are highly variable perennial herbaceous plants with long thick roots and almost no stem. The leaves are borne in a basal rosette, and are variable in size and shape, with a maximum length of 45 cm (18 in). They are usually either elliptical in shape or wider towards the end (obovate), with varying degrees of hairiness.
 W
WDr. Sebastian Martin was an Indian Christian Evangelist in Vasai, Mumbai, Maharashtra. He was the founder Ashirward Prayer Centre. He gained notoriety for claiming chronic illnesses particularly renal problems in public spectacles. He was booked under Black Magic Act for allegedly fraudulently claiming to cure patients. Ironically, he died of renal failure after being released on bail.
 W
WDuring the Middle Ages magic in Europe took on many forms. Instead of being able to identify one type of magician, there were many who practiced several types of magic in these times, including: monks, priests, physicians, surgeons, midwives, folk healers, and diviners.
 W
WMoon magic is associated with the Moon. There is a belief common to many cultures that working rituals at the time of different phases of the moon can bring about physical or psychological change or transformation. These rituals have historically occurred on or around the full moon and to a lesser extent the new moon. Such practices are common amongst adherents of neopagan and witchcraft systems such as Wicca. Witches in Greek and Roman literature, particularly those from Thessaly, were regularly accused of "drawing down the Moon" by use of a magic spell. The trick serves to demonstrate their powers, to perform a love spell or to extract a magical juice from the Moon. These beliefs would seem to be consistent with many other cultures traditions, for instance; casting of the i ching is often done during the full moon's apex.
 W
WNavaratna is a Sanskrit compound word meaning "nine gems" or "ratnas". Jewellery created in this style has important cultural significance in many southern, and south-eastern Asian cultures as a symbol of wealth, status, and also as having other claimed talismanic benefits to health and wellbeing. The setting of the stones is believed to hold mystical powers, tied to astrology, mythology and intrinsically linked to the Indian religions of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. The historic origin of the significance behind the nine gems has proved impossible to trace but is tied to mythological concepts around cosmology and astrology and the "Navagrahas", or "nine celestial gods".
 W
WNecromancy is the practice of magic or black magic involving communication with the dead – either by summoning their spirits as apparitions, visions or raising them bodily – for the purpose of divination, imparting the means to foretell future events, discover hidden knowledge, to bring someone back from the dead, or to use the dead as a weapon. Sometimes referred to as "Death Magic", the term may also sometimes be used in a more general sense to refer to black magic or witchcraft.
 W
WNkisi or Nkishi are spirits or an object that a spirit inhabits. It is frequently applied to a variety of objects used throughout the Congo Basin in Central Africa, especially in the Territory of Cabinda that are believed to contain spiritual powers or spirits. The term and its concept have passed with the Atlantic slave trade to the Americas.
 W
WThe Odic force is the name given in the mid-19th century to a hypothetical vital energy or life force by Baron Carl von Reichenbach. Von Reichenbach coined the name from that of the Norse god Odin in 1845.
 W
WOriental Magic, by Idries Shah, is a study of magical practices in diverse cultures from Europe and Africa, through Asia to the Far East. Originally published in 1956 and still in print today, it was the first of this author’s 35 books. The work was launched with the encouragement of the anthropologist, Professor Louis Marin, who in his preface to the book stressed its “scholarly accuracy” and “real contribution to knowledge”.
 W
WPetosiris to Nechepso is a letter describing an ancient divination technique using numerology and a diagram. It is likely to be a pseudepigraph. Petosiris and Nechepso are considered to be the founders of astrology in some traditions. One translation of this letter into Latin is attributed to Saint Bede, and can be found in Cotton Tiberius.
 W
WRenaissance humanism saw a resurgence in hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of ceremonial magic.
 W
WThere is some evidence that, in addition to being a writing system, runes historically served purposes of magic. This is the case from earliest epigraphic evidence of the Roman to Germanic Iron Age, with non-linguistic inscriptions and the alu word. An erilaz appears to have been a person versed in runes, including their magic applications.
 W
WThe Secret Lore of Magic is a book by Idries Shah on the subject of magical texts. First published in 1957, it includes several major source-books of magical arts, translated from French, Latin, Hebrew and other tongues, annotated and fully illustrated with numerous diagrams, signs and characters. Together with Oriental Magic, which appeared in the preceding year, it provided an important literary-anthropological survey of magical literature and is a comprehensive reference for psychologists, ethnologists and others interested in the rise and development of human beliefs.
 W
WSīmiyā’ also rūḥāniyya, or ‘ilm al-ḥikma is a doctrine found commonly within Sufi-occult traditions that may be deduced upon the notion of "linking the superior natures with the inferior...", and broadly described as theurgy. This is confirmed further by al-Majrīṭī, who claims to reveal the techniques by which it is possible to convoke the rūḥāniyya of the celestial bodies. Theologian Abū Ḥāmid al-Ghazālī, the preacher and writer al-Kāshifī, and the Sufi Muḥyī al-Dīn Ibn al-'Arabī are amongst the most pre-eminent contributors. But al-Būnī, author of the two-volume Shams al-Ma‘ārif, is as likely as not a considerable focal point for the craft. The 13th-century Hermetic thinker had transcribed a whole corpus of material, all of which was subsumed under the spiritual science, and a majority of his works are still used as prototypes for present-day magical practice and literature. The term sīmiyā’ was the synonym of rūḥāniyya, which meant 'spirituality'. This was to be contrasted with the more lesser conformed sorcery (siḥr), deemed forbidden in Islam.
 W
WA Slavic dragon is any dragon in Slavic mythology, including the Russian zmei, Ukrainian zmiy, and its counterparts in other Slavic cultures: the Bulgarian zmey, the Slovak drak and šarkan, Czech drak, Polish żmij, the Serbo-Croatian zmaj, the Macedonian zmey (змеј). The Romanian zmeu is also a Slavic dragon, but a non-cognate etymology has been proposed.
 W
WTasseography is a divination or fortune-telling method that interprets patterns in tea leaves, coffee grounds, or wine sediments.
 W
WA tchitcherik or tchitcherik sakwa is a statue of the ancestors of the Moba of northern Togo and Ghana.
 W
WIn medieval lore, Tempestarii were weather making magicians who dwelt amongst the common people and possessed the power to raise or prevent storms at will. For this reason, anyone reputed as a weather-maker was the subject of respect, fear, and hatred in rural areas.
 W
WThomas Aquinas was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, Catholic priest, and Doctor of the Church. An immensely influential philosopher, theologian, and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism, he is also known within the latter as the Doctor Angelicus, the Doctor Communis, and the Doctor Universalis. The name Aquinas identifies his ancestral origins in the county of Aquino in present-day Lazio, Italy. Among other things, he was a prominent proponent of natural theology and the father of a school of thought known as Thomism. He argued that God is the source of both the light of natural reason and the light of faith. His influence on Western thought is considerable, and much of modern philosophy developed or opposed his ideas, particularly in the areas of ethics, natural law, metaphysics, and political theory.
 W
WA touch piece is a coin or medal believed to cure disease, bring good luck, influence people's behaviour, carry out a specific practical action, etc.
 W
WTraité sur les apparitions des esprits et sur les vampires ou les revenans de Hongrie, de Moravie, &c. is one of the many works by an Abbot monk named Antoine Augustin Calmet, an exegete and an 18th century Lorraine scholar of the Benedictine Order; also known as Dom Calmet. The work was published in 2 volumes that dealt with the extensive investigation into occult matters regarding the apparitions of angels, demons and other spirits.
 W
WTsentsak are invisible pathogenic projectiles or magical darts utilized in indigenous and mestizo shamanic practices for the purposes of sorcery and healing throughout much the Amazon Basin. Anthropologists identify them as objects referenced in emic accounts that represent indigenous beliefs. Tsentak are not recognized in scientific medicine.
 W
WUshi-no-Toki-Mairi or ushi no koku mairi (丑の刻参り) refers to a prescribed method of laying a curse upon a target that is traditional to Japan, so-called because it is conducted during the hours of the Ox. The practitioner—typically a scorned woman—while dressed in white and crowning herself with an iron ring set with three lit candles upright, hammers nails into a sacred tree of the Shinto shrine. In the modern-day common conception, the nails are driven through a straw effigy of the victim, impaled upon the tree behind it. The ritual must be repeated seven days running, after which the curse is believed to succeed, causing death to the target, but being witnessed in the act is thought to nullify the spell. The Kifune Shrine in Kyoto is famously associated with the ritual.
 W
WWhite magic has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for selfless purposes. Practitioners of white magic have been given titles such as wise men or women, healers, white witches or wizards. Many of these people claimed to have the ability to do such things because of knowledge or power that was passed on to them through hereditary lines, or by some event later in their lives. White magic was practiced through healing, blessing, charms, incantations, prayers, and songs. With respect to the philosophy of left-hand path and right-hand path, white magic is the benevolent counterpart of malicious black magic.
 W
WYantra tattooing or Sak Yant is a form of tattooing using Indian yantra designs. It consists of sacred geometrical, animal and deity designs accompanied by Pali phrases that are said to offer power, protection, fortune, charisma and other benefits for the bearer. Sak Yant designs originated from the Khmer Empire