 W
WThe behavioural despair test is a test, centered on a rodent's response to the threat of drowning, whose result has been interpreted as measuring susceptibility to negative mood. It is commonly used to measure the effectiveness of antidepressants, although significant criticisms of its interpretation have been made.
 W
WThe flowerpot technique is an animal testing technique used in sleep deprivation studies. It is designed to allow NREM sleep but prevent restful REM sleep. The test is usually performed with rats.
 W
WThe light-dark box test (LDB) is a popular animal model used in pharmacology to assay unconditioned anxiety responses in rodents. The extent to which behavior in the LDB measures anxiety is controversial.
 W
WMarble burying is an animal model used in scientific research to depict anxiety or obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) behavior. It is based on the observation that rats and mice will bury either harmful or harmless objects in their bedding. While widely used there is significant controversy over the interpretation of its results.
 W
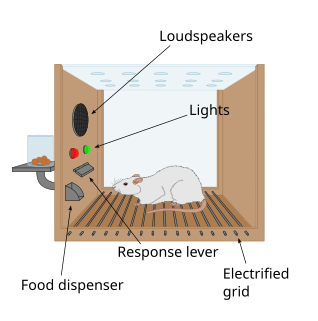
WAn operant conditioning chamber is a laboratory apparatus used to study animal behavior. The operant conditioning chamber was created by B. F. Skinner while he was a graduate student at Harvard University. It may have been inspired by Jerzy Konorski's studies. It is used to study both operant conditioning and classical conditioning.
 W
WThe tail flick test is a test of the pain response in animals, similar to the hot plate test. It is used in basic pain research and to measure the effectiveness of analgesics, by observing the reaction to heat. It was first described by D'Amour and Smith in 1941.
 W
WThe tail suspension test (TST) is an experimental method used in scientific research to measure stress in rodents. It is based on the observation that if a rat is subjected to short term inescapable stress then the rat will become immobile. It is used to measure the effectiveness of antidepressant-like agents but there is significant controversy over its interpretation and usefulness.
 W
WThe UFAW Handbook is a manual about care of animals used in animal testing. It is presented by the Universities Federation for Animal Welfare.
 W
WVivisection is surgery conducted for experimental purposes on a living organism, typically animals with a central nervous system, to view living internal structure. The word is, more broadly, used as a pejorative catch-all term for experimentation on live animals by organizations opposed to animal experimentation, but the term is rarely used by practising scientists. Human vivisection, such as live organ harvesting, has been perpetrated as a form of torture.