 W
WAn andén, Spanish for "platform", is a stair-step like terrace dug into the slope of a hillside for agricultural purposes. The term is most often used to refer to the terraces built by pre-Columbian cultures in the Andes mountains of South America. Andenes had several functions, the most important of which was to increase the amount of cultivatable land available to farmers by leveling a planting area for crops. The best known examples of andenes are in Peru, especially in the Sacred Valley near the Inca capital of Cuzco and in the Colca Canyon. Many andenes have survived for more than 500 years and are still in use by farmers throughout the region.
 W
WThe Cairns Group is an interest group of 19 agricultural exporting countries, composed of Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Indonesia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, the Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, Uruguay, and Vietnam.
 W
WThe foot plough is a type of plough used like a spade with the foot in order to cultivate the ground.
 W
WIncan agriculture was the culmination of thousands of years of farming and herding in the high-elevation Andes mountains of South America, the coastal deserts, and the rainforests of the Amazon basin. These three radically different environments were all part of the Inca Empire and required different technologies for agriculture. Inca agriculture was also characterized by the variety of crops grown, the lack of a market system and money, and the unique mechanisms by which the Incas organized their society. Andean civilization was "pristine"—one of five civilizations worldwide which were indigenous and not derivative from other civilizations. Most Andean crops and domestic animals were likewise pristine—not known to other civilizations. Potatoes, tomatoes, chile peppers, and quinoa were among the many unique crops; Camelids and guinea pigs were the unique domesticated animals.
 W
WThe International Potato Center is a research facility based in Lima, Peru, that seeks to reduce poverty and achieve food security on a sustained basis in developing countries through scientific research and related activities on potato, sweet potato, other root and tuber crops, and on the improved management of natural resources in the Andes and other mountain areas. It was established in 1971 by decree of the Peruvian government.
 W
WThis is a list of Ministers of Agriculture and Irrigation of Peru.
 W
WThe Ministry of Agricultural Development and Irrigation (MIDAGRI) is the government ministry in charge of the agricultural sector. The current minister is Federico Tenorio.
 W
WThe Pernil Alto archaeological site is located in Rio Grande District of Palpa province in the Ica Region of Peru. Although the site was occupied earlier, archaeologists traced the adoption of agriculture by the inhabitants from about 3800 BCE to 3000 BCE. The excavators cite radiocarbon dates which establish Pernil Alto as the oldest known inland and sedentary agricultural village in the Central Andes of Peru and Bolivia. The date at which agriculture became the main source of subsistence for the inhabitants of Pernil Alto was 3300 BCE.
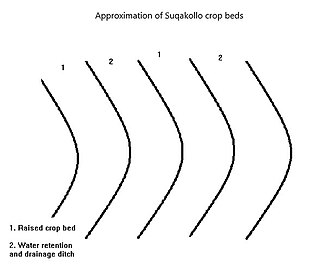 W
WSuqakollos are elevated crop fields designed to promote water conservation in agriculture. Originating in the highlands of the Puno Region in Peru, Suqakollo fields were implemented by indigenous Peruvians to supply food crops with water through the creation of specialized stepwells.