 W
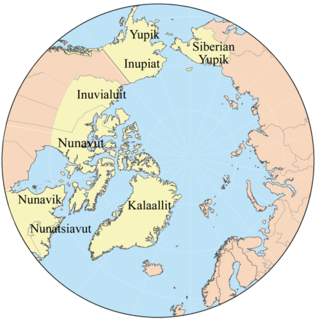
WThe Eskimo–Aleut, Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, or Eskaleut languages are a language family native to Alaska, Nunavut, northern Northwest Territories, northern Quebec (Nunavik), northern Labrador (Nunatsiavut), Greenland and far eastern Russia. It is also known as Eskaleutian, Eskaleutic or Inuit–Yupik-Unangan.
 W
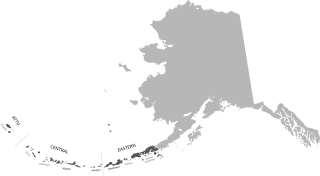
WAleut or Unangam Tunuu is the language spoken by the Aleut (Unangax̂) living in the Aleutian Islands, Pribilof Islands, Commander Islands, and the Alaska Peninsula. Aleut is the sole language in the Aleut branch of the Eskimo–Aleut language family. The Aleut language consists of three dialects, including Eastern, Atkan, and Attuan.
 W
WBible translations into Eskimo-Aleut languages include:
 W
WSirenik Yupik, Sireniki Yupik, Sirenik, or Sirenikskiy is an extinct Eskimo–Aleut language. It was spoken in and around the village of Sireniki (Сиреники) in Chukotka Peninsula, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. The language shift has been a long process, ending in total language death. In January 1997, the last native speaker of the language, a woman named Vyjye, died. Ever since that point, the language has been extinct; nowadays, all Sirenik Eskimos speak Siberian Yupik or Russian.
 W
WEskimology or Inuitology is a complex of humanities sciences studying languages, history, literature, folklore, culture, and ethnology of people speaking Eskimo–Aleut languages and Eskimo (Inuit–Yupik)–Aleut peoples in chronological and comparative context. This includes ethnic groups from the Chukchi Peninsula on the eastern tip of Siberia of Russian Federation to Alaska of the United States, Northern Canada, and Greenland of Denmark. Originally, an Eskimologist or Inuitologist was primarily a linguist or philologist who researches Eskimo languages.
 W
WEurasiatic is a proposed language macrofamily that would include many language families historically spoken in northern, western, and southern Eurasia.
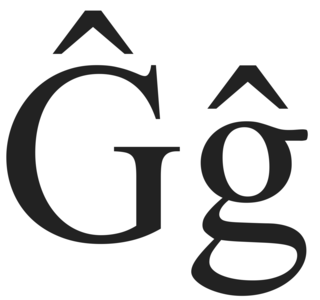 W
WĜ or ĝ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing a voiced postalveolar affricate, and is equivalent to a voiced postalveolar affricate or a voiced retroflex affricate.
 W
WThe Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and to some extent in the subarctic in Labrador. The related Yupik languages are spoken in western and southern Alaska and in the far east of Russia, but are severely endangered in Russia today and spoken only in a few villages on the Chukchi Peninsula. The Inuit live primarily in three countries: Greenland, Canada, and the United States.
 W
WUralo-Siberian is a hypothetical language family consisting of Uralic, Yukaghir, Eskimo–Aleut, possibly Nivkh and formerly Chukotko-Kamchatkan. It was proposed in 1998 by Michael Fortescue, an expert in Eskimo–Aleut and Chukotko-Kamchatkan, in his book Language Relations across Bering Strait. In 2011, Fortescue removed Chukotko-Kamchatkan from the proposal.