 W
WThe Baháʼí Faith is a relatively new religion teaching the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the Middle East, where it has faced ongoing persecution since its inception. The religion is estimated to have over five million adherents, known as Baháʼís, spread throughout most of the world's countries and territories.
 W
WChristianity is an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest religion, with about 2.5 billion followers. Its adherents, known as Christians, make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Christ, whose coming as the Messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible and chronicled in the New Testament.
 W
WDruze are members of an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group originating in Western Asia. They practice Druzism, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of Hamza ibn Ali ibn Ahmad and the sixth Fatimid caliph, al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah, and ancient Greek philosophers like Plato, Aristotle, Pythagoras, and Zeno of Citium. Adherents of the Druze religion are called The People of Monotheism (Al-Muwaḥḥidūn).
 W
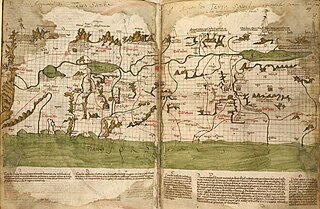
WThe Holy Land is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River. Traditionally, it is synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy Land" usually refers to a territory roughly corresponding to the modern State of Israel, the Palestinian territories, western Jordan, and parts of southern Lebanon and southwestern Syria. Jews, Christians, and Muslims regard it as holy.
 W
WJudaism is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people, also sometimes called Israelites. Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of the covenant that God established with the Children of Israel. It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. The Torah is part of the larger text known as the Tanakh or the Hebrew Bible, and supplemental oral tradition represented by later texts such as the Midrash and the Talmud. With between 14.5 and 17.4 million adherents worldwide, Judaism is the tenth largest religion in the world.
 W
WRastafari, also known as the Rastafari movement or Rastafarianism, is a religion that developed in Jamaica during the 1930s. It is classified as both a new religious movement and a social movement by scholars of religion. There is no central authority in control of the movement and much diversity exists among practitioners, who are known as Rastafari, Rastafarians, or Rastas.
 W
WThe Samaritan religion, also known as Samaritanism, is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion of the Samaritan people. The Samaritans adhere to the Samaritan Torah, which they believe is the original, unchanged Torah, as opposed to the Torah used by Jews. In addition to the Samaritan Torah, Samaritans also revere their version of the Book of Joshua and recognize some Biblical figures, such as Eli.
 W
WYazdânism, or the Cult of Angels, is a proposed pre-Islamic Mithraic religion of the Kurds. The term was introduced and proposed by Kurdish and Belgian scholar Mehrdad Izady to represent what he considers the "original" religion of the Kurds.