 W
WAn Egyptian fraction is a finite sum of distinct unit fractions, such as
 W
WThe abacus, also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool which has been used since ancient times. It was used in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, centuries before the adoption of the Arabic numeral system. The exact origin of the abacus has not yet emerged. It consists of rows of movable beads, or similar objects, strung on a wire. They represent digits. One of the two numbers is set up, and the beads are manipulated to perform an operation such as addition, or even a square or cubic root.
 W
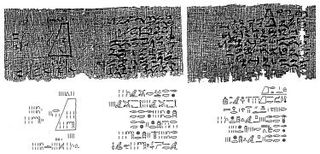
WThe Berlin Papyrus 6619, simply called the Berlin Papyrus when the context makes it clear, is one of the primary sources of ancient Egyptian mathematics. One of the two mathematics problems on the Papyrus may suggest that the ancient Egyptians knew the Pythagorean theorem.
 W
WEgyptian geometry refers to geometry as it was developed and used in Ancient Egypt. Their geometry was a necessary outgrowth of surveying to preserve the layout and ownership of farmland, which was flooded annually by the Nile river.
 W
WMathematics in Ancient Egypt: A Contextual History is a book on ancient Egyptian mathematics by Annette Imhausen. It was published by the Princeton University Press in 2016.
 W
WThe Moscow Mathematical Papyrus, also named the Golenishchev Mathematical Papyrus after its first non-Egyptian owner, Egyptologist Vladimir Golenishchev, is an ancient Egyptian mathematical papyrus containing several problems in arithmetic, geometry, and algebra. Golenishchev bought the papyrus in 1892 or 1893 in Thebes. It later entered the collection of the Pushkin State Museum of Fine Arts in Moscow, where it remains today.
 W
WThe Rhind Mathematical Papyrus is one of the best known examples of ancient Egyptian mathematics. It is named after Alexander Henry Rhind, a Scottish antiquarian, who purchased the papyrus in 1858 in Luxor, Egypt; it was apparently found during illegal excavations in or near the Ramesseum. It dates to around 1550 BC. The British Museum, where the majority of the papyrus is now kept, acquired it in 1865 along with the Egyptian Mathematical Leather Roll, also owned by Henry Rhind. There are a few small fragments held by the Brooklyn Museum in New York City and an 18 cm (7.1 in) central section is missing. It is one of the two well-known Mathematical Papyri along with the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus. The Rhind Papyrus is larger than the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus, while the latter is older.
 W
WThe Saqqara ostracon is an ostracon, an Egyptian antiquity, tracing to the period of Djoser,